Human Placenta-Derived ECM Supports Tri-Lineage Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 32840229
- PMCID: PMC7691852
- DOI: 10.15283/ijsc20074
Human Placenta-Derived ECM Supports Tri-Lineage Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
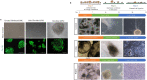
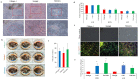
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) hold great promise for future applications in drug discovery and cell therapies. hPSC culture protocols require specific substrates and medium supplements to support cell expansion and lineage specific differentiation. The animal origin of these substrates is a severe limitation when considering the translation of hPSC derivatives to the clinic and in vitro disease modeling. The present study evaluates the use of a human placenta-derived extracellular matrix (ECM) hydrogel, HuGentraⓇ, to support tri-lineage differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs). Lineage-specific embryoid bodies (EBs) were plated onto three separate matrices, and differentiation efficiency was evaluated based on morphology, protein, and gene expression. HuGentra was found to support the differentiation of hiPSCs to all three germ layers: ectodermal, mesodermal, and endodermal lineages. hiPSCs differentiated into neurons, cardiomyocytes, and hepatocytes on HuGentra had similar morphology, protein, and gene expression compared to differentiation on Matrigel or other cell preferred matrices. HuGentra can be considered as a suitable human substrate for hiPSC differentiation.
Keywords: Differentiation; Human ECM; Tri-lineage; hiPSC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are currently or formally employed by Lifenet Health.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Three-Dimensional Trilineage Differentiation Conditions for Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 May 9;12(5):503. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12050503. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428122 Free PMC article.
-
Neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular matrix as a new platform for neural differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells.Biomater Biosyst. 2022 Nov 11;8:100070. doi: 10.1016/j.bbiosy.2022.100070. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biomater Biosyst. 2022. PMID: 36824374 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospun polystyrene scaffolds as a synthetic substrate for xeno-free expansion and differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells.Acta Biomater. 2016 Dec;46:266-277. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.09.032. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27667015
-
Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Male Germ Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(5):622-629. doi: 10.2174/1574888X15666200705214223. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 32628592 Review.
-
Lessons from the heart: mirroring electrophysiological characteristics during cardiac development to in vitro differentiation of stem cell derived cardiomyocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Feb;67:12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.12.011. Epub 2013 Dec 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24370890 Review.
Cited by
-
Placenta-on-a-Chip as an In Vitro Approach to Evaluate the Physiological and Structural Characteristics of the Human Placental Barrier upon Drug Exposure: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 27;12(13):4315. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134315. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445348 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kondo Y, Iwao T, Nakamura K, Sasaki T, Takahashi S, Kamada N, Matsubara T, Gonzalez FJ, Akutsu H, Miyagawa Y, Okita H, Kiyokawa N, Toyoda M, Umezawa A, Nagata K, Matsunaga T, Ohmori S. An efficient method for differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells retaining drug metabolizing activity. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2014;29:237–243. doi: 10.2133/dmpk.DMPK-13-RG-104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lian X, Hsiao C, Wilson G, Zhu K, Hazeltine LB, Azarin SM, Raval KK, Zhang J, Kamp TJ, Palecek SP. Robust cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells via temporal modulation of canonical Wnt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:E1848–E1857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200250109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

