Nanomaterial assisted bulk scale synthesis of 2-methyl-6-nitroquinoline
- PMID: 32837922
- PMCID: PMC7415172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.103
Nanomaterial assisted bulk scale synthesis of 2-methyl-6-nitroquinoline
Abstract
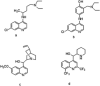
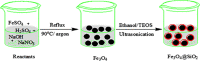
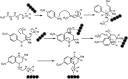
Quinolines are an interesting class of moieties with various medicinal chemistry uses. The most prominent is their ability to be used as the last line of therapy for bacterial and viral infections including recent COVID-19. The synthesis of quinoline is through a cyclization reaction and overall reaction yields are about 20%. The bulky ring and the associated crowding of functional groups limit the catalyst options. In this publication, the use of Fe3O4@SiO2 for enhancing yield improvements, especially for heterocyclics is reported. The use of the 40 nm sized silica functionalized magnetite nanoparticles seems to help in both condensation and cyclization steps of representative 2-methyl-6-nitroquinoline. Reaction time reduction due to surface enabled catalysis of nanoparticles is 110 min to 80 min. The reaction yield has doubled due to the presence of catalyst and the mechanism suggests this drastic result is due to stabilization of unstable intermediate on the acidic surface of the silica coating. This near homogeneous catalysis of 40 nm sized, silica functionalized, magnetite nanoparticles have far reaching applications in bulk drug industry for drugs like chloroquine & hydroxychloroquine, the two essential drugs for prophylactic use for COVID-1.
Keywords: 2-methyl-6-nitroquinolin; Bulk Scale Synthesis; Fe3O4@SiO2; Quinoline; Silica functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles (SMNP).
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Selection and peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the International Conference on Newer Trends and Innovation in Mechanical Engineering: Materials Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


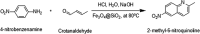

References
-
- Sharma R., Patil S., Maurya P. Drug discovery studies on quinoline-based derivatives as potential antimalarial agents. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2014;25:189–203. - PubMed
-
- Ramírez-Prada J., Robledo S.M., Vélez I.D., Crespo M.del P., Quiroga J., Abonia R., Montoya A., Svetaz L., Zacchino S., Insuasty B. Synthesis of novel quinoline–based 4,5–dihydro–1 H –pyrazoles as potential anticancer, antifungal, antibacterial and antiprotozoal agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017;131:237–254. - PubMed
-
- Xu M., Wagerle T., Long J.K., Lahm G.P., Barry J.D., Smith R.M. Insecticidal quinoline and isoquinoline isoxazolines. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014;24:4026–4030. - PubMed
-
- Ghorab M.M., Alsaid M.S. Anti-breast cancer activity of some novel quinoline derivatives. Acta Pharm. 2015;65:271–283. - PubMed
-
- Paloque L., Verhaeghe P., Casanova M., Castera-Ducros C., Dumètre A., Mbatchi L., Hutter S., Kraiem-M’Rabet M., Laget M., Remusat V., Rault S., Rathelot P., Azas N., Vanelle P. Discovery of a new antileishmanial hit in 8-nitroquinoline series. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012;54:75–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
