Rifampicin-Induced Pneumonitis Mimicking Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia Infection
- PMID: 32840240
- PMCID: PMC7478429
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.927586
Rifampicin-Induced Pneumonitis Mimicking Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia Infection
Abstract
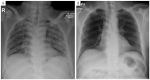
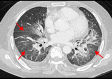
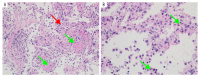
BACKGROUND Rifampicin-induced pneumonitis is an infrequent occurrence, with only a few cases reported in the literature. Furthermore, this condition constitutes a diagnostic challenge, particularly in the era of COVID-19 infection. Here, we report a case of rifampicin-induced pneumonitis with clinical, imaging, and histological features of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which required severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) testing to exclude a diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia. CASE REPORT A 43-year-old man on anti-TB treatment for TB meningitis developed new-onset fever, fatigue, hypoxemic respiratory failure, and bilateral pulmonary opacities. His clinical, chest X-ray, and CT thorax findings of ARDS were similar to both rifampicin-induced pneumonitis and severe COVID-19 pneumonia. However, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing from a nasopharyngeal swab and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) via the GeneXpert system was negative for SARS-CoV-2. A detailed workup, including lung biopsy, revealed drug-induced pneumonitis as the cause of his presentation. His pneumonitis improved after discontinuation of rifampicin and recurred following the rifampicin challenge. CONCLUSIONS This case highlights the importance of early, rapid, and accurate testing for SARS-CoV-2 during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients presenting with acute respiratory symptoms, so that accurate diagnosis and early patient management are not delayed for patients with treatable causes of acute and severe lung diseases. Timely identification of rifampicin-induced pneumonitis via a high clinical suspicion, detailed workup, and histopathological analysis is required to avoid permanent damage to the lungs.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Grobbelaar M, Louw GE, Sampson SL, et al. Evolution of rifampicin treatment for tuberculosis. Infect Genet Evol. 2019;74:103937. - PubMed
-
- Akira M, Ishikawa H, Yamamoto S. Drug-induced pneumonitis: Thin-section CT findings in 60 patients. Radiology. 2002;224(3):852–60. - PubMed
-
- Camus P, Fanton A, Bonniaud P, et al. Interstitial lung disease induced by drugs and radiation. Respiration. 2004;71(4):301–26. - PubMed
-
- Rossi SE, Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, et al. Pulmonary drug toxicity: Radiologic and pathologic manifestations. Radiographics. 2000;20(5):1245–59. - PubMed
-
- Koma Y, Goto K, Yoshida C, et al. Pneumonitis induced by rifampicin: A case report and literature review. Intern Med. 2013;52(4):473–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

