Coexistence of recurrent chromosomal abnormalities and the Philadelphia chromosome in acute and chronic myeloid leukemias: report of five cases and review of literature
- PMID: 32831907
- PMCID: PMC7437057
- DOI: 10.1186/s13039-020-00501-6
Coexistence of recurrent chromosomal abnormalities and the Philadelphia chromosome in acute and chronic myeloid leukemias: report of five cases and review of literature
Abstract
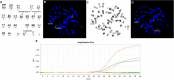
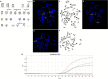
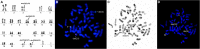
Progression of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is frequently accompanied by cytogenetic evolution. Additional genetic abnormalities are seen in 10-20% of CML cases at the time of diagnosis, and in 60-80% of cases of advanced disease. Unbalanced chromosomal changes such as an extra copy of the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph), trisomy 8, and i(17)(q10) are common. Balanced chromosomal translocations, such as t(3;3), t(8;21), t(15;17), and inv(16) are typically found in acute myeloid leukemia, but rarely occur in CML. Translocations involving 11q23, t(8;21), and inv(16) are relatively common genetic abnormalities in acute leukemia, but are extremely rare in CML. In the literature to date, there are at least 76 Ph+ cases with t(3;21), 47 Ph+ cases with inv(16), 16 Ph+ cases with t(8;21), and 9 Ph+ cases with t(9;11). But most of what has been published is now over 30 years old, without the benefit of modern immunophenotyping to confirm diagnosis, and before the introduction of treatment regimes such as TKI. In this study, we explored the rare concomitant occurrence of coexistence current chromosomal translocation and t(9;22) in CML or acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; Balanced chromosomal abnormalities; Chronic myelogenous leukemia; Clonal evolution; t(9;22).
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zaccaria A, Testoni N, Valenti AM, Luatti S, Tonelli M, Marzocchi G, et al. Chromosome abnormalities additional to the Philadelphia chromosome at the diagnosis of chronic myelogenous leukemia: pathogenetic and prognostic implications. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2010;199:76–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2010.02.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N, et al. Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia – a Europe against Cancer program. Leukemia. 2003;17:2318–2357. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403135. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

