α-Ketoglutarate attenuates Wnt signaling and drives differentiation in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 32832918
- PMCID: PMC7442208
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-020-0035-5
α-Ketoglutarate attenuates Wnt signaling and drives differentiation in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Genetic-driven deregulation of the Wnt pathway is crucial but not sufficient for colorectal cancer (CRC) tumourigenesis. Here, we show that environmental glutamine restriction further augments Wnt signaling in APC mutant intestinal organoids to promote stemness and leads to adenocarcinoma formation in vivo via decreasing intracellular alpha-ketoglutarate (aKG) levels. aKG supplementation is sufficient to rescue low-glutamine induced stemness and Wnt hyperactivation. Mechanistically, we found that aKG promotes hypomethylation of DNA and histone H3K4me3, leading to an upregulation of differentiation-associated genes and downregulation of Wnt target genes, respectively. Using CRC patient-derived organoids and several in vivo CRC tumour models, we show that aKG supplementation suppresses Wnt signaling and promotes cellular differentiation, thereby significantly restricting tumour growth and extending survival. Together, our results reveal how metabolic microenvironment impacts Wnt signaling and identify aKG as a potent antineoplastic metabolite for potential differentiation therapy for CRC patients.
Keywords: Wnt signaling; cancer metabolism; colon cancer; epigenetics; glutamine.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
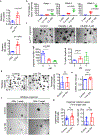
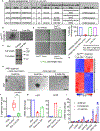

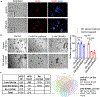

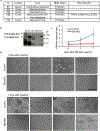
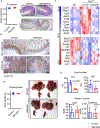
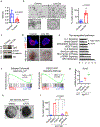


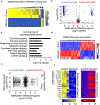
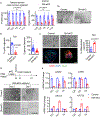
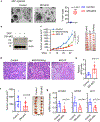
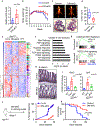
Comment in
-
Restraining colorectal cancer with αKG.Nat Cancer. 2020 Mar;1(3):267-269. doi: 10.1038/s43018-020-0044-4. Nat Cancer. 2020. PMID: 35122033 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kinzler KW & Vogelstein B Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell 87, 159–170 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

