Prognostic significance of Rab27 expression in solid cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32839520
- PMCID: PMC7445175
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71104-9
Prognostic significance of Rab27 expression in solid cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
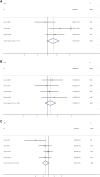
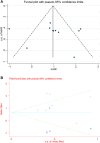
Rab27 is an essential molecule of vesicle fusion and trafficking in exosome secretion process, which plays important roles in cancer progression and metastasis. Recent studies reported that Rab27 expression is also associated with cancer prognosis. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis to reveal the prognostic significance of Rab27 expression in solid cancer. Data were extracted by searching on PubMed, Embase and Cochrane library until February 15 2020. Pooled hazard ratio (HR) with confidence interval (CI) was calculated to evaluate the association between Rab27 expression and survival in solid cancer. Ten studies with 1434 cancer patients were including for this meta-analysis. High expression of Rab27 was associated with poor survival (HR 2.67, 95% CI 1.52-4.69, p = 0.001). High expression of Rab27A was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis (HR 1.53, 95% CI 1.00-2.34, p = 0.048). High expression of Rab27B was significantly correlated with lymph node and distant metastasis (HR 2.15, 95% CI 1.56-2.95, p < 0.001; HR 6.80, 95% CI 3.12-14.85, p < 0.001), and higher TNM stage (HR 2.55, 95% CI 1.78-3.65, p < 0.001). This meta-analysis revealed that Rab27 expression could be a potential prognostic marker in solid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

