Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Angina Pectoris
- PMID: 32839370
- PMCID: PMC12320014
- DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.2.78
Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Angina Pectoris
Abstract
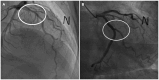
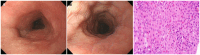
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an immune or antigen-mediated chronic inflammatory esophageal disorder that is relatively rare in Asian countries. The main symptoms of EoE are dysphagia and food impaction. Although chest pain is a symptom of EoE, it is also a symptom of coronary heart disease. This paper reports a case of EoE with angina pectoris in a 45-year-old male who was referred to the authors' hospital for chest pain. He was diagnosed with angina pectoris because of mild stenosis in the left coronary artery on coronary angiography. On the other hand, the symptoms did not improve with angina medication therapy. Therefore, he underwent a chest CT scan, which revealed esophageal thickening. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was performed. His endoscopic findings showed linear furrows with edema, and >90 eosinophils existed per high-power field on the histology findings. He was diagnosed with EoE. Through additional examinations, he was also diagnosed with asthma. The patient was treated with a proton pump inhibitor and a fluticasone inhaler. His symptoms and abnormal endoscopic findings disappeared after eight weeks of treatment. This case shows that physicians should consider the possibility of the symptoms for EoE when unexplained chest pain persists.
Keywords: Angina pectoris; Chest pain; Eosinophilic esophagitis; Proton pump inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Kim GH, Park YS, Jung KW, et al. An increasing trend of eosinophilic esophagitis in Korea and the clinical implication of the biomarkers to determine disease activity and treatment response in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019;25:525–533. doi: 10.5056/jnm19066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

