Draft for internal testing Scientific Committee guidance on appraising and integrating evidence from epidemiological studies for use in EFSA's scientific assessments
- PMID: 32831946
- PMCID: PMC7433401
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2020.6221
Draft for internal testing Scientific Committee guidance on appraising and integrating evidence from epidemiological studies for use in EFSA's scientific assessments
Abstract
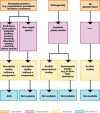
EFSA requested its Scientific Committee to prepare a guidance document on appraising and integrating evidence from epidemiological studies for use in EFSA's scientific assessments. The guidance document provides an introduction to epidemiological studies and illustrates the typical biases of the different epidemiological study designs. It describes key epidemiological concepts relevant for evidence appraisal. Regarding study reliability, measures of association, exposure assessment, statistical inferences, systematic error and effect modification are explained. Regarding study relevance, the guidance describes the concept of external validity. The principles of appraising epidemiological studies are illustrated, and an overview of Risk of Bias (RoB) tools is given. A decision tree is developed to assist in the selection of the appropriate Risk of Bias tool, depending on study question, population and design. The customisation of the study appraisal process is explained, detailing the use of RoB tools and assessing the risk of bias in the body of evidence. Several examples of appraising experimental and observational studies using a Risk of Bias tool are annexed to the document to illustrate the application of the approach. This document constitutes a draft that will be applied in EFSA's assessments during a 1-year pilot phase and be revised and complemented as necessary. Before finalisation of the document, a public consultation will be launched.
Keywords: Epidemiological studies; evidence appraisal; exposure assessment; hazard characterisation; risk assessment.
© 2020 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Guidance for establishing and applying tolerable upper intake levels for vitamins and essential minerals: Draft for internal testing.EFSA J. 2022 Jan 24;20(1):e200102. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.e200102. eCollection 2022 Jan. EFSA J. 2022. PMID: 35106096 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific Committee guidance on appraising and integrating evidence from epidemiological studies for use in EFSA's scientific assessments.EFSA J. 2024 Jul 5;22(7):e8866. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8866. eCollection 2024 Jul. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 38974922 Free PMC article.
-
Guidance on the use of the weight of evidence approach in scientific assessments.EFSA J. 2017 Aug 3;15(8):e04971. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4971. eCollection 2017 Aug. EFSA J. 2017. PMID: 32625632 Free PMC article.
-
EFSA's scientific activities and achievements on the risk assessment of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) during its first decade of existence: looking back and ahead.Transgenic Res. 2014 Feb;23(1):1-25. doi: 10.1007/s11248-013-9741-4. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Transgenic Res. 2014. PMID: 23963741 Review.
-
EFSA's OpenFoodTox: An open source toxicological database on chemicals in food and feed and its future developments.Environ Int. 2021 Jan;146:106293. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106293. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Environ Int. 2021. PMID: 33395940 Review.
Cited by
-
Guidance for establishing and applying tolerable upper intake levels for vitamins and essential minerals: Draft for internal testing.EFSA J. 2022 Jan 24;20(1):e200102. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.e200102. eCollection 2022 Jan. EFSA J. 2022. PMID: 35106096 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific opinion on the tolerable upper intake level for iron.EFSA J. 2024 Jun 12;22(6):e8819. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8819. eCollection 2024 Jun. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 38868106 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific opinion on the tolerable upper intake level for vitamin B6.EFSA J. 2023 May 17;21(5):e08006. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8006. eCollection 2023 May. EFSA J. 2023. PMID: 37207271 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific opinion on the tolerable upper intake level for manganese.EFSA J. 2023 Dec 8;21(12):e8413. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8413. eCollection 2023 Dec. EFSA J. 2023. PMID: 38075631 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific Committee guidance on appraising and integrating evidence from epidemiological studies for use in EFSA's scientific assessments.EFSA J. 2024 Jul 5;22(7):e8866. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8866. eCollection 2024 Jul. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 38974922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adami HO, Berry CL, Breckenridge CB, Smith LL, Swenberg JA, Trichopoulos D, Weiss NS and Pastoor TP, 2011. Toxicology and epidemiology: improving the science with a framework for combining toxicological and epidemiological evidence to establish causal inference. Toxicological Sciences, 122, 223–234. 10.1093/toxsci/kfr113 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality , 2002. Systems to rate the strength of scientific evidence. Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No 47, Publication No 02‐E019 Rockville: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
