Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes Are Susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 32835305
- PMCID: PMC7323681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100052
Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes Are Susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
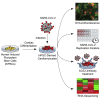
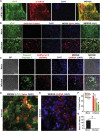
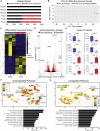
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). COVID-19 is defined by respiratory symptoms, but cardiac complications including viral myocarditis are also prevalent. Although ischemic and inflammatory responses caused by COVID-19 can detrimentally affect cardiac function, the direct impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on human cardiomyocytes is not well understood. Here, we utilize human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) as a model to examine the mechanisms of cardiomyocyte-specific infection by SARS-CoV-2. Microscopy and RNA sequencing demonstrate that SARS-CoV-2 can enter hiPSC-CMs via ACE2. Viral replication and cytopathic effect induce hiPSC-CM apoptosis and cessation of beating after 72 h of infection. SARS-CoV-2 infection activates innate immune response and antiviral clearance gene pathways, while inhibiting metabolic pathways and suppressing ACE2 expression. These studies show that SARS-CoV-2 can infect hiPSC-CMs in vitro, establishing a model for elucidating infection mechanisms and potentially a cardiac-specific antiviral drug screening platform.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cardiology; cardiomyocytes; cardiovascular biology; coronavirus; heart; induced pluripotent stem cells; stem cell; viral myocarditis.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes are Susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 Infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Apr 21:2020.04.21.051912. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.21.051912. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell Rep Med. 2020 Jul 21;1(4):100052. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100052. PMID: 32511402 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ramaiah A., Arumugaswami V. Insights into Cross-species Evolution of Novel Human Coronavirus 2019-nCoV and Defining Immune Determinants for Vaccine Development. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.01.29.925867. - DOI
-
- Hoffmann, M., Kleine-Weber, H., Schroeder, S., Kruger, N., Herrler, T., and Erichsen, S., Schiergens, T.S., Herrler, G., Wu, N.-H., Nitsche, A., Müller, M.A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 181, 271–280. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

