COVID-19 Vaccines: A Race Against Time in the Middle of Death and Devastation!
- PMID: 32837093
- PMCID: PMC7286271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2020.06.003
COVID-19 Vaccines: A Race Against Time in the Middle of Death and Devastation!
Abstract
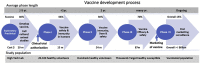
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has turned into a global human tragedy and economic devastation. Governments have implemented lockdown measures, blocked international travel, and enforced other public containment measures to mitigate the virus morbidity and mortality. As of today, no drug has the power to fight the infection and bring normalcy to the utter chaos. This leaves us with only one choice namely an effective and safe vaccine that shall be manufactured as soon as possible and available to all countries and populations affected by the pandemic at an affordable price. There has been an unprecedented fast track path taken in Research & Development by the World community for developing an effective and safe vaccine. Platform technology has been exploited to develop candidate vaccines in a matter of days to weeks, and as of now, 108 such vaccines are available. Six of these vaccines have entered clinical trials. As clinical trials are "rate-limiting" and "time-consuming", many innovative methods are in practice for a fast track. These include parallel phase I-II trials and obtaining efficacy data from phase IIb trials. Human "challenge experiments" to confirm efficacy in humans is under serious consideration. The availability of the COVID-19 vaccine has become a race against time in the middle of death and devastation. There is an atmosphere of tremendous hype around the COVID-19 vaccine, and developers are using every moment to make claims, which remain unverified. However, concerns are raised about a rush to deploy a COVID-19 vaccine. Applying "Quick fix" and "short cuts" can lead to errors with disastrous consequences.
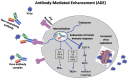
Keywords: ADE, Antibody-Dependent Enhancement; CEPI, Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations; COVID-19; COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019; MERS-CoV, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus; MHC, Major Histocompatibility Complex; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; WHO, World Health Organization; coronavirus; platform technology clinical trials; vaccine.
© 2020 Indian National Association for Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have none to declare.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. Naming the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and the Virus that Causes it.https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica... [updated March 11. Available from:
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic.https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 [updated March 11. Available from:
-
- Anonymous . Dadax Limited.; 2020. Worldometer. Covid-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. The United States.https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?utm_campaign=homeAdvegas1? [updated May 4th, 2020. Available from:
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

