Chinese medical drugs for coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32834992
- PMCID: PMC7385501
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imr.2020.100477
Chinese medical drugs for coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Integration of Chinese medical drugs (CMD) and western medicine (WM) has been widely used in the treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). This systematic review aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of CMD for COVID-19.
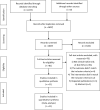
Method: A literature search was performed in six databases from injection to June 2020. Both randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs were considered as eligible. The quality of included RCTs were assessed by Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool, and Review Manager 5.3 software was used to do meta-analysis.
Result: Eleven studies with 1259 patients were included in this study. CMD included herbal decoction and Chinese patent medicine. The methodological quality was evaluated as generally unclear. The results of meta-analysis showed that the integration of CMD and WM had better efficacy than WM in number of patients turned to severe and critical type (RR = 0.47, 95% CI=[0.32, 0.69], P < 0.0001), length of hospital stay (MD= -7.95, 95% CI=[-14.66, -1.24], P = 0.02), defervescence time (MD= -1.20, 95% CI=[-2.03, -0.38], P = 0.004), cough resolution rate (RR = 1.37, 95% CI=[1.15, 1.64], P = 0.0004), fatigue resolution rate (RR = 1.37, 95% CI=[1.02, 1.83], P = 0.04), and tachypnea resolution rate (RR = 2.20, 95% CI=[1.11, 4.39], P = 0.02). As for safety, there was no significant difference between two groups.
Conclusion: CMD may bring potential benefit to patients suffered from COVID-19. However, the quality of included trials is not good enough. High quality study with core outcome set are still required.
Keywords: Chinese medical drug; Core outcome set; Coronavirus disease 2019; Integrative medicine; Meta analysis; Systematic review.
.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine as an Auxiliary Treatment for COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Altern Complement Med. 2021 Mar;27(3):225-237. doi: 10.1089/acm.2020.0310. Epub 2020 Nov 20. J Altern Complement Med. 2021. PMID: 33252246
-
Add-on effect of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 20;16(8):e0256429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256429. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34415962 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Tanreqing injection for cough caused by acute trachea-bronchitis disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117429. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117429. Epub 2023 Nov 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38007165
-
Efficacy and safety of the Chinese herbal medicine Xiao-qing-long-tang for allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 28;297:115169. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115169. Epub 2022 Mar 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35257842
-
Efficacy of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Treating COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of RCTs.Front Public Health. 2021 Jul 8;9:622707. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.622707. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34307269 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Machine Learning Approach for Recommending Herbal Formulae with Enhanced Interpretability and Applicability.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 31;12(11):1604. doi: 10.3390/biom12111604. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358954 Free PMC article.
-
A review of natural products, their effects on SARS-CoV-2 and their utility as lead compounds in the discovery of drugs for the treatment of COVID-19.Med Chem Res. 2022;31(1):40-51. doi: 10.1007/s00044-021-02826-2. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Med Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 34873386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative medicine for COVID-19: Researches and evidence.Integr Med Res. 2020 Sep;9(3):100496. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2020.100496. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Integr Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32834994 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Practicing traditional Chinese medicine in the COVID-19 pandemic in Switzerland - an exploratory study.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Sep 15;22(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03715-w. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 36109731 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions for COVID-19: An overview of systematic reviews.Integr Med Res. 2022 Sep;11(3):100842. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2022.100842. Epub 2022 Mar 13. Integr Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35308033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gao Y.Q. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 based on its pathophysiological mechanisms. Chin J Pathophysiol. 2020;36 568-572+576. [In Chinese, English abstract]
-
- Wang H.J., Du S.H., Yue X., Chen C.X. Review and prospect of pathological features of corona virus disease. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;36:16–20. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

