Pleuri-Segmental Ipsilateral Nonsyndromic Infantile Hemangioma Responding Favorably to Oral Propranolol
- PMID: 32832465
- PMCID: PMC7413448
- DOI: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_455_19
Pleuri-Segmental Ipsilateral Nonsyndromic Infantile Hemangioma Responding Favorably to Oral Propranolol
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
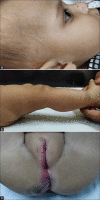
Figures

References
-
- Leaute-Labreze C, Prey S, Ezzedine K. Infantile haemangioma: Part I.Pathophysiology, epidemiology, clinical features, life cycle and associated structural abnormalities. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:1245–53. - PubMed
-
- Yu X, Zhang J, Wu Z, Liu M, Chen R, Gu Y, et al. LUMBAR syndrome: A case manifesting as cutaneous infantile hemangiomas of the lower extremity, perineum and gluteal region, and a review of published work. J Dermatol. 2017;44:808–12. - PubMed
-
- Phan TA, Adams S, Wargon O. Segmental haemangiomas of infancy: A review of 14 cases. Australas J Dermatol. 2006;47:242–7. - PubMed
-
- Khanna D, Chakravarty P, Arora P, Jain R, Mittal M. Large multifocal cutaneous hemangioma along lines of Blaschko with cardiac failure treated with propranolol. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:e18–22. - PubMed
-
- Dakshayani B, Benakappa A. Multiple segmental hemangiomas over one half of the body-A rare feature of PHACES syndrome. Indian J Pediatr. 2016;83:83–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

