The Effects of Alpha-Linolenic Acid on the Secretory Activity of Astrocytes and β Amyloid-Associated Neurodegeneration in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells: Alpha-Linolenic Acid Protects the SH-SY5Y cells against β Amyloid Toxicity
- PMID: 32832007
- PMCID: PMC7428942
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8908901
The Effects of Alpha-Linolenic Acid on the Secretory Activity of Astrocytes and β Amyloid-Associated Neurodegeneration in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells: Alpha-Linolenic Acid Protects the SH-SY5Y cells against β Amyloid Toxicity
Abstract
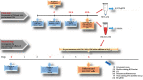
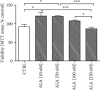
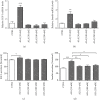
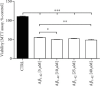
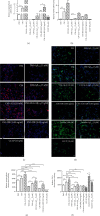
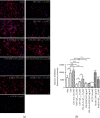
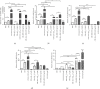
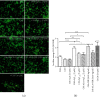
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder. Amyloid β- (Aβ-) induced mitochondrial dysfunction may be a primary process triggering all the cascades of events that lead to AD. Therefore, identification of natural factors and endogenous mechanisms that protect neurons against Aβ toxicity is needed. In the current study, we investigated whether alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), as a natural product, would increase insulin and IGF-I (insulin-like growth factor I) release from astrocytes. Moreover, we explored the protective effect of astrocytes-derived insulin/IGF-I on Aβ-induced neurotoxicity, with special attention paid to their impact on mitochondrial function of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. The results showed that ALA induced insulin and IGF-I secretion from astrocytes. Our findings demonstrated that astrocyte-derived insulin/insulin-like growth factor I protects differentiated SH-SY5Y cells against Aβ 1-42-induced cell death. Moreover, pretreatment with conditioned medium (CM) and ALA-preactivated CM (ALA-CM) protected the SH-SY5Y cells against Aβ 1-42-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by reducing the depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane, increasing mitochondrial biogenesis, restoring the balance between fusion and fission processes, and regulation of mitophagy and autophagy processes. Our study suggested that astrocyte-derived insulin/insulin-like growth factor I suppresses Aβ 1-42-induced cytotoxicity in the SH-SY5Y cells by protecting against mitochondrial dysfunction. Moreover, the neuroprotective effects of CM were intensified by preactivation with ALA.
Copyright © 2020 Anna Litwiniuk et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synergy in Disruption of Mitochondrial Dynamics by Aβ (1-42) and Glia Maturation Factor (GMF) in SH-SY5Y Cells Is Mediated Through Alterations in Fission and Fusion Proteins.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;56(10):6964-6975. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1544-z. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30949973 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acid attenuates amyloid β1-42-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibits the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells.Neurochem Int. 2024 Sep;178:105772. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105772. Epub 2024 May 22. Neurochem Int. 2024. PMID: 38789043
-
Fucosterol exerts protection against amyloid β-induced neurotoxicity, reduces intracellular levels of amyloid β and enhances the mRNA expression of neuroglobin in amyloid β-induced SH-SY5Y cells.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jan;121:207-213. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.021. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30300695
-
An Extract from Shrimp Processing By-Products Protects SH-SY5Y Cells from Neurotoxicity Induced by Aβ25-35.Mar Drugs. 2017 Mar 22;15(3):83. doi: 10.3390/md15030083. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28327516 Free PMC article.
-
Oleanolic acid protects against cognitive decline and neuroinflammation-mediated neurotoxicity by blocking secretory phospholipase A2 IIA-activated calcium signals.Mol Immunol. 2018 Jul;99:95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.04.015. Epub 2018 May 7. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29747052
Cited by
-
Exosomes Derived From M2 Microglia Cells Attenuates Neuronal Impairment and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease Through the PINK1/Parkin Pathway.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Apr 28;16:874102. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.874102. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35573832 Free PMC article.
-
Flaxseed Oil Alleviates Trimethyltin-Induced Cell Injury and Inhibits the Pro-Inflammatory Activation of Astrocytes in the Hippocampus of Female Rats.Cells. 2024 Jul 11;13(14):1184. doi: 10.3390/cells13141184. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39056766 Free PMC article.
-
Actin Polymerization Defects Induce Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cellular Models of Nemaline Myopathies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;12(12):2023. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122023. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136143 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome NLRP3 Potentially Links Obesity-Associated Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance with Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 25;22(11):5603. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115603. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetaldehyde Induces Cytotoxicity via Triggering Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Overactive Mitophagy.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jun;59(6):3933-3946. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02828-0. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35438433
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

