An Integrated Multi-Function Heterogeneous Biochemical Circuit for High-Resolution Electrochemistry-Based Genetic Analysis
- PMID: 32835412
- PMCID: PMC9306392
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202010648
An Integrated Multi-Function Heterogeneous Biochemical Circuit for High-Resolution Electrochemistry-Based Genetic Analysis
Abstract
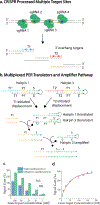
Modular construction of an autonomous and programmable multi-functional heterogeneous biochemical circuit that can identify, transform, translate, and amplify biological signals into physicochemical signals based on logic design principles can be a powerful means for the development of a variety of biotechnologies. To explore the conceptual validity, we design a CRISPR-array-mediated primer-exchange-reaction-based biochemical circuit cascade, which probes a specific biomolecular input, transform the input into a structurally accessible form for circuit wiring, translate the input information into an arbitrary sequence, and finally amplify the prescribed sequence through autonomous formation of a signaling concatemer. This upstream biochemical circuit is further wired with a downstream electrochemical interface, delivering an integrated bioanalytical platform. We program this platform to directly analyze the genome of SARS-CoV-2 in human cell lysate, demonstrating the capability and the utility of this unique integrated system.
Keywords: CRISPR; bioanalytical chemistry; electrochemistry; genetic circuits; primer exchange reaction.
© 2020 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intrinsic signal amplification by type III CRISPR-Cas systems provides a sequence-specific SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic.Cell Rep Med. 2021 Jun 15;2(6):100319. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100319. Epub 2021 May 27. Cell Rep Med. 2021. PMID: 34075364 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the amplification-free SERS-based CRISPR/Cas12a platform in the identification of SARS-CoV-2 from clinical samples.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Sep 8;19(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01021-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34496881 Free PMC article.
-
A simple and rapid method to assay SARS-CoV-2 RNA based on a primer exchange reaction.Chem Commun (Camb). 2022 Apr 5;58(28):4484-4487. doi: 10.1039/d2cc00488g. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022. PMID: 35302142
-
CRISPR-based biosensing systems: a way to rapidly diagnose COVID-19.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2021 Jun;58(4):225-241. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2020.1849010. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2021. PMID: 33245685 Review.
-
Mechanistic insights of CRISPR/Cas nucleases for programmable targeting and early-stage diagnosis: A review.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 May 1;203:114033. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114033. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 35131696 Review.
Cited by
-
Unified-amplifier based primer exchange reaction (UniAmPER) enabled detection of SARS-CoV-2 from clinical samples.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2022 Apr 15;357:131409. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2022.131409. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2022. PMID: 35035095 Free PMC article.
-
A PAM-free CRISPR/Cas12a ultra-specific activation mode based on toehold-mediated strand displacement and branch migration.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 11;50(20):11727-11737. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac886. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36318259 Free PMC article.
-
The Trend of CRISPR-Based Technologies in COVID-19 Disease: Beyond Genome Editing.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Feb;65(2):146-161. doi: 10.1007/s12033-021-00431-7. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35091986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clustered Regularly Interspaced short palindromic repeats-Based Microfluidic System in Infectious Diseases Diagnosis: Current Status, Challenges, and Perspectives.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Dec;9(34):e2204172. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204172. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 36257813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-based tools: Alternative methods for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Clin Biochem. 2021 Mar;89:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.12.011. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Clin Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33428900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li J, Green AA, Yan H, Fan C, Nature Chemistry 2017, 9, 1056–1067; - PMC - PubMed
- Woods D, Doty D, Myhrvold C, Hui J, Zhou F, Yin P, Winfree E, Nature 2019, 567, 366–372; - PubMed
- Cherry KM, Qian L, Nature 2018, 559, 370–376; - PubMed
- Hanewich-Hollatz MH, Chen Z, Hochrein LM, Huang J, Pierce NA, ACS Central Science 2019, 5, 1241–1249; - PMC - PubMed
- Mao C, LaBean TH, Reif JH, Seeman NC, Nature 2000, 407, 493–496. - PubMed
-
- Kelley SO, Mirkin CA, Walt DR, Ismagilov RF, Toner M, Sargent EH, Nature nanotechnology 2014, 9, 969; - PMC - PubMed
- Tan W, Li L, Xu S, Yan H, Li X, Yazd HS, Li X, Huang T, Cui C, Jiang J, Angewandte Chemie International Edition, n/a; - PubMed
- Samanta D, Ebrahimi SB, Mirkin CA, Advanced Materials 2020, 32, 1901743; - PMC - PubMed
- Yang F, Li Q, Wang L, Zhang G-J, Fan C, ACS Sensors 2018, 3, 903–919; - PubMed
- Furst AL, Muren NB, Hill MG, Barton JK, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, 111, 14985–14989; - PMC - PubMed
- Kim J, Campbell AS, de Ávila BE-F, Wang J, Nature Biotechnology 2019, 37, 389–406; - PMC - PubMed
- Yang Y, Gao W, Chemical Society Reviews 2019, 48, 1465–1491; - PubMed
- Bariya M, Nyein HYY, Javey A, Nature Electronics 2018, 1, 160–171;
- Gao W, Zdrachek E, Xie X, Bakker E, Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2020, 59, 2294–2298; - PubMed
- Ranallo S, Rossetti M, Plaxco KW, Vallée-Bélisle A, Ricci F, Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2015, 54, 13214–13218; - PMC - PubMed
- Dai Y, Liu CC, Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2019, 58, 12355–12368; - PubMed
- Rossetti M, Brannetti S, Mocenigo M, Marini B, Ippodrino R, Porchetta A, Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2020, 59, 14973–14978. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y, Tilley RD, Gooding JJ, Journal of the American Chemical Society 2019, 141, 1162–1170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

