Transthoracic Echocardiography in Prone Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Feasibility Study
- PMID: 32832914
- PMCID: PMC7417147
- DOI: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000179
Transthoracic Echocardiography in Prone Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
Objectives: Patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome are at risk for developing cardiac dysfunction which is independently associated with worse outcomes. Transthoracic echocardiography is an ideal imaging modality for goal-directed assessment and optimization of cardiac function and volume status. Prone positioning, while demonstrated to improve oxygenation, offload the right ventricle, and reduce short-term mortality in acute respiratory distress syndrome, has previously precluded transthoracic echocardiography on these patients. The purpose of this study was to assess the ability to perform focused transthoracic echocardiography examinations on acute respiratory distress syndrome patients in the prone position.
Design: We performed a cross-sectional study of critically ill patients hospitalized for acute respiratory distress syndrome due to coronavirus disease 2019.
Setting: This study was conducted in medical and surgical intensive units in a tertiary hospital.
Patients: We examined 27 mechanically ventilated and prone patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to coronavirus disease 2019. Participants were examined at the time of enrollment in an ongoing clinical trial (NCT04306393), and no patients were excluded from echocardiographic analysis.
Interventions: None.
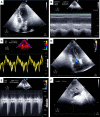
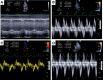
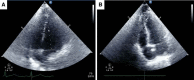
Measurements and main results: We were able to perform transthoracic echocardiography and obtain satisfactory images for quantitative assessment of right ventricular function in 24 out of 27 (88.9%) and left ventricular function in 26 out of 27 (96.3%) of patients in the prone position, including many who were obese and on high levels of positive end-expiratory pressure (≥ 15 cm H2O).
Conclusions: Transthoracic echocardiography can be performed at the prone patient's bedside by critical care intensivists. These findings encourage the use of focused transthoracic echocardiography for goal-directed cardiac assessment in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients undergoing prone positioning.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; coronavirus disease 2019; critical care; prone; transthoracic echocardiography; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transthoracic echocardiography of patients in prone position ventilation during the COVID-19 pandemic: an observational and retrospective study.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Nov;38(11):2303-2309. doi: 10.1007/s10554-022-02659-z. Epub 2022 Jun 26. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36434340 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Right Ventricular Function With CT and Echocardiography in Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation.Crit Care Explor. 2021 Feb 22;3(2):e0345. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000345. eCollection 2021 Feb. Crit Care Explor. 2021. PMID: 33634265 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting Evidence-Based Practice in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review.Crit Care Explor. 2021 Apr 26;3(4):e0391. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000391. eCollection 2021 Apr. Crit Care Explor. 2021. PMID: 33912832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Experts consensus on the management of the right heart function in critically ill patients].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Dec 1;56(12):962-973. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2017.12.017. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29202543 Chinese.
-
Acute cor pulmonale in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A comprehensive review.World J Crit Care Med. 2021 Mar 9;10(2):35-42. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v10.i2.35. eCollection 2021 Mar 9. World J Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33728264 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac function in critically ill patients with severe COVID: A prospective cross-sectional study in mechanically ventilated patients.J Crit Care. 2022 Dec;72:154166. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2022.154166. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 36244256 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiography in Prone Positioned Critically Ill Patients: A Wealth of Information from a Single View.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jun 14;12(6):1460. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12061460. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prone Chest Radiographs: Distinguishing Features and Identification of Support Devices.Lung. 2022 Aug;200(4):441-445. doi: 10.1007/s00408-022-00545-y. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Lung. 2022. PMID: 35708780 Free PMC article.
-
Transthoracic echocardiography of patients in prone position ventilation during the COVID-19 pandemic: an observational and retrospective study.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Nov;38(11):2303-2309. doi: 10.1007/s10554-022-02659-z. Epub 2022 Jun 26. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36434340 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonography in the intensive care unit: a bibliometrics analysis.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Jan 30;16(1):623-631. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1190. Epub 2024 Jan 15. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38410606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guérin C, Reignier J, Richard JC, et al. ; PROSEVA Study Group. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:2159–2168 - PubMed
-
- Ugalde D, Medel JN, Romero C, et al. Transthoracic cardiac ultrasound in prone position: A technique variation description. Intensive Care Med. 2018; 44:986–987 - PubMed
-
- Rudski LG, Lai WW, Afilalo J, et al. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: A report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010; 23:685–713; quiz 786–788 - PubMed
-
- Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015; 28:1–39.e14 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

