AI4COVID-19: AI enabled preliminary diagnosis for COVID-19 from cough samples via an app
- PMID: 32839734
- PMCID: PMC7318970
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imu.2020.100378
AI4COVID-19: AI enabled preliminary diagnosis for COVID-19 from cough samples via an app
Abstract
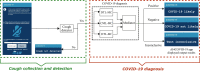
Background: The inability to test at scale has become humanity's Achille's heel in the ongoing war against the COVID-19 pandemic. A scalable screening tool would be a game changer. Building on the prior work on cough-based diagnosis of respiratory diseases, we propose, develop and test an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered screening solution for COVID-19 infection that is deployable via a smartphone app. The app, named AI4COVID-19 records and sends three 3-s cough sounds to an AI engine running in the cloud, and returns a result within 2 min.
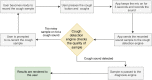
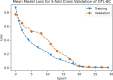
Methods: Cough is a symptom of over thirty non-COVID-19 related medical conditions. This makes the diagnosis of a COVID-19 infection by cough alone an extremely challenging multidisciplinary problem. We address this problem by investigating the distinctness of pathomorphological alterations in the respiratory system induced by COVID-19 infection when compared to other respiratory infections. To overcome the COVID-19 cough training data shortage we exploit transfer learning. To reduce the misdiagnosis risk stemming from the complex dimensionality of the problem, we leverage a multi-pronged mediator centered risk-averse AI architecture.
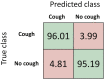
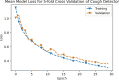
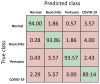
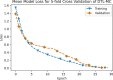
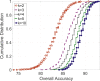
Results: Results show AI4COVID-19 can distinguish among COVID-19 coughs and several types of non-COVID-19 coughs. The accuracy is promising enough to encourage a large-scale collection of labeled cough data to gauge the generalization capability of AI4COVID-19. AI4COVID-19 is not a clinical grade testing tool. Instead, it offers a screening tool deployable anytime, anywhere, by anyone. It can also be a clinical decision assistance tool used to channel clinical-testing and treatment to those who need it the most, thereby saving more lives.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; COVID-19; Pre-screening; Preliminary medical diagnosis; Public healthcare.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak situation. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 [Online]. Available.
-
- BBC Coronavirus in South Korea: how ‘trace, test and treat’ may be saving lives. 2020. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-51836898 Accessed on: Mar. 31, 2020. [Online]. Available.
-
- Science Not wearing masks to protect against coronavirus is a ‘big mistake,’ top Chinese scientist says. 2020. https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2020/03/not-wearing-masks-protect-agains... Accessed on: April. 1, 2020. [Online]. Available.
-
- Cascella M., Rajnik M., Cuomo A., Dulebohn S.C., Di Napoli R. StatPearls Publishing; 2020. ‘‘Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus (COVID-19),’’ in StatPearls [Internet] - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
