Partial derivative Nonlinear Global Pandemic Machine Learning prediction of COVID 19
- PMID: 32834609
- PMCID: PMC7315984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110056
Partial derivative Nonlinear Global Pandemic Machine Learning prediction of COVID 19
Abstract
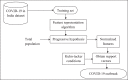
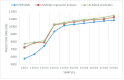
The recent worldwide outbreak of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) opened new challenges for the research community. Machine learning (ML)-guided methods can be useful for feature prediction, involved risk, and the causes of an analogous epidemic. Such predictions can be useful for managing and intercepting the outbreak of such diseases. The foremost advantages of applying ML methods are handling a wide variety of data and easy identification of trends and patterns of an undetermined nature.In this study, we propose a partial derivative regression and nonlinear machine learning (PDR-NML) method for global pandemic prediction of COVID-19. We used a Progressive Partial Derivative Linear Regression model to search for the best parameters in the dataset in a computationally efficient manner. Next, a Nonlinear Global Pandemic Machine Learning model was applied to the normalized features for making accurate predictions. The results show that the proposed ML method outperformed state-of-the-art methods in the Indian population and can also be a convenient tool for making predictions for other countries.
Keywords: Global Pandemic; Kuhn-tucker; Linear Regression; Machine Learning; Nonlinear; Partial Derivative; Progressive.
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

