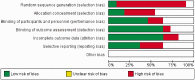
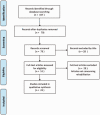
Rehabilitation of patients post-COVID-19 infection: a literature review
- PMID: 32840156
- PMCID: PMC7450453
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060520948382
Rehabilitation of patients post-COVID-19 infection: a literature review
Abstract
Rehabilitation is important for patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. Given the lack of guidelines in English on the rehabilitation of these patients, we conducted a review of the most recent reports. We performed this literature review using the principal research databases and included randomized trials, recommendations, quasi-randomized or prospective controlled clinical trials, reports, guidelines, field updates, and letters to the editor. We identified 107 studies in the database search, among which 85 were excluded after screening the full text or abstract. In total, 22 studies were finally included. The complexity of the clinical setting and the speed of spread of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, which leads to rapid occupation of beds in the intensive care unit, make it necessary to discharge patients with COVID-19 who have mild symptoms as soon as possible. For these reasons, it is necessary to formulate rehabilitation programs for these patients, to help them restore physical and respiratory function and to reduce anxiety and depression, particularly patients with comorbidities and those who live alone or in rural settings, to restore a good quality of life.
Keywords: Rehabilitation; coronavirus disease 2019; intensive care; physical function; respiratory function; review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Considerations for Postacute Rehabilitation for Survivors of COVID-19.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020 May 8;6(2):e19462. doi: 10.2196/19462. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020. PMID: 32369030 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation of a Post-Intensive Care Unit Patient After Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020 Dec;99(12):1092-1095. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000001606. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 33002914
-
Respiratory rehabilitation in elderly patients with COVID-19: A randomized controlled study.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020 May;39:101166. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101166. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32379637 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Recommendations for respiratory rehabilitation of coronavirus disease 2019 in adult].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2020 Apr 12;43(4):308-314. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20200228-00206. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32294814 Review. Chinese.
-
Physical therapy rehabilitation after hospital discharge in patients affected by COVID-19: a systematic review.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Aug 16;23(1):535. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08313-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37587411 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
To contrast and reverse skeletal muscle weakness by Full-Body In-Bed Gym in chronic COVID-19 pandemic syndrome.Eur J Transl Myol. 2021 Mar 26;31(1):9641. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2021.9641. Eur J Transl Myol. 2021. PMID: 33709653 Free PMC article.
-
Post-COVID-19 syndrome symptoms after mild and moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 3;9:1017257. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1017257. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36262270 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Physiotherapy on Rehabilitation and Quality of Life in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Review of Findings from Key Studies Published 2020-2022.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Oct 12;28:e938141. doi: 10.12659/MSM.938141. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 36221250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effectiveness of POST-DISCHARGE telerehabilitation practices in COVID-19 patients: Tele-COVID study-randomized controlled trial.Ann Thorac Med. 2022 Apr-Jun;17(2):110-117. doi: 10.4103/atm.atm_543_21. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Ann Thorac Med. 2022. PMID: 35651892 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation Strategies for Cognitive and Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID-19.Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2022;10(3):182-187. doi: 10.1007/s40141-022-00352-9. Epub 2022 May 14. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2022. PMID: 35602927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Situation update worldwide, as of 16 April 2020. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases (accessed 29 July 2020).
-
- Khot WY, Nadkar MY. The 2019 Novel Coronavirus Outbreak–A Global Threat. J Assoc Physicians India 2020; 68: 67–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical