Doctor-patient distancing: an early experience of telemedicine for postoperative neurosurgical care in the time of COVID-19
- PMID: 32834718
- PMCID: PMC7376313
- DOI: 10.1186/s41983-020-00212-0
Doctor-patient distancing: an early experience of telemedicine for postoperative neurosurgical care in the time of COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Telemedicine remains an important tool of healthcare services delivery especially in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Its advantages include saving the time and money of the patients and the prevention of infection among healthcare providers.
Objectives: In this study, we aim to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of telemedicine visits in providing postoperative care of neurosurgical patients.
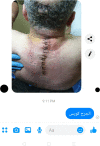
Materials and methods: We conducted this prospective study on 30 neurosurgical patients who were evaluated after surgery via telemedicine visits for 30 days. During the virtual visits, we discussed the clinical progress of patients, wound status, treatment modification, the time of return to work, postoperative complications, and the radiological data of the patients. All the patients were given an emergency number to call in case of urgent issues. The satisfaction of patients and doctors was measured with the aid of two questionnaires.
Results: The patients' age ranged from 18 to 65 years. Twenty patients were male and 10 patients were female. We performed 20 cranial operations and 10 spinal operations. Most patients needed more than 4 h to reach the hospital. The total number of telemedicine visits was 67 visits. We received about 62 emergency calls. Pain management, seizures control, wound infection, and hydrocephalus is among issues that were evaluated and managed via telemedicine visits. The overall satisfaction rate among patients and doctors was 90% and 95%, respectively.
Conclusion: Virtual outpatient clinics seem to be a safe and effective way of postoperative care especially in the time of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Postoperative; Telemedicine.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous