Predictive Factors for Failure of Noninvasive Ventilation in Adult Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Clinical Study
- PMID: 32831978
- PMCID: PMC7421696
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/1324348
Predictive Factors for Failure of Noninvasive Ventilation in Adult Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Clinical Study
Abstract
Background: Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) has been reported to be beneficial for patients with acute respiratory failure in intensive care unit (ICU); however, factors that influence the clinical outcome of NIV were unclarified. We aim to determine the factors that predict the failure of NIV in critically ill patients with acute respiratory failure (ARF). Setting. Adult mixed ICU in a medical university affiliated hospital. Patients and Methods. A retrospective clinical study using data from critical adult patients with initial NIV admitted to ICU in the period August 2016 to November 2017. Failure of NIV was regarded as patients needing invasive ventilation. Logistic regression was employed to determine the risk factor(s) for NIV, and a predictive model for NIV outcome was set up using risk factors.
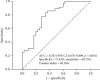
Results: Of 101 included patients, 50 were unsuccessful. Although more than 20 variables were associated with NIV failure, multivariate logistic regression demonstrated that only ideal body weight (IBW) (OR 1.110 (95%1.027-1.201), P=0.009), the maximal heart rate during NIV period (HR-MAX) (OR 1.024 (1.004-1.046), P=0.021), the minimal respiratory rate during NIV period (RR-MIN) (OR 1.198(1.051-1.365), P=0.007), and the highest body temperature during NIV period (T-MAX) (OR 1.838(1.038-3.252), P=0.037) were independent risk factors for NIV failure. We set up a predictive model based on these independent risk factors, whose area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was 0.783 (95% CI: 0.676-0.899, P < 0.001), and the sensitivity and specificity of model were 68.75% and 71.43%, respectively, with the optimal cut-off value of 0.4863.
Conclusion: IBW, HR-MAX, RR-MIN, and T-MAX were associated with NIV failure in patients with ARF. A predictive model based on the risk factors could help to discriminate patients who are vulnerable to NIV failure.
Copyright © 2020 Qimin Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Diamantaki E., Proklou A., Pediaditis E., Amargianitakis V., Kondili E. Acute respiratory failure before ICU admission: a practical approach. Mechanical Ventilation in Critically Ill Cancer Patients. 2018;2:91–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49256-8_10. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical