Novel monoclonal antibodies to the SERINC5 HIV-1 restriction factor detect endogenous andvirion-associated SERINC5
- PMID: 32835602
- PMCID: PMC7531522
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2020.1802187
Novel monoclonal antibodies to the SERINC5 HIV-1 restriction factor detect endogenous andvirion-associated SERINC5
Abstract
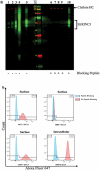
SERINC5 is a multi-pass transmembrane protein that is thought to play a role in serine incorporation during cellular membrane biosynthesis. This protein has also been identified as a human immunodeficiency virus Type 1 (HIV-1) restriction factor. The paucity of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against SERINC5 has posed a challenge for the study of the endogenous protein. Here we report the development of novel anti-SERINC5 mAbs that target three distinct loops on the protein. We demonstrate that these SERINC5 mAbs can be used to detect endogenously expressed SERINC5 protein in various cell lines using Western blot, whole-cell ELISA, flow cytometry, and immunocytochemistry. We further show that some of these antibodies can detect SERINC5 that is present in HIV-1 viral stocks. These antibodies will aid in the characterization of the functions and mechanisms of action of SERINC5 in different cell types.
Keywords: HIV-1 restriction factor; SERINC5; immunocytochemistry; monoclonal antibody; multi-pass transmembrane protein; serine incorporator; virus capture.
Figures
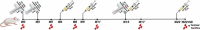

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
