Polarization and public health: Partisan differences in social distancing during the coronavirus pandemic
- PMID: 32836504
- PMCID: PMC7409721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpubeco.2020.104254
Polarization and public health: Partisan differences in social distancing during the coronavirus pandemic
Abstract
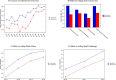
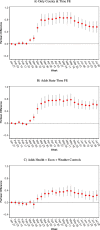
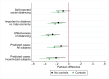
We study partisan differences in Americans' response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Political leaders and media outlets on the right and left have sent divergent messages about the severity of the crisis, which could impact the extent to which Republicans and Democrats engage in social distancing and other efforts to reduce disease transmission. We develop a simple model of a pandemic response with heterogeneous agents that clarifies the causes and consequences of heterogeneous responses. We use location data from a large sample of smartphones to show that areas with more Republicans engaged in less social distancing, controlling for other factors including public policies, population density, and local COVID cases and deaths. We then present new survey evidence of significant gaps at the individual level between Republicans and Democrats in self-reported social distancing, beliefs about personal COVID risk, and beliefs about the future severity of the pandemic.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Health behaviors; Media trust; Political polarization.
© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Abatzoglou John T. Development of gridded surface meteorological data for ecological applications and modeling. Int. J. Climatol. 2011;33(1):121–131.
-
- Aleem Zeeshan. A new poll shows a startling partisan divide on the dangers of the coronavirus. Vox. 2020 https://www.vox.com/2020/3/15/21180506/coronavirus-poll-democrats-republ... March 15.
-
- Allcott Hunt, Boxell Levi, Conway Jacob, Ferguson Billy, Gentzkow Matthew, Goldman Benny. 2020. The Effect of Stay-at-home Orders on Mobility, Economic, and Health Outcomes during the Coronavirus Pandemic. (Working Paper)
-
- Andersen Martin. 2020. Early Evidence on Social Distancing in Response to COVID-19 in the United States. (Working Paper)
-
- Ash Elliott, Galletta Sergio, Hangartner Dominik, Margalit Yotam, Pinna Matteo. 2020. The Effect of Fox News on Health Behavior During COVID-19. (Working Paper)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

