Crisis and disaster management in the light of the Islamic approach: COVID-19 pandemic crisis as a model (a qualitative study using the grounded theory)
- PMID: 32837321
- PMCID: PMC7323116
- DOI: 10.1002/pa.2217
Crisis and disaster management in the light of the Islamic approach: COVID-19 pandemic crisis as a model (a qualitative study using the grounded theory)
Abstract
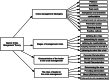
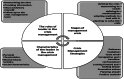
The current study sought to generate a theory from the data on crisis management in Islam, and also aimed to identify the strategies used by leaders in the crisis management process. The grounded theory approach was applied, which is one of the qualitative designs. The content of the verses of the Noble Qur'an and the hadiths of the Prophet Muhammad that dealt with the issue of crises were analyzed. The results of the qualitative analysis of the verses of the Qur'an and the hadiths of the Prophet's noble Sunnah have resulted in four concepts that constitute a broad conceptual theory of crisis management according to the Islamic approach. These concepts are: Crisis management strategies in Islam, the stages of crisis management, the characteristics of a leader who manages crises, and the roles of a leader during the crisis management process. A number of assumptions have been made of this generated theory about Islamic crisis management model. In light of the results of this study, recommendations were formulated that indicate the necessity of training leaders in the Islamic approach to crisis management, its strategies and its scientific steps in crisis management. These results have wide applications in the field of training leaders, and also recommend future studies to verify the assumptions of the theory that emerged from the data in this study on crisis management in Islam (COVID-19 pandemic crisis as a model).
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Public Affairs published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abu Farah, Y. (2009). Crisis management, integrated entrance. Amman, Jordan: Athraa for Publishing and Distribution.
-
- Abu Khalil, M. (2001). The position of principals of basic education schools on some crises and planning to face them. The Future of Arab Education, 7(21), 259–318.
-
- Ahmed, A. (2002). Management of the educational crisis in schools, causes and treatment. Cairo, Egypt: Dar Al‐Fikr Al‐Arabi.
-
- Al Eid, N. A. , Arnout, B. A. , & Almoied, A. A. (2020). Leader's spiritual intelligence and religiousness: Skills, factors affecting, and their effects on performance (a qualitative study by grounded theory). Journal of Public Affairs, 2020, e2129. 10.1002/pa.2129 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources