Investigation of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM Antibodies in the Patients with COVID-19 by Three Different ELISA Test Kits
- PMID: 32838175
- PMCID: PMC7377663
- DOI: 10.1007/s42399-020-00409-7
Investigation of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM Antibodies in the Patients with COVID-19 by Three Different ELISA Test Kits
Abstract
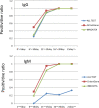
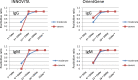
We examined anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM antibodies in 45 serum samples from 26 patients with COVID-19, who were admitted in our hospital by using three different ELISA kits. All patients had pneumonia at admission, and 7 patients required mechanical ventilator support and grouped in severe case. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM antibodies turned to be partially positive between the 6th and 10th days, more than 84% positive between the 11th and 15th days, and 100% after the 16th day. One ELISA kit revealed poorer sensitivity for anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM antibody. Negative conversion of IgM antibody was not observed in the 30th day in our cohort. All three ELISA kits showed no false positive reaction for negative serum samples. Between severe and moderate cases, there was no significant difference in the trends of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM antibody.
Keywords: Antibody; COVID-19; ELISA; SARS-CoV-2.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Situation report–140. https://wwwwhoint/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200608-covid-19-sitrep-140pdf/sfvrsn=2f310900_2 (accessed, June 9, 2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous