Effectiveness of Intravitreal Ranibizumab in Nonvitrectomized and Vitrectomized Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema: A Two-Year Retrospective Analysis
- PMID: 32832135
- PMCID: PMC7428899
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2561251
Effectiveness of Intravitreal Ranibizumab in Nonvitrectomized and Vitrectomized Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema: A Two-Year Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
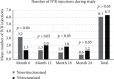
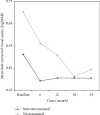
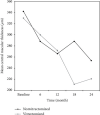
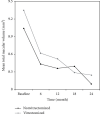
The aim of this study was to compare the effectiveness of intravitreal ranibizumab (IVR) injections for the treatment of diabetic macular edema (DME) in eyes with and without previous vitrectomy. The medical records of 28 eyes (11 vitrectomized and 17 nonvitrectomized) of 28 patients (mean age, 59.0 ± 9.6 years; male to female ratio 1 : 1) who were diagnosed with DME and had received IVR treatment were reviewed retrospectively. The indications of vitrectomy in 11 vitrectomized eyes were intravitreal hemorrhage (n = 8) and epiretinal membrane (n = 3). The best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), central macular thickness (CMT), and total macular volume (TMV) were measured at baseline and at months 6, 12, 18, and 24 of the follow-up. The number of IVR injections, the duration between diagnosis of DME and IVR injection, and the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level at baseline were also recorded. Baseline demographics, HbA1c, BCVA, CMT, and TMV values were similar between two groups (p > 0.05). The duration between diagnosis of DME and IVR injections was similar in both groups (16 ± 5 months vs. 13 ± 4 months, respectively; p=0.11). IVR injection was performed 6.3 times in vitrectomized eyes and 6.1 times in nonvitrectomized eyes during the 24-month period (p > 0.05). The mean BCVA improved significantly during the 24-month period in both groups. The improvements in BCVA, in CMT, and in TMV were more significant at month 6 (p=0.036) group, at month 12 (p=0.013), at month 12 (p=0.021), and month 24 (p=0.021) in nonvitrectomized eyes, respectively, while there was no difference in improvements of BCVA, CMT, and TMV in vitrectomized group at each visit. Treatment effected by time in terms of BCVA, CMT, and TMV values in all groups (p=0.0004, p < 0.0001, p < 0.0001, respectively), not by time-group interaction and group (all p values >0.05). In conclusion, IVR treatment for DME is equally effective in both groups. However, the response to treatment is seen earlier in nonvitrectomized eyes compared to vitrectomized eyes.
Copyright © 2020 Ozgun Melike Gedar Totuk et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the Effectiveness of Intravitreal Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema in Vitrectomized and Nonvitrectomized Eyes.Ophthalmologica. 2016;236(2):67-73. doi: 10.1159/000446992. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Ophthalmologica. 2016. Corrected and republished in: Ophthalmologica. 2017 Jul 11;238 Suppl 1:21-27. doi: 10.1159/000477513. PMID: 27362944 Corrected and republished. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of the dexamethasone implant in vitrectomized and nonvitrectomized eyes with diabetic macular edema: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 1;13:1029584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1029584. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36532786 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone intravitreal implant in vitrectomized versus nonvitrectomized eyes for treatment of patients with persistent diabetic macular edema.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Nov;30(9):709-16. doi: 10.1089/jop.2014.0010. Epub 2014 Sep 26. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25259834
-
Comparison of Intravitreal Dexamethasone Implant and Ranibizumab in Vitrectomized Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema.J Ophthalmol. 2021 Sep 10;2021:8882539. doi: 10.1155/2021/8882539. eCollection 2021. J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34540287 Free PMC article.
-
Fluocinolone Acetonide Intravitreal Implant 190 μg (ILUVIEN®) in Vitrectomized versus Nonvitrectomized Eyes for the Treatment of Chronic Diabetic Macular Edema.Ophthalmic Res. 2018;59(2):68-75. doi: 10.1159/000484091. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Ophthalmic Res. 2018. PMID: 29248913
Cited by
-
Diabetic macular edema treatment guidelines in India: All India Ophthalmological Society Diabetic Retinopathy Task Force and Vitreoretinal Society of India consensus statement.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov;69(11):3076-3086. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1469_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34708746 Free PMC article.
-
Recommendations for diabetic macular edema management by retina specialists and large language model-based artificial intelligence platforms.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2024 Feb 28;10(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40942-024-00544-6. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2024. PMID: 38419083 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of intravitreal ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema in vitrectomized versus non-vitrectomized eyes: a Meta-analysis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Apr 18;17(4):729-735. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.04.18. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38638245 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

