COVID-19 Pandemic: from Molecular Biology, Pathogenesis, Detection, and Treatment to Global Societal Impact
- PMID: 32837855
- PMCID: PMC7382994
- DOI: 10.1007/s40495-020-00229-2
COVID-19 Pandemic: from Molecular Biology, Pathogenesis, Detection, and Treatment to Global Societal Impact
Abstract
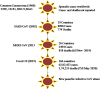
Purpose of review: In December 2019, there was an outbreak of viral disease in Wuhan, China which raised the concern across the whole world. The viral disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or novel coronavirus or COVID-19 (CoV-19) is known as a pandemic. After SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-related CoV, COVID-19 is the third most pathogenic virus, hazardous to humans which have raised worries concerning the capacity of current security measures and the human services framework to deal with such danger.
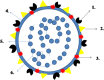
Recent findings: According to WHO, the mortality rate of COVID-19 exceeded that of SARS and MERS in view of which COVID-19 was declared as public health emergency of international concern. Coronaviruses are positive-sense RNA viruses with single stranded RNA and non-segmented envelopes. Recently, genome sequencing confirmed that COVID-19 is similar to SARS-CoV and bat coronavirus, but the major source of this pandemic outbreak, its transmission, and mechanisms related to its pathogenicity to humans are not yet known.
Summary: In order to prevent the further pandemic and loss to humanity, scientists are studying the development of therapeutic drugs, vaccines, and strategies to cure the infections. In this review, we present a brief introduction to emerging and re-emerging pathogens, i.e., coronavirus in humans and animals, its taxonomic classification, genome organization, its replication, pathogenicity, impact on socioeconomic growth, and drugs associated with COVID-19.
Keywords: Coronavirus; MERS-CoV; RNA genomes; SARS-CoV.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel coronavirus pathogen in humans and animals: an overview on its social impact, economic impact, and potential treatments.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Dec;28(48):68071-68089. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16809-8. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34664166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 2020 Pandemic: Current SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Development.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 19;11:1880. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01880. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak - an update on the status.Mil Med Res. 2020 Mar 13;7(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0. Mil Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32169119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Strategies of Antiviral Drug Discovery for COVID-19.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:671263. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671263. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The novel zoonotic COVID-19 pandemic: An expected global health concern.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2020 Mar 31;14(3):254-264. doi: 10.3855/jidc.12671. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2020. PMID: 32235085
Cited by
-
Exploring the conformational dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 SL4 hairpin by combining optical tweezers and base analogues.Nanoscale. 2024 Jan 3;16(2):752-764. doi: 10.1039/d3nr04110g. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38087988 Free PMC article.
-
The Case Fatality Rate in COVID-19 Patients With Cardiovascular Disease: Global Health Challenge and Paradigm in the Current Pandemic.Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2020;6(6):315-324. doi: 10.1007/s40495-020-00239-0. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32953401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Evolution of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2: Hazardous and More Hazardous Strains Behind the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic and Their Targeting by Drugs and Vaccines.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Dec 14;11:763687. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.763687. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34970505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms Underlying COVID-19 Pathogenesis.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 2;9(9):1142. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091142. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the relevance of SARS-Cov-2 infection and ferroptosis within the heart of COVID-19 patients.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 24;10(17):e36567. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36567. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39263089 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
