SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cells Exhibit Phenotypic Features of Helper Function, Lack of Terminal Differentiation, and High Proliferation Potential
- PMID: 32839763
- PMCID: PMC7437502
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100081
SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cells Exhibit Phenotypic Features of Helper Function, Lack of Terminal Differentiation, and High Proliferation Potential
Abstract
Convalescing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients mount robust T cell responses against SARS-CoV-2, suggesting an important role of T cells in viral clearance. To date, the phenotypes of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells remain poorly defined. Using 38-parameter CyTOF, we phenotyped longitudinal specimens of SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from nine individuals who recovered from mild COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4+ T cells were exclusively Th1 cells and predominantly Tcm cells with phenotypic features of robust helper function. SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T cells were predominantly Temra cells in a state of less terminal differentiation than most Temra cells. Subsets of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells express CD127, can proliferate homeostatically, and can persist for over 2 months. Our results suggest that long-lived and robust T cell immunity is generated following natural SARS-CoV-2 infection and support an important role of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in host control of COVID-19.
Keywords: CD127; COVID-19; CyTOF; IL7; SARS-CoV-2; T cells; convalescent individuals; homeostatic proliferation; mild COVID-19.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

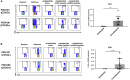
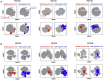
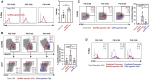
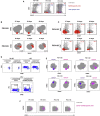

Update of
-
SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells exhibit unique features reflecting robust helper function, lack of terminal differentiation, and high proliferative potential.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 3:2020.06.08.138826. doi: 10.1101/2020.06.08.138826. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell Rep Med. 2020 Sep 22;1(6):100081. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100081. PMID: 32577663 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
-
- Zhang X., Tan Y., Ling Y., Lu G., Liu F., Yi Z., Jia X., Wu M., Shi B., Xu S. Viral and host factors related to the clinical outcome of COVID-19. Nature. 2020;583:437–440. - PubMed
-
- Huang L., Shi Y., Gong B., Jiang L., Liu X., Yang J., Tang J., You C., Jiang Q., Long B. Blood single cell immune profiling reveals the interferon-MAPK pathway mediated adaptive immune response for COVID-19. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.03.15.20033472. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

