Impacts of epidemic outbreaks on supply chains: mapping a research agenda amid the COVID-19 pandemic through a structured literature review
- PMID: 32836615
- PMCID: PMC7298926
- DOI: 10.1007/s10479-020-03685-7
Impacts of epidemic outbreaks on supply chains: mapping a research agenda amid the COVID-19 pandemic through a structured literature review
Abstract
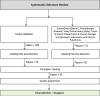
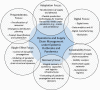
The coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak shows that pandemics and epidemics can seriously wreak havoc on supply chains (SC) around the globe. Humanitarian logistics literature has extensively studied epidemic impacts; however, there exists a research gap in understanding of pandemic impacts in commercial SCs. To progress in this direction, we present a systematic analysis of the impacts of epidemic outbreaks on SCs guided by a structured literature review that collated a unique set of publications. The literature review findings suggest that influenza was the most visible epidemic outbreak reported, and that optimization of resource allocation and distribution emerged as the most popular topic. The streamlining of the literature helps us to reveal several new research tensions and novel categorizations/classifications. Most centrally, we propose a framework for operations and supply chain management at the times of COVID-19 pandemic spanning six perspectives, i.e., adaptation, digitalization, preparedness, recovery, ripple effect, and sustainability. Utilizing the outcomes of our analysis, we tease out a series of open research questions that would not be observed otherwise. Our study also emphasizes the need and offers directions to advance the literature on the impacts of the epidemic outbreaks on SCs framing a research agenda for scholars and practitioners working on this emerging research stream.
Keywords: Adaptation; COVID-19; Digitalization; Epidemic outbreaks; Influenza; Pandemic; Preparedness; Recovery; Resilience; Ripple effect; Structured literature review; Supply chain; Sustainability.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
OR-methods for coping with the ripple effect in supply chains during COVID-19 pandemic: Managerial insights and research implications.Int J Prod Econ. 2021 Feb;232:107921. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107921. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Int J Prod Econ. 2021. PMID: 32952301 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the impacts of epidemic outbreaks on global supply chains: A simulation-based analysis on the coronavirus outbreak (COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2) case.Transp Res E Logist Transp Rev. 2020 Apr;136:101922. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2020.101922. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Transp Res E Logist Transp Rev. 2020. PMID: 32288597 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pandemic related supply chain studies: A systematic review.Transp Res E Logist Transp Rev. 2021 Apr;148:102271. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2021.102271. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Transp Res E Logist Transp Rev. 2021. PMID: 33613082 Free PMC article.
-
The implications of Industry 4.0 on supply chains amid the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review.F1000Res. 2021 Oct 5;10:1008. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.73138.2. eCollection 2021. F1000Res. 2021. PMID: 35387274 Free PMC article.
-
Supply chain disruption during the COVID-19 pandemic: Recognizing potential disruption management strategies.Int J Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022 Jun 1;75:102983. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.102983. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022. PMID: 35475018 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
System dynamics model for an agile pharmaceutical supply chain during COVID‑19 pandemic in Iran.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 11;19(1):e0290789. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290789. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38206960 Free PMC article.
-
OR-methods for coping with the ripple effect in supply chains during COVID-19 pandemic: Managerial insights and research implications.Int J Prod Econ. 2021 Feb;232:107921. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107921. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Int J Prod Econ. 2021. PMID: 32952301 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of epidemic outbreaks (COVID-19) on global supply chains: A case of trade between Turkey and China.Socioecon Plann Sci. 2023 Feb;85:101494. doi: 10.1016/j.seps.2022.101494. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Socioecon Plann Sci. 2023. PMID: 36514316 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of COVID-19 outbreak on employee performance - Moderating role of industry 4.0 base technologies.Int J Prod Econ. 2021 Apr;234:108075. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108075. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Int J Prod Econ. 2021. PMID: 36569040 Free PMC article.
-
A multicountry, multicommodity stochastic game theory network model of competition for medical supplies inspired by the Covid-19 pandemic.Int J Prod Econ. 2021 Jun;236:108074. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108074. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Int J Prod Econ. 2021. PMID: 35615460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldrighetti R, Zennaro I, Battini D, Finco S. Healthcare supply chain simulation with disruption considerations: A case study from Northern Italy. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management. 2019;20:81–102. doi: 10.1007/s40171-019-00223-8. - DOI
-
- Amiri-Aref M, Farahani RZ, Hewitt M, Klibi W. Equitable location of facilities in a region with probabilistic barriers to travel. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review. 2019;127:66–85. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2019.04.010. - DOI
-
- Anparasan AA, Lejeune M. Analyzing the response to epidemics: Concept of evidence-based Haddon matrix. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management. 2017;7(3):266–283. doi: 10.1108/JHLSCM-06-2017-0023. - DOI
-
- Anparasan AA, Lejeune M. Resource deployment and donation allocation for epidemic outbreaks. Annals of Operations Research. 2019;283(1–2):9–32. doi: 10.1007/s10479-016-2392-0. - DOI
-
- Anparasan AA, Lejeune MA. Data laboratory for supply chain response models during epidemic outbreaks. Annals of Operations Research. 2018;270(1–2):53–64. doi: 10.1007/s10479-017-2462-y. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous