TRPA1 as a therapeutic target for nociceptive pain
- PMID: 32838583
- PMCID: PMC7610834
- DOI: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1815191
TRPA1 as a therapeutic target for nociceptive pain
Abstract
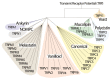
Introduction: Chronic pain affects approximatively 30-50% of the population globally. Pathologies such as migraine, diabetic neuropathy, nerve injury and treatment with chemotherapeutic agents, can induce chronic pain. Members of the transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, including the TRP ankyrin 1 (TRPA1), have a major role in pain.
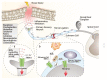
Areas covered: We focus on TRPA1 as a therapeutic target for pain relief. The structure, localization, and activation of the channel and its implication in different pathways to signal pain are described. This paper underlines the role of pharmacological interventions on TRPA1 to reduce pain in numerous pain conditions. We conducted a literature search in PubMed up to and including July 2020.
Expert opinion: Our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the sensitization of central and peripheral nociceptive pathways is limited. Preclinical evidence indicates that, in murine models of pain diseases, numerous mechanisms converge on the pathway that encompasses oxidative stress and Schwann cell TRPA1 to sustain chronic pain. Programs to identify and develop treatments to attenuate TRPA1-mediated chronic pain have emerged from this knowledge. Antagonists explored as a novel class of analgesics have a new and promising target in the TRPA1 expressed by peripheral glial cells.
Keywords: Inflammatory pain; TRP ankyrin 1 (TRPA1); Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) channels; neuropathic pain; nociception.
Conflict of interest statement
F De Logu, P Geppetti and R.Nassini are founding scientists of FloNext Srl. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Nilius B, Appendino G, Owsianik G. The transient receptor potential channel TRPA1: from gene to pathophysiology. Pflugers Arch. 2012;464:425–458. [•• Comprehensive review on TRP channels.] - PubMed
-
- Clapham DE, Runnels LW, Strübing C. The TRP ion channel family. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:387–396. [•• Comprehensive review on TRP channels.] - PubMed
-
- Logashina YA, Korolkova YV, Kozlov SA, et al. Biochem. Vol. 84. Pleiades Publishing; 2019. TRPA1 channel as a regulator of neurogenic inflammation and pain: structure, function, role in pathophysiology, and therapeutic potential of ligands; pp. 101–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
