Information management research and practice in the post-COVID-19 world
- PMID: 32836635
- PMCID: PMC7304950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102175
Information management research and practice in the post-COVID-19 world
Abstract
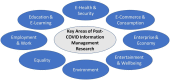
COVID-19 has radically transformed many aspects of human life and global society both now and for many years to come. A key aspect of the transformation has been increased digitalization and the accelerated implementation of previously predicted trends that have been discussed for many years in the information management literature. Human endeavour has encouraged us to adapt to the "new normal" through immediate necessity in areas such as work, education, healthcare, entertainment and leisure, and online commerce. This new environment has provided unprecedented opportunities for the information management research community to develop research that will have a significant impact on practice in these and other areas. We are essentially at the pinnacle of new developments in the digital space and must seek to develop exemplars that can help to signpost the future direction of digital global society for the benefit of all. Notwithstanding, the problems of digitalization have also been exacerbated and must be further understood and ameliorated in the post-COVID world. This paper examines opportunities and problems in information management brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic. It details implications for research and practice.
Keywords: COVID-19; Digitalization; Innovation; Pandemic; Research impact; Research opportunities.
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- ACI Worldwide . 2020. Global eCommerce retail sales up 209 percent in April. Available online: https://www.aciworldwide.com/news-and-events/press-releases/2020/may/glo... [Accessed 12th June 2020]
-
- Barnes S.J. SSRN; 2016. Understanding virtual reality in marketing: Nature, implications and potential. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2909100 [Accessed 12th June 2020]
-
- Barnes S.J., Pressey A.D., Scornavacca E. Mobile ubiquity: Understanding the impact of cognitive absorption on smartphone addiction. Computers in Human Behavior. 2019;90:246–258.
-
- Baruch Y. Teleworking: Benefits and pitfalls as perceived by professionals and managers. New Technology, Work and Employment. 2000;15(1):34–49.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources