Identification of DNA methylation patterns and biomarkers for clear-cell renal cell carcinoma by multi-omics data analysis
- PMID: 32832275
- PMCID: PMC7409785
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.9654
Identification of DNA methylation patterns and biomarkers for clear-cell renal cell carcinoma by multi-omics data analysis
Abstract
Background: Tumorigenesis is highly heterogeneous, and using clinicopathological signatures only is not enough to effectively distinguish clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and improve risk stratification of patients. DNA methylation (DNAm) with the stability and reversibility often occurs in the early stage of tumorigenesis. Disorders of transcription and metabolism are also an important molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis. Therefore, it is necessary to identify effective biomarkers involved in tumorigenesis through multi-omics analysis, and these biomarkers also provide new potential therapeutic targets.
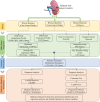
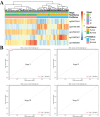
Method: The discovery stage involved 160 pairs of ccRCC and matched normal tissues for investigation of DNAm and biomarkers as well as 318 cases of ccRCC including clinical signatures. Correlation analysis of epigenetic, transcriptomic and metabolomic data revealed the connection and discordance among multi-omics and the deregulated functional modules. Diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers were obtained by the correlation analysis, the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) and the LASSO-Cox methods. Two classifiers were established based on random forest (RF) and LASSO-Cox algorithms in training datasets. Seven independent datasets were used to evaluate robustness and universality. The molecular biological function of biomarkers were investigated using DAVID and GeneMANIA.
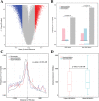
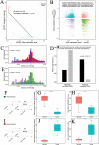
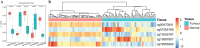
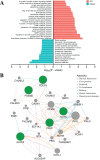
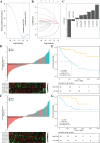
Results: Based on multi-omics analysis, the epigenetic measurements uniquely identified DNAm dysregulation of cellular mechanisms resulting in transcriptomic alterations, including cell proliferation, immune response and inflammation. Combination of the gene co-expression network and metabolic network identified 134 CpG sites (CpGs) as potential biomarkers. Based on the LASSO and RF algorithms, five CpGs were obtained to build a diagnostic classifierwith better classification performance (AUC > 99%). A eight-CpG-based prognostic classifier was obtained to improve risk stratification (hazard ratio (HR) > 4; log-rank test, p-value < 0.01). Based on independent datasets and seven additional cancers, the diagnostic and prognostic classifiers also had better robustness and stability. The molecular biological function of genes with abnormal methylation were significantly associated with glycolysis/gluconeogenesis and signal transduction.
Conclusion: The present study provides a comprehensive analysis of ccRCC using multi-omics data. These findings indicated that multi-omics analysis could identify some novel epigenetic factors, which were the most important causes of advanced cancer and poor clinical prognosis. Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers were identified, which provided a promising avenue to develop effective therapies for ccRCC.
Keywords: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC); DNA methylation (DNAm); Diagnostic biomarkers; Multi-omics; Prognostic biomarkers.
© 2020 Liu and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Atschekzei F, Hennenlotter J, Janisch S, Grosshennig A, Trankenschuh W, Waalkes S, Peters I, Dork T, Merseburger AS, Stenzl A, Kuczyk MA, Serth J. SFRP1 CpG island methylation locus is associated with renal cell cancer susceptibility and disease recurrence. Epigenetics. 2012;7(5):447–457. doi: 10.4161/epi.19614. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Awakura Y, Nakamura E, Ito N, Kamoto T, Ogawa O. Methylation-associated silencing of SFRP1 in renal cell carcinoma. Oncology Reports. 2008;20:1257–1263. - PubMed
-
- Becket E, Chopra S, Duymich CE, Lin JJ, You JS, Pandiyan K, Nichols PW, Siegmund KD, Charlet J, Weisenberger DJ, Jones PA, Liang G. Identification of DNA methylation–independent epigenetic events underlying clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Research. 2016;76(7):1954–1964. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2622. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

