Purification and Characterization of Novel Collagen Peptides against Platelet Aggregation and Thrombosis from Salmo salar
- PMID: 32832753
- PMCID: PMC7439260
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01340
Purification and Characterization of Novel Collagen Peptides against Platelet Aggregation and Thrombosis from Salmo salar
Abstract
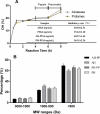
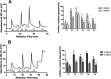
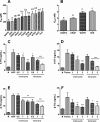
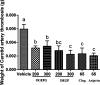
Collagen is a rich source of bioactive peptides and is widely distributed in the skin and bone tissue. In this study, collagen from Salmo salar skin was hydrolyzed with Alcalase or Protamex followed by simulated digestion, YMC ODS-A C18 separation, and ESI-MS/MS analysis. A total of 19 peptides were identified and synthesized for investigation of their antiplatelet activities. Hyp-Gly-Glu-Phe-Gly (OGEFG) and Asp-Glu-Gly-Pro (DEGP) exhibited the most potent activity against ADP-induced platelet aggregation among them with IC50 values of 277.17 and 290.00 μM, respectively, and inhibited the release of β-TG and 5-HT in a dose-dependent manner significantly. Single oral administration of OGEFG and DEGP also inhibited thrombus formation in a ferric chloride-induced arterial thrombosis model at a dose of 200 μmol/kg body weight and did not prolong the bleeding time or cause an immune response in mice. Therefore, our findings indicated that collagen peptides had a potential to be developed into an effective specific medical food in the prevention of thrombotic diseases.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel di-peptide Met-Glu from collagen hydrolysates inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombus formation via regulation of Gq-mediated signaling.J Food Biochem. 2020 Sep;44(9):e13352. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13352. Epub 2020 Jul 13. J Food Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32662128
-
Novel Peptide Motifs Containing Asp-Glu-Gly Target P2Y12 and Thromboxane A2 Receptors to Inhibit Platelet Aggregation and Thrombus Formation.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Jan 26;70(3):785-793. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06159. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35016500
-
The Pro-Gly or Hyp-Gly Containing Peptides from Absorbates of Fish Skin Collagen Hydrolysates Inhibit Platelet Aggregation and Target P2Y12 Receptor by Molecular Docking.Foods. 2021 Jul 5;10(7):1553. doi: 10.3390/foods10071553. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34359423 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Hyp-Gly-containing antiplatelet peptides from collagen hydrolysate after simulated gastrointestinal digestion and intestinal absorption.Food Funct. 2020 Jun 24;11(6):5553-5564. doi: 10.1039/d0fo00219d. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32520033
-
Tripeptide Hyp-Asp-Gly from collagen peptides inhibited platelet activation via regulation of PI3K/Akt-MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway.J Food Sci. 2022 Jul;87(7):3279-3293. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16215. Epub 2022 Jun 15. J Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 35703476
Cited by
-
Combination of age-adjusted d-dimer, platelet distribution width and other factors predict preoperative deep venous thrombosis in elderly patients with femoral neck fracture.BMC Surg. 2024 Dec 31;24(1):426. doi: 10.1186/s12893-024-02724-5. BMC Surg. 2024. PMID: 39736660 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Oral Administration of Collagen Peptide OG-5 on Advanced Atherosclerosis Development in ApoE-/- Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 31;16(21):3752. doi: 10.3390/nu16213752. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519585 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insights on Hyp-Gly-Containing Peptides as Antiplatelet Compounds through Topomer CoMFA and CoMSIA Analysis.Foods. 2023 Feb 10;12(4):777. doi: 10.3390/foods12040777. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36832851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McNeil J. J.; Wolfe R.; Woods R. L.; Tonkin A. M.; Donnan G. A.; Nelson M. R.; Reid C. M.; Lockery J. E.; Kirpach B.; Storey E.; Shah R. C.; Williamson J. D.; Margolis K. L.; Ernst M. E.; Abhayaratna W. P.; Stocks N.; Fitzgerald S. M.; Orchard S. G.; Trevaks R. E.; Beilin L. J.; Johnston C. I.; Ryan J.; Radziszewska B.; Jelinek M.; Malik M.; Eaton C. B.; Brauer D.; Cloud G.; Wood E. M.; Mahady S. E.; Satterfield S.; Grimm R.; Murray A. M.; Effect of Aspirin on Cardiovascular Events and Bleeding in the Healthy Elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1509–1518. 10.1056/NEJMoa1805819. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McNeil J. J.; Nelson M. R.; Woods R. L.; Lockery J. E.; Wolfe R.; Reid C. M.; Kirpach B.; Shah R. C.; Ives D. G.; Storey E.; Ryan J.; Tonkin A. M.; Newman A. B.; Williamson J. D.; Margolis K. L.; Ernst M. E.; Abhayaratna W. P.; Stocks N.; Fitzgerald S. M.; Orchard S. G.; Trevaks R. E.; Beilin L. J.; Donnan G. A.; Gibbs P.; Johnston C. I.; Radziszewska B.; Grimm R.; Murray A. M.; Effect of Aspirin on All-Cause Mortality in the Healthy Elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1519–1528. 10.1056/NEJMoa1803955. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

