[Recommendations for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) in COVID-19 Patients]
- PMID: 32837601
- PMCID: PMC7286215
- DOI: 10.1007/s00740-020-00349-x
[Recommendations for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) in COVID-19 Patients]
Abstract
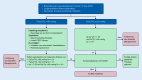
The pandemic from the SARS-CoV‑2 Virus is currently challenging health care systems all over the world. Maintaining appropriate staffing and resources in healthcare facilities is essential to guarantee a safe work environment for healthcare personnel and safe patient care. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) represents a valuable therapeutic option in patients with severe heart or lung failure. Although only a limited proportion of COVID-19 patients develops respiratory or circulatory failure that is refractory to conventional therapies, it is of utmost importance to clearly define criteria for the use of ECMOs in this steadily growing patient population. The ECMO working group of the Medical University of Vienna has established the following recommendations for ECMO support in COVID-19 patients.
Die aktuelle COVID-19-Pandemie, die durch das SARS-CoV‑2 ausgelöst wird, hat bereits in vielen betroffenen Ländern zu gravierenden Ressourcenengpässen der jeweiligen Gesundheitssysteme geführt. Obwohl sehr viele COVID-19-Patienten nur moderate Symptome zeigen, entwickelt eine Subgruppe ein schweres respiratorisches oder auch kardiales Versagen. Die extrakorporale Membranoxygenierung (ECMO) stellt eine wertvolle Therapieoption für Patienten mit therapierefraktärem Lungen- oder Herzversagen dar. Es bedarf klarer Empfehlungen, die den ECMO-Einsatz in dieser zahlenmäßig stetig steigenden Patientenpopulation regeln. Die ECMO-Arbeitsgruppe der Medizinischen Universität Wien hat daher die folgenden Empfehlungen für eine ECMO-Unterstützung bei COVID-19-Patienten formuliert.
Keywords: Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome; Canulation; Criteria; Indications; Recommendations.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Similar articles
-
Recommendations for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in COVID-19 patients : Consensus paper of the Medical University of Vienna.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2020 Nov;132(21-22):671-676. doi: 10.1007/s00508-020-01708-8. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2020. PMID: 32621065 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal lung support technologies - bridge to recovery and bridge to lung transplantation in adult patients: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(5):1-47. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074408 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome: a narrative review.J Intensive Care. 2023 Feb 8;11(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40560-023-00654-7. J Intensive Care. 2023. PMID: 36755270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) - in the treatment of severe, life-threatening respiratory failure.Wiad Lek. 2019;72(9 cz 2):1822-1828. Wiad Lek. 2019. PMID: 31622273
-
COVID-19 and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1353:173-195. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-85113-2_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 35137374 Review.
References
-
- ELSO (2020) ELSO guidance document: ECMO for COVID-19 patients with severe cardiopulmonary failure. https://www.elso.org/. Zugegriffen: 24.03.2020 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous