Influencing factors of COVID-19 spreading: a case study of Thailand
- PMID: 32837844
- PMCID: PMC7301627
- DOI: 10.1007/s10389-020-01329-5
Influencing factors of COVID-19 spreading: a case study of Thailand
Abstract
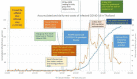
Aim: A novel corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was declared as pandemic by WHO as global level and local levels in many countries. The movement of people might be one influencing factor, this paper aims to report the situation COVID-19 and spreading in Thailand, including influencing factors of spreading and control.
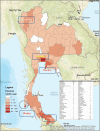
Subject and method: Infected, confirmed COVID-19 data were obtained from the official website of the Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health. Tourist data was downloaded from Ministry of Tourism and Sports. Researchers analyzed the situation from the first found case in Thailand until 15 April 2020 with the timeline of important influencing factors. Correlation coefficients of tourist data and infected case was calculated by person correlation coefficient.
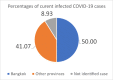
Results: The number of infected cases was significant associated (correlation coefficient > 0.7) with economic factor, namely; number of visitors, generated income from both Thai and foreigner tourist (p value <0.01). The influencing factors of slow increased rate were the enforcement and implementation of both central and local government regulation, the strength of the Thai health care system, the culture and social relation, the partnership among various governmental and private sectors.
Conclusion: We found that the number of tourist and their activities were significant associated with number of infected, confirmed COVID-19 cases. The public education and social supporting were the key roles for regulation enforcement and implementation.
Keywords: COVID-19; Disease spreading; Influencing factors; Thailand; Tourist factors.
© Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bangkok-Post (2019) Thailand's healthcare ranked sixth best in the world. https://www.bangkokpost.com/thailand/general/1746289/thailands-healthcar.... Accessed 15 April 2020
-
- Chappell B (2020) Coronavirus: COVID-19 Is Now Officially A Pandemic, WHO Says. https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2020/03/11/814474930/coronavir.... Accessed 25 April 2020
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous