Effects of miR-218-1-3p and miR-149 on proliferation and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 32831915
- PMCID: PMC7439122
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.11957
Effects of miR-218-1-3p and miR-149 on proliferation and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
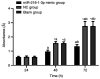
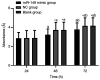
The aim of the present study was to explore the effects of miR-218-1-3p and miR-149 on the biological function of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells A549. Paired NSCLC and adjacent tissues were obtained from 50 NSCLC patients admitted to Shandong Provincial Chest Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University (Jinan, China) from April 2015 to May 2018. The expression levels of miR-218-1-3p and miR-149 were detected by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). The lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells were assigned into the blank group (without transfection), negative control (NC) group (transfected with miRNA NC), and the transfected groups miR-218-1-3p mimic and miR-149 mimic groups. Proliferation and cell growth were determined by CCK-8 assay and cell invasion ability in vitro was assessed by Transwell assay. Flow cytometry was carried out for the detection of cell apoptosis. RT-qPCR results showed that the expression levels of miR-218-1-3p and miR-149 in NSCLC tissues were significantly lower than those in adjacent tissues (P<0.001). At 48 and 72 h, the cell growth of the A549 cells in the miR-218-1-3p mimic and miR-149 mimic groups was significantly lower than that in the NC and blank groups (P<0.05). The number of invasive cells in the miR-218-1-3p mimic and miR-149 mimic groups was significantly lower than that in the NC and blank groups (P<0.05). The apoptotic rate of A549 cells in the miR-218-1-3p mimic and miR-149 mimic groups was significantly higher than that in the NC and blank groups (P<0.05). In conclusion, upregulation of miR-218-1-3p and miR-149 can inhibit the proliferation, invasion and migration of A549 cells in NSCLC, thereby promoting the apoptosis of A549 cells. Thus, miR-218-1-3p and miR-149 can be used as new molecular targets for the diagnosis and treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: A549 cells; apoptosis; miR-149; miR-218-1-3p; non-small cell lung cancer; proliferation.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of miR-490-5p, miR-148a-3p and miR-608 in bladder cancer and their effects on the biological characteristics of bladder cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2019 May;17(5):4437-4442. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10143. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30988813 Free PMC article.
-
miR-210-3p regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting SIN3A.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Oct;18(4):2565-2573. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7867. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31555365 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-183 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Down-Regulating MTA1.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(1):93-106. doi: 10.1159/000488412. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29587281
-
Inhibition of microRNA-196a might reverse cisplatin resistance of A549/DDP non-small-cell lung cancer cell line.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):2387-94. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4017-7. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26376998
-
Effect of microRNA-135a on Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Apoptosis and Tumor Angiogenesis Through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(4):1431-1446. doi: 10.1159/000479207. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715819
Cited by
-
Cathepsin-facilitated invasion of BMI1-high hepatocellular carcinoma cells drives bile duct tumor thrombi formation.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 3;14(1):7033. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42930-y. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37923799 Free PMC article.
-
A diagnostic miRNA panel to detect recurrence of ovarian cancer through artificial intelligence approaches.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jan;149(1):325-341. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04468-2. Epub 2022 Nov 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36378340 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Body Fluids: A More Promising Biomarker for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Oct 5;13:7663-7675. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S330881. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34675663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
