Maintenance treatment with antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia
- PMID: 32840872
- PMCID: PMC9702459
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008016.pub3
Maintenance treatment with antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: The symptoms and signs of schizophrenia have been linked to high levels of dopamine in specific areas of the brain (limbic system). Antipsychotic drugs block the transmission of dopamine in the brain and reduce the acute symptoms of the disorder. An original version of the current review, published in 2012, examined whether antipsychotic drugs are also effective for relapse prevention. This is the updated version of the aforesaid review.
Objectives: To review the effects of maintaining antipsychotic drugs for people with schizophrenia compared to withdrawing these agents.
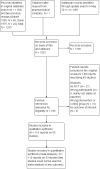
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's Study-Based Register of Trials including the registries of clinical trials (12 November 2008, 10 October 2017, 3 July 2018, 11 September 2019).
Selection criteria: We included all randomised trials comparing maintenance treatment with antipsychotic drugs and placebo for people with schizophrenia or schizophrenia-like psychoses.
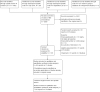
Data collection and analysis: We extracted data independently. For dichotomous data we calculated risk ratios (RR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) on an intention-to-treat basis based on a random-effects model. For continuous data, we calculated mean differences (MD) or standardised mean differences (SMD), again based on a random-effects model.
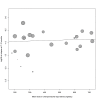
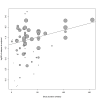
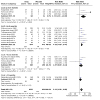
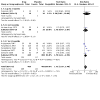
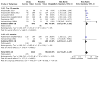
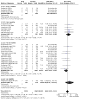
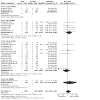
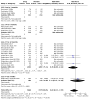
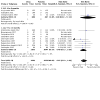
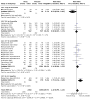
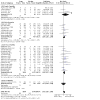
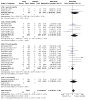
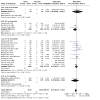
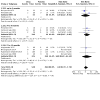
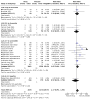
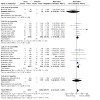
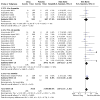
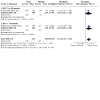
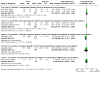
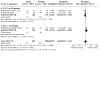
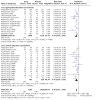
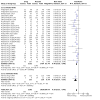
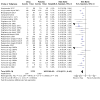
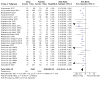
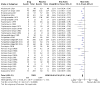
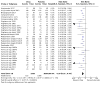
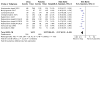
Main results: The review currently includes 75 randomised controlled trials (RCTs) involving 9145 participants comparing antipsychotic medication with placebo. The trials were published from 1959 to 2017 and their size ranged between 14 and 420 participants. In many studies the methods of randomisation, allocation and blinding were poorly reported. However, restricting the analysis to studies at low risk of bias gave similar results. Although this and other potential sources of bias limited the overall quality, the efficacy of antipsychotic drugs for maintenance treatment in schizophrenia was clear. Antipsychotic drugs were more effective than placebo in preventing relapse at seven to 12 months (primary outcome; drug 24% versus placebo 61%, 30 RCTs, n = 4249, RR 0.38, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.45, number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 3, 95% CI 2 to 3; high-certainty evidence). Hospitalisation was also reduced, however, the baseline risk was lower (drug 7% versus placebo 18%, 21 RCTs, n = 3558, RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.57, NNTB 8, 95% CI 6 to 14; high-certainty evidence). More participants in the placebo group than in the antipsychotic drug group left the studies early due to any reason (at seven to 12 months: drug 36% versus placebo 62%, 24 RCTs, n = 3951, RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.65, NNTB 4, 95% CI 3 to 5; high-certainty evidence) and due to inefficacy of treatment (at seven to 12 months: drug 18% versus placebo 46%, 24 RCTs, n = 3951, RR 0.37, 95% CI 0.31 to 0.44, NNTB 3, 95% CI 3 to 4). Quality of life might be better in drug-treated participants (7 RCTs, n = 1573 SMD -0.32, 95% CI to -0.57 to -0.07; low-certainty evidence); probably the same for social functioning (15 RCTs, n = 3588, SMD -0.43, 95% CI -0.53 to -0.34; moderate-certainty evidence). Underpowered data revealed no evidence of a difference between groups for the outcome 'Death due to suicide' (drug 0.04% versus placebo 0.1%, 19 RCTs, n = 4634, RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.12 to 2.97,low-certainty evidence) and for the number of participants in employment (at 9 to 15 months, drug 39% versus placebo 34%, 3 RCTs, n = 593, RR 1.08, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.41, low certainty evidence). Antipsychotic drugs (as a group and irrespective of duration) were associated with more participants experiencing movement disorders (e.g. at least one movement disorder: drug 14% versus placebo 8%, 29 RCTs, n = 5276, RR 1.52, 95% CI 1.25 to 1.85, number needed to treat for an additional harmful outcome (NNTH) 20, 95% CI 14 to 50), sedation (drug 8% versus placebo 5%, 18 RCTs, n = 4078, RR 1.52, 95% CI 1.24 to 1.86, NNTH 50, 95% CI not significant), and weight gain (drug 9% versus placebo 6%, 19 RCTs, n = 4767, RR 1.69, 95% CI 1.21 to 2.35, NNTH 25, 95% CI 20 to 50).
Authors' conclusions: For people with schizophrenia, the evidence suggests that maintenance on antipsychotic drugs prevents relapse to a much greater extent than placebo for approximately up to two years of follow-up. This effect must be weighed against the adverse effects of antipsychotic drugs. Future studies should better clarify the long-term morbidity and mortality associated with these drugs.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00111189 NCT00658645 NCT00704509.
Copyright © 2020 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Anna Ceraso: none to declare. Jessie Lin: none to declare. Johannes Schneider‐Thoma: none to declare. Spyridon Siafis: none to declare. Magdolna Tardy: none to declare. Katja Komossa: none to declare. Stephan Heres: received speaker honoraria from Janssen‐Cilag, Eli Lilly, Sanofi‐Aventis, Otsuka, Lundbeck and Johnson & Johnson; accepted travel or hospitality payment from Janssen‐Cilag, Sanofi‐Aventis, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Bristol‐Myers‐Squibb, AstraZeneca, Lundbeck, Novartis and Eli Lilly; participated in clinical trials sponsored or supported by Eli Lilly, Janssen Cilag, Johnson & Johnson, Bristol‐Myers‐Squibb, AstraZeneca, Lundbeck, Novartis, Servier, Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Organon, Roche and Merck; and received honoraria for participation in advisory‐boards or activities as a consultant from Lundbeck, Otsuka, Eli Lilly, Roche, Teva, Janssen and Johnson & Johnson. Werner Kissling: has received honoraria for board memberships, consulting and lectures from Janssen and Eli Lilly; honoraria for development of educational materials from Janssen; grant support from Janssen and AstraZeneca; and travel/accommodation expenses from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Janssen. John M Davis: none to declare. Stefan Leucht: In the last three years Stefan Leucht has received honoraria for lectures or consulting from LB Pharma, Otsuka, Lundbeck, Boehringer Ingelheim, LTS Lohmann, Janssen, Johnson&Johnson, TEVA, MSD, Sandoz, SanofiAventis, Angelini, Recordati, Sunovion, Geodon Richter.
Figures















Update of
-
Maintenance treatment with antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD008016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008016.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 11;8:CD008016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008016.pub3. PMID: 22592725 Updated.
Comment in
-
Schizophrenia: Use of Antipsychotic Drugs for Maintenance Therapy.Am Fam Physician. 2021 Oct 1;104(4):355-356. Am Fam Physician. 2021. PMID: 34652116 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Aripiprazole 2003 {published data only}6164
-
- Baker RA, Meyer JM, Kaplita S, Forbes A, Grossman F, Pikalov A, Marcus RN. Long-term effects of aripiprazole on the lipid profiles of patients with schizophrenia in a 26-week placebo-controlled trial. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2007;33(2):S419. [CSZG: 15132]
-
- Carson W, McQuade R, Saha A, Torbeyns A, Stock E. Aripiprazole versus placebo for relapse prevention in patients with chronic schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;12(Suppl 3):S288. [CSZG: 9067]
-
- Carson W, Pigott T, Saha A, Ali M, McQuade RD, Torbeyns AF, et al. Aripiprazole vs placebo in the treatment of stable, chronic schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17-22; San Francisco, California, USA. 2003. [CSZG: 9986]
-
- Carson W, Weiden P, Waldeck R, Tafesse E, Cislo P, L'Italien G, Iwamoto T. Aripiprazole is not associated with increased diabetes risk: a long-term model. Schizophrenia Research 2004;67(Suppl 1):181. [CSZG: 13175]
-
- Carson WH, Ingenito GG, McQuade RD, Stock EG, Iwamoto T. Schizophrenia: safety/tolerability of aripiprazole. In: Proceedings of the 12th World Congress of Psychiatry; 2002 Aug 24-29; Yokohama, Japan. 2002. [CSZG: 19426]
Aripiprazole 2017 {published data only}16575
-
- Correll C, Kohegyi E, Zhao C, Baker RA, McQuade R, Salzman P, et al. Oral aripiprazole is an effective maintenance treatment in adolescents with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014:S349-S350. [CSZG: 29288]
-
- Correll CU, Kohegyi E, Zhao C, Baker RA, McQuade R, Salzman PM, et al. Oral aripiprazole as maintenance treatment in adolescent schizophrenia: results from a 52-week, randomized, placebo-controlled withdrawal study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2017;56(9):784-92. [CSZG: 36321] - PubMed
-
- NCT01149655. A long-term multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of aripiprazole (opc 14597) as maintenance treatment in adolescent patients with schizophrenia. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01149655 2010. [CSZG: 21085]
Aripiprazole depot 2012 {published data only}12553
-
- Baker R, Fleischhacker W, Sanchez R, Perry P, Jin N, Johnson B, et al. Long-term safety and tolerability of once-monthly aripiprazole intramuscular depot for maintenance treatment in schizophrenia. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2012;15:111. [CSZG: 28035]
-
- Baker RA, Carson WH, Perry PP, Sanchez R, Zhao J, McQuade RD, et al. Effects of aripiprazole once-monthly vs placebo on domains of personal and social performance in younger and older patients with schizophrenia. CNS Spectrums 2013;18(6):376-7. [CSZG: 28526]
-
- Baker RA, Eramo A, Carson WH, Perry P, Sanchez R, Zhao J, et al. Effects of aripiprazole once-monthly vs. placebo on domains of personal and social performance in younger and older patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2013;39(Suppl 1):S321-S322. [CSZG: 28131]
-
- Baker RA, Eramo A, Nylander AG, Tsai LF, Peters-Strickland TS, Kostic D, et al. The effect of previous dose or oral aripiprazole (10 or 30 mg/day) on the efficacy and tolerability of aripiprazole once-monthly: Results from post-hoc analyses from two double-blind, randomized, controlled trials. Schizophrenia Research 2014;153:S293. [CSZG: 29386]
-
- Carson WH, Perry PP, Sanchez R, Jin N, Forbes RA, McQuade RD, et al. Effects of ARI-IM-depot on secondary efficacy outcomes in maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2012;15:112-3. [CSZG: 28030]
Asenapine 2011 {published data only}10424
-
- Kane JM, Mackle M, Snow-Adami L, Zhao J, Szegedi A, Panagides J. A randomised placebo-controlled trial of asenapine for the prevention of relapse of schizophrenia after long-term treatment. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2011;72(3):349-55. [CSZG: 22873] - PubMed
-
- Kane JM, Mackle M, Snow-Adami L, Zhao J, Szegedi A, Panagides J. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of asenapine in prevention of relapse after long-term treatment of schizophrenia. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;13:223. [CSZG: 21634]
-
- Mackle M, Snow-Adami L, Zhao J, Szegedi A, Panagides J. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of asenapine in prevention of relapse after long-term treatment of schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2009;19(Suppl 3):S543. [CSZG: 19377]
-
- NCT00150176. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of asenapine in the prevention of relapse after long-term treatment of schizophrenia. https://www.ClinicalTrials.gov/ct/show/ 2005. [CSZG: 14708]
-
- The NHSC . Asenapine (Saphris) for schizophrenia. Report 2010. [CSZG: 21910]
Brexpiprazole 2017 {published data only}26950
-
- Baker R, Hobart M, Forbes A, Ouyang J, Weiller E. Effect of brexpiprazole on long-term functioning in adults with schizophrenia. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 2017;51(Suppl 1):148. [CSZG: 35955]
-
- Correll CU, Shi L, Weiss C, Hobart M, Eramo A, Duffy RA, et al. Successful switching of patients with acute schizophrenia from another antipsychotic to brexpiprazole: comparison of clinicians' choice of cross-titration schedules in a post-hoc analysis of a randomized double-blind maintenance treatment study. CNS Spectrums 2019;24(5):507-17. - PubMed
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Hobart M, Ouyang J, Forbes A, Pfister S, McQuade R, et al. Brexpiprazole (OPC-34712) efficacy and safety as maintenance therapy in adults with schizophrenia: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2015;25:S527. [CSZG: 33322] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Hobart M, Ouyang J, Forbes A, Pfister S, McQuade RD, et al. Efficacy and sfety of Brexpiprazole (OPC-34712) as maintenance treatment in adults with schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2017;20(1):11-21. [CSZG: 35475] - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCT01668797. Efficacy, Safety, and tolerability of Brexpiprazole (OPC-34712) as maintenance treatment in adults with schizophrenia. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01668797 2012. [CSZG: 35608]
Cariprazine 2016 {published data only}18421
-
- Correll CU, Potkin SG, Durgam S, Chang CT, Szatmari B, Laszlovszky I, et al. Sustained remission with cariprazine treatment: post-hoc analysis of a randomised, double-blind, schizophrenia relapse prevention trial. Europan Neuropsychopharmacology 2017;27((Suppl. 4)):S935-S936. [CSZG: 37757]
-
- Correll CU, Potkin SG, Zhong Y, Harsányi J, Szatmári B, Earley W. Long-term remission with cariprazine treatment in patients with schizophrenia: a post-hoc analysis of a randomized, double-blind, placebo.controlled relapse prevention trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2019;80(2):18m12495. - PubMed
-
- Durgam S, Earley W, Li R, Li D, Lu K, Laszlovszky I, et al. Corrigendum to "Long-term cariprazine treatment for the prevention of relapse in patients with schizophrenia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial" [Schizophr. Res. 176 (2016) 264-71]. Schizophrenia Research 2017;InPress:InPress. [CSZG: 35204] - PubMed
-
- Durgam S, Earley W, Li R, Li D, Lu K, Laszlovszky I, et al. Long-term cariprazine treatment for the prevention of relapse in patients with schizophrenia: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2015;25:S512-3. [CSZG: 33317]
-
- Durgam S, Earley W, Li R, Li D, Lu K, Laszlovszky I, et al. Long-term cariprazine treatment for the prevention of relapse in patients with schizophrenia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Schizophrenia Research 2016;176(2-3):264-71. [CSZG: 35204] - PubMed
Chlorpromazine 1959 {published data only}2474
-
- Shawver JR, Gorham DR, Leskin LW, Good WW, Kabnick DE. Comparison of chlorpromazine and reserpine in maintenance drug therapy. Diseases of the Nervous System 1959;20:452-7. [CSZG: 2560] - PubMed
Chlorpromazine 1962 {published data only}759
-
- Freeman LS, Alson E. Prolonged withdrawal of chlorpromazine in chronic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1962;23:522-5. [CSZG: 809] - PubMed
Chlorpromazine 1968 {published data only}3766
-
- Crane GE. Tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenic patients treated with psychotropic drugs. Agressologie 1968;9(2):209-16. [CSZG: 3170] - PubMed
-
- De Long SL. Incidence and significance of chlorpromazine-induced eye changes. Diseases of the Nervous System 1968;29:19-22. [CSZG: 18229] - PubMed
-
- Gardos G, Cole JO, LaBrie RA. A 12-year follow-up study of chronic schizophrenics. Psychopharmacology 1982;33:983-4. [CSZG: 853] - PubMed
-
- Prien RF, Cole JO, Belkin NF. Relapse in chronic schizophrenics following abrupt withdrawal of tranquillizing medication. British Journal of Psychiatry 1968;115:679-86. [CSZG: 3951] - PubMed
-
- Prien RF, Cole JO. High dose chlorpromazine therapy in chronic schizophrenia. Report of National Institute of Mental Health - psychopharmacology research branch collaborative study group. Archives of General Psychiatry 1968;18:482-95. [CSZG: 3950] - PubMed
Chlorpromazine 1973 {published data only}1800
-
- Goldberg SC, Schooler NR, Hogarty GE, Roper M. Prediction of relapse in schizophrenic outpatients treated by drug and sociotherapy. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34:171-84. [CSZG: 1873] - PubMed
-
- Hogarty G, Goldberg SC. Drug and social therapy in schizophrenic outpatients. Unknown Source 1994:18. [CSZG: 5049]
-
- Hogarty GE, Goldberg S, Schooler N. Proceedings: drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1974;10(4):47. [CSZG: 4745] - PubMed
-
- Hogarty GE, Goldberg SC, Schooler NR, Ulrich RF. Drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. II. Two-year relapse rates. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31:603-8. [CSZG: 1876] - PubMed
-
- Hogarty GE, Goldberg SC, Schooler NR. Drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. III. Adjustment of nonrelapsed patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31:609-18. [CSZG: 1875] - PubMed
Chlorpromazine 1975 {published data only}1827
-
- Elie R, Gagnon MA, Gauthier R, Jequier JC. Effects of neuroleptic withdrawal on the drug-induced extrapyramidal syndrome of chronic schizophrenia [Effets d'un sevrage neuroleptique sur le syndrome extrapyramidal medicamenteux de la schizophrenie chronique]. Union Medicale du Canada 1975;104:909-14. [CSZG: 1911] - PubMed
Chlorpromazine 1976 {published data only}208
-
- Andrews P, Hall JN, Snaith RP. A controlled trial of phenothiazine withdrawal in chronic schizophrenic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1976;128:451-5. [CSZG: 226] - PubMed
Fluphenazine 1979 {published data only}2340
-
- Rifkin A, Quitkin F, Kane J, Klein DF, Ross D. The effect of fluphenazine upon social and vocational functioning in remitted schizophrenics. Biological Psychiatry 1979;14:499-508. [CSZG: 2428] - PubMed
-
- Rifkin A, Quitkin F, Kane J, Klein DF. Fluphenazine decanoate, oral fluphenazine, and placebo in the treatment of remitted schizophrenics. II. Rating scale data. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1977;13:40-50. [CSZG: 2424] - PubMed
-
- Rifkin A, Quitkin F, Klein DF. Fluphenazine decanoate, oral fluphenazine, and placebo in treatment of remitted schizophrenics. II. Rating scale data. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34:15-9. [CSZG: 3959] - PubMed
-
- Rifkin A, Quitkin F, Rabiner CJ, Klein DF. Comparison of fluphenazine decanoate, oral fluphenazine, and placebo in remitted outpatient schizophrenics. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1976;12:24-6. [CSZG: 2426] - PubMed
-
- Rifkin A, Quitkin F, Rabiner CJ, Klein DF. Fluphenazine decanoate, fluphenazine hydrochloride given orally, and placebo in remitted schizophrenics. I. Relapse rates after one year. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34:43-7. [CSZG: 3960] - PubMed
Fluphenazine 1980 {published data only}3772
-
- Gelenberg AJ, Doller JC, Schooler NR, Mieske M, Severe J, Mandel MR. Acute extrapyramidal reactions with fluphenazine hydrochloride and fluphenazine decanoate. American Journal of Psychiatry 1979;136:217-9. [CSZG: 3961] - PubMed
-
- Levine J, Schooler NR, Severe J, Escobar J, Gelenberg A, Mandel M, et al. Discontinuation of oral and depot fluphenazine in schizophrenic patients after one year of continuous medication: a controlled study. Advances in Biochemical Psychopharmacology 1980;24:483-93. [CSZG: 1683] - PubMed
-
- Mandel MR, Severe JB, Schooler NR, Gelenberg AJ, Mieske M. Development and prediction of postpsychotic depression in neuroleptic-treated schizophrenics. Archives of General Psychiatry 1982;39:197-203. [CSZG: 3962] - PubMed
-
- Schooler NR, Levine J, NIMH-PRB Collaborative Fluphenazine Study Group. The initiation of long-term pharmacotherapy in schizophrenia: dosage and side effect comparisons between oral and depot fluphenazine. Pharmacopsychiatry 1976;9:159-69. [CSZG: 3964] - PubMed
-
- Schooler NR, Levine J, Severe JB, Brauzer B, DiMascio A, Klerman GL, et al. Prevention of relapse in schizophrenia. An evaluation of fluphenazine decanoate. Archives of General Psychiatry 1980;37:16-24. [CSZG: 3965] - PubMed
Fluphenazine 1982 {published data only}1251
-
- Kane JM, Rifkin A, Quitkin F, Nayak D, Ramos-Lorenzi J. Fluphenazine vs. placebo in patients with remitted, acute first-episode schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1982;39:70-3. [CSZG: 1304] - PubMed
-
- Kane JM, Rifkin A, Woerner M, Reardon G. Low-dose neuroleptics in outpatient schizophrenics. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1982;18:20-1. [CSZG: 1602]
Fluphenazine depot 1968 {published data only}1259
-
- Keskiner A, Holden JMC, Itil TM. Maintenance treatment of schizophrenic outpatients with a depot phenothiazine. Psychosomatics 1968;9:166-71. [CSZG: 1312] - PubMed
-
- Keskiner A, Simeon J, Fink M, Itil TM. Long-acting phenothiazine (fluphenazine decanoate) treatment of psychosis. Archives of General Psychiatry 1968;18:477-81. - PubMed
-
- King DJ, Devaney N, Cooper SJ, Blomqvist M, Mitchel MJ. Pharmacokinetics and antipsychotic effect of remoxipride in chronic schizophrenic patients. Journal of Psychopharmacology 1990;4:83-9. [CSZG: 1323] - PubMed
-
- Kinross-Wright J, Charalampous KD. A controlled study of a very long-acting phenothiazine preparation. International Journal of Neuropsychiatry 1965;1:66-70. [CSZG: 1335]
Fluphenazine depot 1973 {published data only}3723
-
- Hankoff LD, Engelhardt DM, Freedman N, Mann D, Maroolis R. Denial of illness in schizophrenic outpatients: effects of psychopharmacological treatment. Archives of General Psychiatry 1960;3:657-66. [CSZG: 959] - PubMed
-
- Hirsch SR, Gaind R, Rohde PD, Stevens BC, Wing JK. Outpatient maintenance of chronic schizophrenic patients with long-acting fluphenazine: double-blind placebo trial. Report to the Medical Research Council Committee on Clinical Trials in Psychiatry. British Medical Journal 1973;1:633-7. [CSZG: 3799] - PMC - PubMed
Fluphenazine depot 1979a {published data only}1444
-
- Dotti A, Bersani G, Rubino IA, Eliseo C. Double-blind trial of fluphenazine decanoate against placebo in ambulant maintenance treatment of chronic schizophrenics [Studio in doppio cieco della flufenazina decanoato versus placebo nella terapia ambulatoriale di mantenimento di pazienti schizofrenici cronici]. Rivista di Psichiatria 1979;14:374-83. [CSZG: 1514]
Fluphenazine depot 1979b {published data only}1233
-
- Kane JM, Rifkin A, Quitkin F, Nayak D, Saraf K, Ramos Lorenzi JR, et al. Low dose fluphenazine decanoate in maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research 1979;1:341-8. [CSZG: 1286] - PubMed
-
- Kane JM. Low dose medication strategies in the maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1983;9(4):528-32. - PubMed
Fluphenazine depot 1981 {published data only}4324
-
- Goldberg SC, Shenoy RS, Sadler A, Hamer R, Ross B. The effects of a drug holiday on relapse and tardive dyskinesia in chronic schizophrenics. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1981;17:116-7. [CSZG: 5007] - PubMed
-
- Shenoy RS, Sadler AG, Goldberg SC, Hamer RM, Ross B. Effects of a six-week drug holiday on symptom status, relapse, and tardive dyskinesia in chronic schizophrenics. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1981;1:141-5. [CSZG: 2577] - PubMed
Fluphenazine depot 1982 {published data only}2098
-
- Odejide OA, Aderounmu AF. Double-blind placebo substitution: withdrawal of fluphenazine decanoate in schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1982;43:195-6. [CSZG: 2184] - PubMed
Fluphenazine depot 1992 {published data only}2407
-
- Sampath G, Shah A, Krska J, Soni SD. Neuroleptic discontinuation in the very stable schizophrenic patient - relapse rates and serum neuroleptic levels. Human Psychopharmacology 1992;7:255-64. [CSZG: 2493]
-
- Soni SD, Mallik A, Schiff AA. Sulpiride in negative schizophrenia: a placebo-controlled double-blind assessment. Human Psychopharmacology 1990;5:233-8. [CSZG: 2697]
Haloperidol 1973 {published data only}2232
-
- Ota KY, Kurland AA. A double-blind comparison of haloperidol oral concentrate, haloperidol solutabs and placebo in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1973;13:99-110. [CSZG: 2318] - PubMed
Haloperidol 1991 {published data only}2385
-
- Ruskin PE, Nyman G. Discontinuation of neuroleptic medication in older, outpatient schizophrenics. A placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1991;179:212-4. [CSZG: 2471] - PubMed
Haloperidol depot 1982 {published data only}3162
-
- Zissis NP, Psaras M, Lyketsos G. Haloperidol decanoate, a new long-acting antipsychotic, in chronic schizophrenics: double-blind comparison with placebo. Current Therapeutic Research 1982;31:650-5. [CSZG: 3256]
Haloperidol depot 1991 {published data only}9291
-
- Eklund K, Forsman A. Minimal effective dose and relapse - double-blind trial: haloperidol decanoate vs. placebo. Clinical Neuropharmacology 1991;14:S7-S15. [CSZG: 747] - PubMed
-
- Eklund K. Low dose of haloperidol decanoate is effective against relapses in schizophrenia patients. A double-blind placebo controlled study. In: Proceedings of the 17th Collegium Internationale Neuro-Psychopharmacologicum Congress; 1990 Sep 10-14; Kyoto, Japan. 1990:287. [CSZG: 12924]
Iloperidone 2016 {published data only}17965
-
- CTRI/2010/091/001409. A clinical trial to study prevention of relapse in patients with schizophrenia reveiving either flexible dose iloperidone or placebo in long-term use.. http://ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/login.php 2010.
-
- NCT01291511. Efficacy in prevention of relapse of schizophrenia in subjects taking either placebo or iloperidone. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01291511 2011. [CSZG: 22671]
Lurasidone 2016 {published data only}18736
-
- NCT01435928. PEARL Schizophrenia Maintenance. http://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01435928 2011. [CSZG: 23439]
-
- Tandon R, Loebel A, Philips D, Pikalov A, Hernandez D Mao Y, et al. Lurasidone for maintenance of efficacy in patients with schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2014;24(Suppl 2):S559-560. [CSZG: 27840]
Olanzapine 1999 {published data only}4622
-
- Dellva MA, Tollefson GD, Mattler CA, Kinon BJ, Grundy SL. A controlled, double-blind investigation of the clozapine discontinuation syndrome with conversion to either olanzapine or placebo. Schizophrenia Research 1999;36:277-8. [CSZG: 5651] - PubMed
-
- Tollefson GD, Dellva MA, Mattler CA, Kane JM, Wirshing DA, Kinon BJ, et al. Controlled, double-blind investigation of the clozapine discontinuation symptoms with conversion to either olanzapine or placebo. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1999;19:435-43. [CSZG: 5305] - PubMed
-
- Tollefson GD, Dellva MA, Mattler CA, Kinon BJ, Grundy SL. A controlled, double-blind investigation of the clozapine discontinuation syndrome with conversion to either olanzapine or placebo. In: Proceedings of the 11th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1998 Oct 31 - Nov 4; Paris, France. 1998. [CSZG: 4859]
Olanzapine 2003 {published data only}14624
-
- Beasley C Jr, Hamilton S, Dossenbach M. Relapse prevention with olanzapine. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2000;10(Suppl 3):S304. [CSZG: 4620]
-
- Beasley CM, Hamilton SH, Dossenbach M. Relapse prevention with olanzapine. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41(1):196-7. [CSZG: 4874]
-
- Beasley CM, Sutton VK, Hamilton SH, Walker DJ, Dossenbach M, Taylor CC, et al. A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial of olanzapine in the prevention of psychotic relapse. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2003;23:582-94. [CSZG: 10010] - PubMed
-
- Beasley CM, Sutton VK, Taylor CC, Sethuraman G, Dossenbach M, Naber D, Pickar D. Does maintenance treatment with atypical antipsychotics worsen quality of life among stable patients with schizophrenia? Neuropsychopharmacology 2005;30(S1):S189. [CSZG: 13107]
-
- Beasley CM, Sutton VK, Taylor CC, Sethuraman G, Dossenbach M, Naber D. Is quality of life among minimally symptomatic patients with schizophrenia better following withdrawal or continuation of antipsychotic treatment? Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2006;26:40-4. [CSZG: 14454] - PubMed
Paliperidone 2007 {published data only}15435
-
- Eerdekens. Evaluate the efficacy in the prevention of recurrence of the symptoms of schizophrenia. Sponsor: Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development, LL.C 2010. [CTG: ]
-
- Kramer M, Kushner S, Sherr J, Vijapurkar U, Lim P, Eerdekens M. Delaying symptom recurrence in patients with schizophrenia with paliperidone extended-release tablets: an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2007;33(2):438. [CSZG: 15185] - PubMed
-
- Kramer M, Kushner S, Vijapurkar U, Lim P, Eerdekens M. Delaying symptom recurrence in patients with schizophrenia treated with paliperidone extended-release tablets. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2006;16(Suppl 4):S386. [CSZG: 13313]
-
- Kramer M, Kushner S, Vijapurkar U, Lim P, Eerdekens M. Delaying symptom recurrence in patients with schizophrenia with paliperidone extended-release tablets: an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2006;9(Suppl 1):S274. [CSZG: 19545]
-
- Kramer M, Simpson G, Maciulis V, Kushner S, Liu Y, Lim P, et al. One-year open-label safety and efficacy study of paliperidone extended-release. CNS Spectrums 2010;15(8):506-14. [CSZG: 20885] - PubMed
Paliperidone 2014 {published data only}22628
-
- Rui Q, Wang Y, Liang S, Liu Y, Wu Y, Wu Q, et al. Relapse prevention study of paliperidone extended-release tablets in Chinese patients with schizophrenia. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 2014;53:45-53. [CSZG: 29320] - PubMed
Paliperidone depot1M 2010 {published data only}11886
-
- Alphs L, Bossie C, Kern-Sliwa J, Ma Y-W, Haskins JT. Paliperidone palmitate: clinical response in subjects with schizophrenia with recent vs. longer-term duration of illness. In: Proceedings of the 162nd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. San Francisco, CA., 2009 May 16-21. [CSZG: 19067]
-
- Emsley R, Nuamah I, Gopal S, Hough D, Fleischhacker WW. Relapse after antipsychotic discontinuation in schizophrenia as a withdrawal phenomenon vs illness recurrence: a post hoc analysis of a randomized placebo-controlled study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2018 Jun;79(4):17m11874. [CSZG: 38184] - PubMed
-
- Emsley R, Nuamah I, Hough D, Gopal S. Treatment response after relapse in a placebo-controlled maintenance trial in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2012;138(1):29-34. [CSZG: 24214] - PubMed
-
- Gopal S, Vijapurkar U, Lim P, Morozova M, Eerdekens M, Hough D. A 52-week open-label study of the safety and tolerability of paliperidone palmitate in patients with schizophrenia. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2011;25(5):685-97. [CSZG: 22903] - PubMed
-
- Gopal S, Vijapurkar U, Lim P, Morozova M, Eerdekens M. Long-term efficacy, safety and tolerability of paliperidone palmitate in patients with schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 162nd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. San Francisco, CA, 2009 May 16-21. [CSZG: 19076]
Paliperidone depot1M 2015 {published data only}16601
-
- Bossie C, Turkoz I, Alphs L, Fu DJ. Monotherapy with once monthly paliperidone palmitate for psychotic, depressive, and manic symptoms in schizoaffective disorder. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2015;41:S303. [CSZG: 29400]
-
- Fu DJ, Alphs L, Lindenmayer JP, Schooler N, Simonson RB, Turkoz I, et al. Paliperidone palmitate long-acting injectable delays psychotic and mood symptom relapse in schizoaffective disorder. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2014;24:S534-5. [CSZG: 27785]
-
- Fu DJ, Bossie C, Turkoz I, Mahalchick L, Alphs L. Paliperidone palmitate treatment response in early and chronic illness schizoaffective disorder patients. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2015;41:S312. [CSZG: 29446]
-
- Fu DJ, Turkoz I, Simonson RB, Walling D, Schooler N, Lindenmayer JP, et al. Effect of paliperidone palmitate once-monthly in improving and maintaining functioning in subjects with schizoaffective disorder using the domains of the personal and social performance scale. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014;39:S365. [CSZG: 29278]
Paliperidone depot3M 2015 {published data only}18982
-
- Berwaerts J, Liu Y, Gopal S, Nuamah I, Xu H, Savitz A, et al. Efficacy and safety of paliperidone palmitate 3 month formulation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2015;41:S302. [CSZG: 29393]
-
- Berwaerts J, Liu Y, Gopal S, Nuamah I, Xu H, Savitz A, et al. Efficacy and safety of paliperidone palmitate 3-month formulation in schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. European Psychiatry 2015;30:272. [CSZG: 32149]
-
- Berwaerts J, Liu Y, Gopal S, Nuamah I, Xu H, Savitz A, et al. Efficacy and safety of the 3-month formulation of paliperidone palmitate vs placebo for relapse prevention of schizophrenia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2015;72(8):830-9. [CSZG: 33027] - PubMed
-
- Chirila C, Zheng Q, Sawyerr G, Nuamah I. Healthcare resource use of paliperidone palmitate 3-month injection vs placebo. In: 168th Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association; Toronto, Canada. May 16-20, 2015. [CSZG: 33035]
Penfluridol 1970 {published data only}279
-
- Baro F, Brugmans J, Dom R, Van Lommel R. Maintenance therapy of chronic psychotic patients with a weekly oral dose of R 16341. A controlled double-blind study. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1970;10:330-41. [CSZG: 297] - PubMed
Penfluridol 1974a {published data only}799
-
- Gallant DM, Mielke DH, Spirtes MA, Swanson WC, Bost R. Penfluridol: an efficacious long-acting oral antipsychotic compound. American Journal of Psychiatry 1974;131:699-702. [CSZG: 849] - PubMed
Penfluridol 1974b {published data only}2354
-
- Roelofs GA. Penfluridol (R 16341) as a maintenance therapy in chronic psychotic patients: a double-blind clinical evaluation. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1974;50:219-24. [CSZG: 2440] - PubMed
Penfluridol 1974c {published data only}2833
-
- Vandecasteele AJ, Vereecken JL. A double-blind clinical evaluation of penfluridol (R 16 341) as a maintenance therapy in schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1974;50:346-53. [CSZG: 2919] - PubMed
Penfluridol 1975 {published data only}1515
-
- Kurland AA, Ota KY, Slotnick VB. Penfluridol: a long-acting oral neuroleptic. A controlled study. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1975;15:611-21. [CSZG: 1586] - PubMed
-
- Kurland AA, Ota KY. Penfluridol: once-a-week oral maintenance neuroleptic in the management of chronic schizophrenics. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1975;11:12-4. [CSZG: 1585] - PubMed
Penfluridol 1987 {published data only}4221
Perphenazine 1963 {published data only}
-
- Whittaker CB, Hoy RM. Withdrawal of perphenazine in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1963;109:422-7. - PubMed
Pimozide 1971 {published data only}1548
-
- Huber W, Serafetinides EA, Colmore JP, Clark M. Pimozide in chronic schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1971;11(4):304-9. [CSZG: 1618] - PubMed
Pimozide 1973 {published data only}1356
-
- Denijs EL, Vereeken JL. Pimozide (OrapR, R 6238) in residual schizophrenia. A clinical evaluation with long-term double-blind follow-up. Psychiatria, Neurologia, Neurochirurgia 1973;76:47-59. [CSZG: 1409] - PubMed
Quetiapine 2007 {published data only}10847
-
- D1441C00131. A 1-year, international, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase IV study to evaluate prevention of relapse in patients in stable condition with chronic schizophrenia receiving either quetiapine fumarate IR (SEROQUEL) or placebo. https://astrazenecagrouptrials.pharmacm.com/ST/Submission/View?id=385 2003.
-
- D1444C00004. A 1-year, international, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallelgroup, placebo-controlled phase iii study to evaluate prevention of relapse in patients in stable condition with chronic schizophrenia receiving either sustained-release quetiapine fumarate (SEROQUEL) or placebo. https://astrazenecagrouptrials.pharmacm.com/ST/Submission/View?id=1418 2006.
-
- NCT00228462. A 1-year, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled phase 3 study to evaluate prevention of relapse in patients in stable chronic schizophrenia receiving either sustained-release quetiapine fumarate (SEROQUEL) or placebo (abbreviated). https://www.ClinicalTrials.gov/ct/show/ 2005. [CSZG: 14874]
-
- Peuskens J, Trivedi JK, Brecher M, Miller F, Study I . Long-term symptomatic remission of schizophrenia with once-daily extended release quetiapine fumarate: Post-hoc analysis of data from a randomized withdrawal, placebo-controlled study. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2010;25(3):183-7. [CSZG: 20670] - PubMed
Quetiapine 2009a {published and unpublished data}12006
-
- NCT00658645. A multinational, randomised, double-blind, fixed-dose, bifeprunox study combining a 12-week placebo-controlled, quetiapine-referenced phase with a 12-month quetiapine-controlled phase in patients with schizophrenia. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00658645?term=NCT00658645&.... [CSZG: 16241]
Quetiapine 2009b {published and unpublished data}12579
-
- NCT00704509. A multinational, randomised, double-blind, fixed-dose, bifeprunox study combining a 12-week placebo-controlled, quetiapine-referenced phase with a 12-month quetiapine-controlled phase in patients with schizophrenia. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00704509?term=NCT00704509&.... [CSZG: 16566]
Quetiapine 2010 {published data only}10486
-
- Chen E, Hui C, Chang WC, Chan S, Lee E, Honer W. The effect of early medication discontinuation on long-term clinical outcome in first episode psychosis. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2018;44(Suppl 1):S97.
-
- Chen E, Hui C, Lam M, Law C, Chiu C, Chung D, et al. Assessing the efficacy of relapse prevention in single episode psychosis patients with stable maintenance treatment for at least 1 year: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled. Early Intervention in Psychiatry 2008;2(Suppl 1):A5. [CSZG: 19113]
-
- Chen EY, Hui CL, Lam M, Law CW, Chiu CP, Chung DW, et al. A double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study of relapse prevention in remitted first-episode psychosis patients following one year of maintenance therapy. Schizophrenia Research 2008;98:11-2. [CSZG: 16325]
-
- Chen EY, Hui CL, Lam M, Law CW, Chiu CP, Chung DW, et al. A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled relapse prevention study in remitted first-episode psychosis patients following one year of maintenance treatment. Early Intervention in Psychiatry 2010;4(Suppl 1):13. [CSZG: 23475]
Trifluoperazine 1969 {published data only}2258
-
- Prien RF, Levine J, Cole JO. High dose trifluoperazine therapy in chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1969;126:305-13. [CSZG: 2344] - PubMed
-
- Prien RF, Levine J, Switalski RW. Discontinuation of chemotherapy for chronic schizophrenics. Hospital and Community Psychiatry 1971;22(1):4-7. [CSZG: 2346] - PubMed
Trifluoperazine 1972 {published data only}951
-
- Hershon HI, Kennedy PF, McGuire RJ. Persistence of extra-pyramidal disorders and psychiatric relapse after withdrawal of long-term phenothiazine therapy. British Journal of Psychiatry 1972;120(554):41-50. [CSZG: 1001] - PubMed
-
- Stevens BC. Role of fluphenazine decanoate in lessening the burden of chronic schizophrenics on the community. Psychological Medicine 1973;3:141-58. [CSZG: 2739] - PubMed
Various drugs 1960 {published data only}877
-
- Gross M, Hitchman IL, Reeves WP, Lawrence J, Newell PC. Discontinuation of treatment with ataractic drugs. A preliminary report. American Journal of Psychiatry 1960;116:931-2. [CSZG: 927] - PubMed
Various drugs 1961 {published data only}6740
-
- Schiele BC, Vestre ND, Stein KE. A comparison of thioridazine, trifluoperazine, chlorpromazine, and placebo: a double-blind controlled study on the treatment of chronic, hospitalized, schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Psychopathology and Quarterly Review of Psychiatry and Neurology 1961;22:151-62. [CSZG: 9157] - PubMed
Various drugs 1962a {published data only}31690
-
- Olson GW, Peterson DB. Intermittent chemotherapy for chronic psychiatric inpatients. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1962;134:1459. [CSZG: 38115] - PubMed
-
- Olson GW, Peterson DB. Sudden removal of tranquilizing drugs from chronic psychiatric patients. Journal of Mental and Nervous Disease 1960;131:252-5. - PubMed
Various drugs 1962b {published data only}2769
-
- Troshinsky C, Aaronson HG, Stone RK. Maintenance phenothiazines in aftercare of schizophrenic patients. Pennsylvania Psychiatric Bulletin 1962;2:11-5. [CSZG: 2855]
Various drugs 1964a {published data only}3067
-
- Caffey EM, Diamond LS, Frank TV, Grasberger JC, Herman L, Klett CJ, et al. Discontinuation or reduction of chemotherapy in chronic schizophrenics. Journal of Chronic Diseases 1964;17:347-58. [CSZG: 3153] - PubMed
-
- Caffey EM, Forrest IS, Frank TV, Klett CJ. Phenothiazine excretion in chronic schizophrenics. American Journal of Psychiatry 1963;120:578-82. [CSZG: 420] - PubMed
Various drugs 1964b {published data only}4149
-
- Marjerrison G, Irvine D, Stewart CN, Williams R, Matheu H, Demay M. Withdrawal of long-term phenothiazines from chronically hospitalized psychiatric patients. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1964;9(4):290-8. [CSZG: 4833] - PubMed
Various drugs 1966a {published data only}3195
-
- Garfield SL, Gershon S, Sletten I, Neubauer H, Ferrel E. Withdrawal of ataractic medication in schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1966;27:321-5. [CSZG: 3289] - PubMed
Various drugs 1966b {published data only}3495
-
- Melnyk WT, Worthington AG, Laverty SG. Abrupt withdrawal of chlorpromazine and thioridazine from schizophrenic in-patients. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1966;11:410-3. [CSZG: 3590]
Various drugs 1968 {published data only}2006
-
- Morton MR. A study of the withdrawal of chlorpromazine or trifluoperazine in chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1968;124:1585-8. [CSZG: 2092] - PubMed
Various drugs 1971 {published data only}3723
-
- Hirsch SR, Gaind R, Rohde PD, Stevens BC, Wing JK. Outpatient maintenance of chronic schizophrenic patients with long-acting fluphenazine: double-blind placebo trial. Report to the Medical Research Council Committee on Clinical Trials in Psychiatry. British Medical Journal 1973;1(854):633-7. [CSZG: 3799] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leff JP, Hirsch SR, Gaind R, Rohde PD, Stevens BC. Life events and maintenance therapy in schizophrenic relapse. British Journal of Psychiatry 1973;123:659-60. - PubMed
Various drugs 1974 {published data only}3237
-
- Gross HS. A double-blind comparison of once-a-day pimozide, trifluoperazine, and placebo in the maintenance care of chronic schizophrenic outpatients. Current Therapeutic Research 1974;16:696-705. [CSZG: 3331] - PubMed
Various drugs 1975 {published data only}3868
-
- Clark ML, Huber WK, Hill D, Wood F, Costiloe JP. Pimozide in chronic schizophrenic outpatients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1975;36(3):137-41. [CSZG: 1235] - PubMed
-
- Clark. Pimozide vs thioridazine vs placebo. Bulletin 1973;9:59-63. [CSZG: 4106]
Various drugs 1981a {published data only}6229
-
- Blackburn HL, Allen JL. Behavioral effects of interrupting and resuming tranquilizing medication among schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1981;133:303-8. [CSZG: 8369] - PubMed
Various drugs 1981b {published data only}442
-
- Cheung HK. Schizophrenics fully remitted on neuroleptics for 3-5 years - to stop or continue drugs? British Journal of Psychiatry 1981;138:490-4. [CSZG: 460] - PubMed
Various drugs 1981c {published data only}3827
-
- Wistedt B, Jorgensen A, Wiles D. A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study. Plasma concentration of fluphenazine and flupenthixol and relapse frequency. Psychopharmacology 1982;78:301-4. [CSZG: 27894] - PubMed
-
- Wistedt B, Palmstierna T. Depressive symptoms in chronic schizophrenic patients after withdrawal of long-acting neuroleptics. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1983;44:369-71. [CSZG: 3068] - PubMed
-
- Wistedt B, Ranta J. Comparative double-blind study of flupenthixol decanoate and fluphenazine decanoate in the treatment of patients relapsing in a schizophrenic symptomatology. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67:378-88. [CSZG: 3069] - PubMed
-
- Wistedt B, Wiles D, Jorgensen A. A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study neurological effects. Psychopharmacology 1983;80:101-5. [CSZG: 3070] - PubMed
-
- Wistedt B. A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study. A controlled study of the clinical effects of the withdrawal of depot fluphenazine decanoate and depot flupenthixol decanoate in chronic schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1981;64:65-84. [CSZG: 27892] - PubMed
Various drugs 1982 {published data only}2081
-
- Nishikawa T, Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Koga I, Uchida Y. Prophylactic effect of neuroleptics in symptom-free schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 1982;77:301-4. [CSZG: 2167] - PubMed
Various drugs 1984a {published data only}
-
- Gardos G, Cole JO, Rapkin RM, LaBrie RA, Baquelod E, Moore P, et al. Anticholinergic challenge and neuroleptic withdrawal. Changes in dyskinesia and symptom measures. Archives of General Psychiatry 1984;41:1030-5. - PubMed
Various drugs 1984b {published data only}2082
-
- Nishikawa T, Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Hoaki Y, Koga I, Uchida Y. Prophylactic effect of neuroleptics in symptom-free schizophrenics: a comparative dose response study of haloperidol and propericiazine. Psychopharmacology 1984;82:153-6. [CSZG: 2168] - PubMed
Various drugs 1986a {published data only}599
-
- Crow TJ, MacMillan JF, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. A randomised controlled trial of prophylactic neuroleptic treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148:120-7. [CSZG: 648] - PubMed
Various drugs 1986b {published data only}2626
-
- Spohn HE, Coyne L, Larson J, Mittleman F, Spray J, Hayes K. Episodic and residual thought pathology in chronic schizophrenics: effect of neuroleptics. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1986;12:394-407. [CSZG: 2712] - PubMed
Various drugs 1989 {published data only}3775
-
- McCreadie RG, Wiles D, Grant S, Crockett GT, Mahmood Z, Livingston MG, et al. The Scottish first episode schizophrenia study. VII two-year follow-up. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1989;80:597-602. [CSZG: 3968] - PubMed
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study II. Treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;150:334-8. [CSZG: 3969] - PubMed
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study V. One-year follow-up. British Journal of Psychiatry 1988;152:470-476. [CSZG: 3970] - PubMed
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study. III. Cognitive performance. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;150:338-340. [CSZG: 16867] - PubMed
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish first episode schizophrenia study. VIII. Five-year follow-up. British Journal of Psychiatry 1992;161:496-500. [CSZG: 2542] - PubMed
Various drugs 1993 {published data only}2205
-
- Gaebel W, Frick U, Kopcke W, Linden M, Mueller P, Mueller Spahn F, et al. Early neuroleptic intervention in schizophrenia: are prodromal symptoms valid predictors of relapse? British Journal of Psychiatry Supplementum 1993;163:8-12. [CSZG: 831] - PubMed
-
- Gaebel W, Janner M, Frommann N, Pietzcker A, Kopcke W, Linden M, et al. First vs multiple episode schizophrenia: two-year outcome of intermittent and maintenance medication strategies. Schizophrenia Research 2002;53(1-2):145-59. [CSZG: 8197] - PubMed
-
- Gaebel W, Moeller HJ. Treatment strategies in first episode schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 12th World Congress of Psychiatry; 2002 Aug 24-29; Yokohama, Japan. 2002. [CSZG: 8597]
-
- Pietzcker A, Gaebel W, Koepcke W, Linden M, Mueller P, Mueller-Spahn F, et al. Intermittent versus maintenance neuroleptic long-term treatment in schizophrenia - 2-year results of a German multicenter study. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1993;27:321-39. [CSZG: 3944]
-
- Pietzcker A, Gaebel W, Kopcke W, Linden M, Muller P, Muller-Spahn, et al. A German multicenter study on the neuroleptic long-term therapy of schizophrenic patients. Preliminary report. Pharmacopsychiatry 1986;19:161-6. [CSZG: 3943]
Various drugs 2011 {published data only}10307
-
- Boonstra G, Burger H, Grobbe DE, Kahn RS. Antipsychotic prophylaxis is needed after remission from a first psychotic episode in schizophrenia patients: results from an aborted randomised trial. International Journal of Psychiatry in Clinical Practice 2011;15(2):128-34. [CSZG: 22940] - PubMed
-
- Boonstra G. Schizophrenia termination of pharmacotherapy-STOP-trial. Current Controlled Trials 2005. [CSZG: 14487] [ISRCTN: 6332944]
Ziprasidone 2002 {published data only}227
-
- Arato M, O'Connor R, Bradbury JE, Meltzer H. Long-term ziprasidone in schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 151st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1998 May 30 - Jun 4; Toronto, Ontario, Canada. 1998. [CSZG: 3189]
-
- Arato M, O'Connor R, Bradbury JE, Meltzer H. The efficacy of ziprasidone in the long-term treatment of negative symptoms and prevention of exacerbation of schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 21st Collegium Internationale Neuro-Psychopharmacologicum Congress; 1998 Jul 12-16; Glasgow, UK. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Cambridge University Press, 1998. [CSZG: 3188]
-
- Arato M, O'Connor R, Bradbury JE, Meltzer H. Ziprasidone in the long-term treatment of negative symptoms and prevention of exacerbation of schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 9th Congress of the Association of European Psychiatrists; 1998 Sep 20-24; Copenhagen, Denmark. 1998. [CSZG: 3190]
-
- Arato M, O'Connor R, Bradbury JE, Meltzer H. Ziprasidone in the long-term treatment of negative symptoms and prevention of exacerbation of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1999;36(1-3):270. [CSZG: 5626]
-
- Arato M, O'Connor R, Meltzer H, Bradbury J. Ziprasidone: efficacy in the prevention of relapse and in the long-term treatment of negative symptoms of chronic schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1997 Sep 13-17; Vienna, Austria. 1997. [CSZG: 245]
Zotepine 2000 {published data only}544
-
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed J, Raniwalla J, Welch C. Zotepine in the prevention of relapse. Biological Psychiatry 1997;42:41s. [CSZG: 17007]
-
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed J, Raniwalla J, Welch C. Zotepine in the prevention of relapse. In: Proceedings of the 6th World Congress of Biological Psychiatry; 1997 June 22-27; Nice, France. 1997. [CSZG: 569]
-
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed J, Welch C, Raniwalla J. Zotepine in the prevention of recurrence: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study for chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 2000;150:237-43. [CSZG: 5732] - PubMed
-
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed JA, Welch CP, Wighton AJ, Appleby P, et al. Zotepine is effective in preventing recurrence in patients with chronic schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 11th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1998 Oct 31 - Nov 4; Paris, France. 1998. [CSZG: 5784]
-
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed JA, Welch CP, Wighton AJ, Appleby P, et al. Zotepine is effective in preventing recurrence in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41:207-8. [CSZG: 4925]
References to studies excluded from this review
Allen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Allen DN, Gilbertson MW, Barry E, Kammen DP, Gurklis JA. Haloperidol improves memory in schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 150th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1997 May 17-22; San Diego, California, USA. 1997.
Bai 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bai YM, Yu SC, Chen JY, Lin CY, Chou P, Lin CC. Risperidone for pre-existing severe tardive dyskinesia: a 48-week prospective follow-up study. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2005;20:79-85. - PubMed
-
- Bai YM, Yu SC, Lin CC. Risperidone for severe tardive dyskinesia: a 12 week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2003;64:1342-8. - PubMed
Bechdolf 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bechdolf A, Mueller H, Gaebel W, Hasan A, Maier W, Juckel G, et al. PREVENT: a randomized controlled trial comparing cognitive behavioural therapy, clinical management and aripiprazole and clinical management and placebo for the prevention of first episode psychosis. Early Intervention in Psychiatry 2016;10(Suppl 1):40.
Bo 2017 {published data only}
-
- Bo Q, Li F, Li X, Wang Z, Dong F, He F, et al. Symptomatic remission in schizophrenia: results from a risperidone maintenance treatment study. Psychiatry Research 2017;258:289-94. - PubMed
Bourin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bourin M, Debelle M, Heisterberg J, Josiassen MK, Ostergaard JB, Sands E. Efficacy of bifeprunox in patients in the post-acute, maintenance phase of schizophrenia: findings from a 6-month study. Schizophrenia Research 2008;98:158.
Branchey 1981 {published data only}
-
- Branchey MH, Branchey LB, Richardson MA. Effects of gradual decrease and discontinuation of neuroleptics on clinical condition and tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1981;17:118-20. - PubMed
-
- Branchey MH, Branchey LB, Richardson MA. Effects of neuroleptic adjustment on clinical condition and tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1981;138:608-12. - PubMed
Breier 1987 {published data only}
-
- Breier A, Wolkowitz OM, Doran AR, Roy A, Boronow J, Hommer DW, et al. Neuroleptic responsivity of negative and positive symptoms in schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1987;144:1549-55. - PubMed
Brown 2018 {published data only}
-
- Sand M, Nakagome K, Cordes J, Brenner R, Gründer G, Keefe R, et al. Effects of BI409306 on positive and negative syndrome scale in schizophrenia: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled phase II trial. Biological Psychiatry 2018;83(9):S207-8.
Cather 2018 {published data only}
-
- Cather C, Brunette MF, Mueser KT, Babbin SF, Rosenheck R, Correll CU, et al. Impact of comprehensive treatment for first episode psychosis and substance use outcomes: a randomized controlled trial. Psychiatry Research 2018;268:303-11. - PubMed
-
- Schooler N, Mueser K, Estroff S, Correll C, Robinson D, Marcy P, et al. Elements of recovery in first episode psychosis: developing measurable criteria. Early Interventions in Psychiatry 2016;10(Suppl 1):149.
Cheng 2019 {published data only}
-
- Cheng Z, Yuan Y, Han X, Yang L, Zeng X, Yang F, et al. Rates and predictors of one year antipsychotic treatment discontinuation in first episode schizophrenia: results from ab open-label randomized "real-world" clinical trial. Psychiatry Research 2019;273:631-40. - PubMed
Chopra 2019 {published data only}
-
- Chopra S, Fornito A, Francey S, O’Donoghue B, Nelson B, Graham J, et al. Gray matter changes in medicated and unmedicated first episode psychosis: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2019;45:S172-3.
Chouinard 1980 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard G, Annable L, Jones BD, Collu R. Lack of tolerance to long-term neuroleptic treatment in dopamine tuberoinfundibular system. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1980;64:353-62. - PubMed
Chouinard 1993 {published data only}
-
- Andris J. Clinical trials van risperidone [Clinical trails van risperidone]. Unknown Source 1997:14.
-
- Chouinard G, Albright PS. Economic and health state utility determinations for schizophrenic patients treated with risperidone or haloperidol. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1997;17(4):298-307. - PubMed
-
- Chouinard G, Arnott W. The effect of risperidone on extrapyramidal symptoms in chronic schizophrenic patients. Biological Psychiatry 1992;31:158.
-
- Chouinard G, Jones B, Remington G, Bloom D, Addington D, MacEwan GW, et al. A Canadian multicenter placebo-controlled study of fixed doses of risperidone and haloperidol in the treatment of chronic schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1993;13(1):25-40. - PubMed
-
- Chouinard G. Effects of risperidone in tardive dyskinesia: an analysis of the Canadian multicenter risperidone study. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1995;15(Suppl 1):S36-44. - PubMed
Claghorn 1974 {published data only}
-
- Claghorn JL, Johnstone EE, Cook TH, Itschner L. Group therapy and maintenance treatment of schizophrenics. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31:361-5. - PubMed
Clark 1967 {published data only}
-
- Clark ML, Ray TS, Paredes A, Ragland RE, Costiloe JP, Smith CW, et al. Chlorpromazine in women with chronic schizophrenia: the effect on cholesterol levels and cholesterol-behavior relationships. Psychosomatic Medicine 1967;29(6):634-42. - PubMed
Collins 1967 {published data only}
-
- Collins AD, Dundas J. A double-blind trial of amitriptyline-perphenazine, perphenazine and placebo in chronic withdrawn inert schizophrenics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1967;113:1425-9. - PubMed
Condray 1995 {published data only}
-
- Condray R, Van Kammen DP, Steinhauer SR, Kasparek A, Yao JK. Language comprehension in schizophrenia: trait or state indicator? Biological Psychiatry 1995;38:287-96. - PubMed
Curson 1985 {published data only}
-
- Curson DA, Barnes TR, Bamber RW, Platt SD, Hirsch SR, Duffy JC. Long term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out patients: the seven year follow up of the Medical Research Council fluphenazine/placebo trial. II. The incidence of compliance problems, side effects, neurotic symptoms and depression. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:469-74. - PubMed
-
- Curson DA, Barnes TR, Bamber RW, Platt SD, Hirsch SR, Duffy JC. Long-term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out-patients: the seven year follow-up of the Medical Research Council fluphenazine- placebo trial I. Course of illness, stability of diagnosis, and the role of a special maintenance clinic. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:464-9. - PubMed
-
- Curson DA, Barnes TR, Bamber RW, Platt SD, Hirsch SR, Duffy JC. Long-term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out-patients: the seven year follow-up of the Medical Research Council fluphenazine/placebo trial. III. Relapse postponement or relapse prevention? The implications for long-term outcome. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:474-80. - PubMed
Degkwitz 1970 {published data only}
-
- Degkwitz R, Bauer MP, Gruber M, Hampel G, Luxenburger O, Richartz M, et al. Time relationship between the appearance of persisting extrapyramidal hyperkineses and psychotic recurrences following sudden interruption of prolonged neuroleptic therapy of chronic schizophrenic patients. Arzneimittelforschung 1970;20(7):890-3. - PubMed
Diamond 1960 {published data only}
-
- Diamond LS, Marks JB. Discontinuance of tranquilizers among chronic schizophrenic patients receiving maintenance dosage. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1960;131:247-51. - PubMed
Double 1993 {published data only}
-
- Double DB, Warren GC, Evans M, Rowlands RP. Efficacy of maintenance use of anticholinergic agents. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1993;88:381-4. - PubMed
-
- Elie R, Morin L, Tetreault L. Effects of ethopropazine and trihexyphenidyl on several parameters of the neuroleptic syndrome [Effets de l'ethopropazine et du trihexyphenidyle sur quelques parametres du syndrome neuroleptique]. Encephale 1972;61:32-52. - PubMed
Durgam 2016 {published data only}
-
- Barabassy A, Szatmàri B, Laszlovszky I, Harsanyi J, Acsai K, Sebe B, et al. Efficacy of cariprazine in the treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia: post hoc analysis versus aripiprazole. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2019;29(Suppl 1):S417-8.
-
- Cutler AJ, Durgam S, Lu K, Laszlovszky I, Szalai E, Edwards J, Earley W. Efficacy of cariprazine in negative, cognitive, social function symptoms in schizophrenia: post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2016;26(2):S551-2.
-
- Durgam S, Earley W, Lu K, Németh G, Laszlovszky I, Szatmari B, Patel M, Nasrallah H. Cariprazine for negative symptoms of schizophrenia: a pooled post-hoc analysis of 2 randomized double-blind placebo and active controlled trials. In: 29th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress. Vienna, Austria, 2016, Sep 17-20.
-
- Marder S, Fleischhacker WW, Earley W, Kaifeng L, Zhong Y, Németh G. Efficacy of cariprazine across symptom domains in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia: pooled analysis from 3 phase II/III studies. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2019;29(1):127-36. - PubMed
Engelhardt 1967 {published data only}
-
- Engelhardt DM, Rosen B, Freedman N, Margolis R. Phenothiazines in prevention of psychiatric hospitalisation. Archives of General Psychiatry 1967;16:98-101. - PubMed
Fleischhacker 2014 {published data only}
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Sanchez R, Perry PP, Jin N, Peters-Strickland T, Johnson BR, et al. Aripiprazole once-monthly for treatment of schizophrenia: double-blind, randomised, non-inferiority study. British Journal of Psychiatriy 2014;205(2):135-44. - PubMed
Francey 2018 {published data only}
-
- Francey S, Nelson B, Jessica G, Lara B, Yuen HP, O'Donoghue B, et al. Antipsychotic medication in first episode psychosis: an RCT to assess the risk benefit ratio. Early Intervention in Psychiatry 2018;12(Suppl 1):70.
-
- Francey S. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of intensive psychosocial treatment plus or minus antipsychotic medication for first episode psychosis with low risk of self harm of aggression. The STAGES study: staged treatment and acceptability guidelines in early psychosis. Early Interventions in Psychiatry 2016;10(Suppl 1):9. - PubMed
-
- O'Donoghue B, Francey SM, Nelson B, Ratheesh A, Allott K, Grahan J, et al. Staged treatment and acceptability guidelines in early psychosis study (STAGES): a randomized placebo-controlled trial of intensive psychosocial treatment plusof minus antipsychotic medication for first episode with low risk of self harm or aggression: study protocol and baseline characteristics of patients. Early Interventions in Psychiatry 2019;13(4):953-60. - PubMed
Freedman 1982 {published data only}
-
- Freedman R, Kirch D, Bell J, Adler LE, Pecevich M, Pachtman E, et al. Clonidine treatment of schizophrenia: double blind comparison to placebo and neuroleptic drugs. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1982;65:35-45. - PubMed
Gallant 1964 {published data only}
-
- Gallant DM, Edwards CG, Bishop MP, Galbraith GC. Withdrawal symptoms after abrupt cessation of antipsychotic compounds: clinical confirmation in chronic schizophrenics. American Journal of Psychiatry 1964;121:491-3. - PubMed
Gitlin 1988 {published data only}
-
- Gitlin MJ, Midha KK, Fogelson D, Nuechterlein KH. Persistence of fluphenazine in plasma after decanoate withdrawal. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1988;8:53-6. - PubMed
Gitlin 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gitlin M, Nuechterlein K, Subotnik KL, Ventura J, Mintz J, Fogelson DL, et al. Clinical outcome following neuroleptic discontinuation in patients with remitted recent-onset schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 2001;158:1835-42. - PubMed
Gleeson 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gleeson J, Wade D, Mcgorry P, Albiston D, Castle D, Gilbert M, et al. Episode ii: prevention of relapse following early psychosis. Schizophrenia Research 2004;70:61-2.
Goldberg 1967 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg SC, Schooler NR, Mattsson N. Paranoid and withdrawal symptoms in schizophrenia: differential symptom reduction over time. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1967;145:158-62. - PubMed
-
- Mefferd RB Jr, Labrosse EH, Gawienowski AM, Williams RJ. Influence of chlorpromazine on certain biochemical variables of chronic male schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1958;127:167-79. - PubMed
Good 1958 {published data only}
-
- Good WW, Sterling M, Holtzman WH. Termination of chlorpromazine with schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1958;115:443-8. - PubMed
-
- Mefferd RB, Labrosse EH, Gawienowski AM, Williams RJ. Influence of chlorpromazine on certain biochemical variables of chronic male schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1958;127:167-79. - PubMed
Greenberg 1966 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg LM, Roth S. Differential effects of abrupt versus gradual withdrawal of chlorpromazine in hospitalized chronic schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1966;123:221-6. - PubMed
Hine 1958 {published data only}
-
- Hine FR. Chlorpromazine in schizophrenic withdrawal and in the withdrawn schizophrenic. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1958;127:220-7. - PubMed
Hirsch 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hirsch SR, Jolley AG, Barnes TR, Liddle PF, Curson DA, Patel A, et al. Dysphoric and depressive symptoms in chronic schizophrenia.. Schizophrenia Research 1989;2(3):259-64. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch SR, Jolley AG. The dysphoric syndrome in schizophrenia and its implications for relapse [Das dysphorische Syndrom in der Schizophrenie und seine Implikationen fuer den Rueckfall]. In: Boeker W//Brenner HD//Waldvogel DM, editors(s). Schizophrenie Als Systemische Stoerung. Die Bedeutung Intermediaerer Prozesse Fuer Theorie Und Therapie. Bern, Switzerland: Verlag Hans Huber, 1989:94-103.
-
- Hirsch SR, Jolley AG. The dysphoric syndrome in schizophrenia and its implications for relapse. British Journal of Psychiatry. Supplements 1989;155(Suppl 5):46-50. - PubMed
Hirsch 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hirsch SR, Bowen JT, Emami J, Cramer P, Jolley A, Haw C, et al. A one year prospective study of the effect of life events and medication in the aetiology of schizophrenic relapse. British Journal of Psychiatry 1996;168:49-56. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch SR, Bowen JT, Emami J. The effect of life events and medication in the aetiology of schizophrenic relapse. Schizophrenia Research 1993;9:266.
Hunt 1967 {published data only}
-
- Hunt PV. A comparison of the effects of oxypertine and trifluoperazine in withdrawn schizophrenics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1967;113:1419-24. - PubMed
Ionescu 1983 {published data only}
-
- Ionescu R, Tiberiu C, Miklos R, Angelescu C, Persiceanu AM. Penfluridol in the maintenance therapy of schizophrenia. Neurologie et Psychiatrie 1983;21:33-41. - PubMed
Janecek 1963 {published data only}
-
- Janecek J, Schiele BC, Bellville T, Anderson R. The effects of withdrawal of trifluoperazine on patients maintained on the combination of tranylcypromine and trifluoperazine: a double-blind study. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1963;85:608-15. - PubMed
Johnstone 1988 {published data only}
-
- Johnstone EC, Crow TJ, Frith CD, Owens DG. The Northwick Park "functional" psychosis study: diagnosis and treatment response. Lancet 1988;2:119-25. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone EC, Crow TJ, Owens DGC, Frith CD. The Northwick Park 'functional' psychosis study. Phase 2 - maintenance treatment. Journal of Psychopharmacology 1991;5:388-95. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone EC, Owens DGC. Does early treatment have an effect on outcome? In: Proceedings of the 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1997 Sep 13-17; Vienna, Austria. 1997.
Keefe 2018 {published data only}
-
- Keefe RS, Harvey PD, Khan A, Saoud JB, Staner C, Davidson M, et al. Cognitive effects of MIN-101 in patients with schizophrenia and negative symptoms: results from a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2018;79(3):17m11753. - PubMed
Kellam 1971 {published data only}
-
- Kellam AM, Jones KS. A double-blind controlled trial of thiothixene and perphenazine in chronic schizophrenics shown to require maintenance therapy. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1971;47:174-85. - PubMed
Lauriello 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lauriello J, McEvoy JP, Rodriguez S, Bossie CA, Lasser RA. Long-acting risperidone vs. placebo in the treatment of hospital inpatients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2005;72:249-58. - PubMed
Lecrubier 1997 {published data only}
-
- Lecrubier Y. Amisulpride in deficit schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 6th World Congress Biological Psychiatry, 1997 Jun 22-27; Nice, France. 1997.
Liu 2018 {published data only}
-
- Liu CC. A proposed alternative between discontinuation and maintenance of antipsychotics: a guided dose reduction trial for patients with remitted psychosis. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2018;44(Suppl 1):S414.
Loo 1997 {published data only}
-
- Loo H, Poirier-Littre MF, Theron M, Rein W, Fleurot O. Amisulpride versus placebo in the medium-term treatment of the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1997;170:18-22. - PubMed
Mahal 1975 {published data only}
-
- Mahal AS, Janakiramaiah N. A double blind placebo controlled trial of pimozide (R6238) on 49 hospitalized chronic schizophrenics. Indian Journal of Psychiatry 1975;17(1):45-55.
Marder 1994 {published data only}
-
- Andris J. Clinical trials van risperidone [Clinical trails van risperidone]. Unknown Source 1997:14.
-
- Czobor P, Volavka J, Meibach RC. Effect of risperidone on hostility in schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1995;15(4):243-9. - PubMed
-
- Czobor P, Volavka J. Quantitative electroencephalogram examination of effects of risperidone in schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1993;13(5):332-42. - PubMed
-
- Lindenmayer JP, =The RSG. Incidence of EPS with risperidone compared with haloperidol and placebo in patients with chronic schizophrenia. In: Proceedings of the 146th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1993 May 22-27; San Francisco, California, USA. 1993.
-
- Marder S. Risperidone versus haloperidol versus placebo in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. Clinical Research Report (RIS-INT-3) 1991.
Mathur 1981 {published data only}
-
- Mathur S, Hall JN. Phenothiazine withdrawal in schizophrenics in a hostel. British Journal of Psychiatry 1981;138:271-2. - PubMed
Meehan 2019 {published data only}
-
- Meehan SR, Zhang P, Hobart M, Hefting N, Baker RA, Weiss C. Short term efficacy of brexpiprazole in patients with schizophrenia with clinically relevant levels of negative symptoms. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2019;29(Suppl 1):S424.
Mefferd 1958 {published data only}
-
- Mefferd RB, Labrosse EH, Gawienowski AM, Williams RJ. Influence of chlorpromazine on certain biochemical variables of chronic male schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1958;127(2):167-79. - PubMed
Mosher 1975 {published data only}
-
- Bola JR, Mosher LR. Treatment of acute psychosis without neuroleptics: two-year outcomes from the Soteria project. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2003;191:219-29. - PubMed
-
- Matthews SM, Roper MT, Mosher LR, Menn AZ. A non neuroleptic treatment for schizophrenia: analysis of the two year postdischarge risk of relapse. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1979;5:322-33. - PubMed
-
- Mosher LR, Menn A, Matthew SM. Soteria: evaluation of a home-based treatment for schizophrenia. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry 1975;45:455-67. - PubMed
-
- Mosher LR, Menn AZ. Community residential treatment for schizophrenia: two year follow up. Hospital and Community Psychiatry 1978;29:715-23. - PubMed
Müller 1982 {published data only}
-
- Müller P, Hartmann W, Jung F, Kind J, Lohrengel S, Steuber H. To prevent relapse of schizophrenic psychoses [Zur Rezidivprophylaxe schizophrener Psychosen]. Ferdinand Enke Verlag Stuttgart 1982;14:1-144.
NCT03559426 {published data only}
-
- NCT03559426. Research into antipsychotic discontinuation and reduction (RADAR): a randomized controlled trial. https://clinicaltrials.gov/.
Nishikawa 1989 {published data only}
-
- Nishikawa T, Tanaka M, Tsuda A, Koga I, Uchida Y. Prophylactic effects of neuroleptics in symptom-free schizophrenics: a comparative dose-response study of timiperone and sulpiride. Biological Psychiatry 1989;25(7):861-6. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa T. Personal Communication. Personal Communication 2009.
Oosthuizen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Oosthuizen PP. Treatment of first episode schizophrenia with low-dose haloperidol: a study in the Western Cape province of South Africa. Dissertation presented for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy at the University of Stellenbosch 2003 March.
Pasamanick 1967 {published data only}
-
- Davis AE, Dinitz S, Pasamanick B. The prevention of hospitalization in schizophrenia: five years after an experimental program. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry 1972;42(3):375-88. - PubMed
-
- Pasamanick B, Scarpitti FR, Dinitz S. Schizophrenic in theCcommunity: an Experimental Study in the Prevention of Hospitalisation. New York: Meredith Publishing Company, 1967.
-
- Pasamanick B, Scarpitti FR, Lefton M, Dinitz F, Wernert JJ, McPheeters H. Home vs hospital care for schizophrenics. JAMA 1964;187(3):177-81. - PubMed
Paul 1972 {published data only}
-
- Paul GL, Tobias LL, Holly BL. Maintenance psychotropic drugs in the presence of active treatment programs. A "triple-blind" withdrawal study with long-term mental patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1972;27:106-15. - PubMed
Peet 1981 {published data only}
-
- Peet M, Middlemiss DN, Yates RA. Propranolol in schizophrenia II. Clinical and biochemical aspects of combining propranolol with chlorpromazine. British Journal of Psychiatry 1981;138:112-7. - PubMed
Pickar 1986 {published data only}
-
- Pickar D, Labarca R, Doran AR, Wolkowitz OM, Roy A, Breier A, et al. Longitudinal measurement of plasma homovanillic acid levels in schizophrenic patients. Correlation with psychosis and response to neuroleptic treatment. Archives of General Psychiatry 1986;43:669-76. - PubMed
Pickar 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pickar D, Bartko JJ. Effect size of symptom status in withdrawal of typical antipsychotics and subsequent clozapine treatment in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 2003;160:1133-8. - PubMed
Pigache 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pigache RM, Norris HN. Measurement of drug action in schizophrenia. Clinical Science 1973;44:28P. - PubMed
-
- Pigache RM, Norris HN. Selective attention as an index of the anti-psychotic action of chlorpromazine in schizophrenia. British Psychological Society Bulletin 1973;20:160.
-
- Pigache RM. Effects of placebo, orphenadrine, and rising doses of chlorpromazine, on PAT performance in chronic schizophrenia. A two year longitudinal study. Schizophrenia Research 1993;10:51-9. - PubMed
-
- Pigache RM. The clinical relevance of an auditory attention task (PAT) in a longitudinal study of chronic schizophrenia with placebo substitution for chlorpromazine. Schizophrenia Research 1993;10:39-50. - PubMed
Ran 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ran MS, Xiang MZ, Chan CL, Leff J, Simpson P, Huang MS, et al. Effectiveness of psychoeducational intervention for rural Chinese families experiencing schizophrenia. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 2003;38:69-75. - PubMed
-
- Ran MS, Xiang MZ, Huang MS. A control study of psychoeducational family intervention for relatives of schizophrenics in a Chinese rural community. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry 2001;34(2):98-101.
-
- Ran MS. Community mental health in China - A randomized controlled trial of psychoeducational family intervention for carers of persons with schizophrenia in a rural area in Chengdu. http://hdl.handle.net/10722/35402 submitted at the University of Hong Kong in March 2002.
Rassidakis 1970 {published data only}
-
- Rassidakis NC, Kondakis X, Papanastassiou A, Michalakeas A. Withdrawal of antipsychotic drugs from chronic psychiatric patients. Bulletin of the Menninger Clinic 1970;34(4):216-22. - PubMed
Ravaris 1965 {published data only}
-
- Ravaris CL, Weaver LA, Brooks GW. A controlled study of fluphenazine enanthate in chronic schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1965;25:33-9. - PubMed
-
- Ravaris CL, Weaver LA, Brooks GW. Further studies with fluphenazine enanthate: II. Relapse rate in patients deprived of medication. American Journal of Psychiatry 1967;124:248-9. - PubMed
Ruiz 1975 {published data only}
-
- Ruiz Ruiz M, Miro Quintana L, Sentis Vilalta J. A clinical study with pimozide in chronic schizophrenics [Estudio clinico con pimocide en las esquizophrenias de evolucion cronica]. Revista de Psiquiatria Y Psicologia Medica de Europa Y America Latinas 1975;12(4):247-56.
Ruiz Veguilla 2013 {published data only}
-
- NCT01765829. Clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of treatment vs discontinuation in a first episode of non-affective psychosis (NONSTOP). https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01765829?term=NCT01765829&... 2013.
Schlossberg 1978 {published data only}
-
- Schlossberg A, Shadmi M. A comparative controlled study of two long-acting phenothiazines: pipotiazine palmitate and fluphenazine decanoate. Current Therapeutic Research 1978;23(5):642-54.
Singer 1971 {published data only}
Singh 1990 {published data only}
-
- Singh H, Hunt JI, Vitiello B, Simpson GM. Neuroleptic withdrawal in patients meeting criteria for supersensitivity psychosis. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1990;51:319-21. - PubMed
Smelson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Smelson DA, Tunis SL, Nyhuis AW, Faries DE, Kinon BJ, Ascher-Svanum H. Antipsychotic treatment discontinuation among individuals with schizophrenia and co-occurring substance use. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2006;26:666-7. - PubMed
Soni 1990 {published data only}
-
- Soni SD, Mallik A, Schiff AA. Sulpiride in negative schizophrenia: a placebo-controlled double-blind assessment. Human Psychopharmacology 1990;5:233-8.
Stuerup 2017 {published data only}
-
- Dolmer S, Nielsen M, Birk M, Mors O, Sturup AE, Albert N, et al. Tailor tapered discontinuation versus maintenance therapy of antipsychotic medication in patients with newly diagnosed schizophrenia spectrum disorders in remission of psychotic symptoms. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2018;44(Suppl 1):S134-S135. - PMC - PubMed
-
- EudraCT 2016-000565-23. TAILOR - a randomized clinical trial: Tapered discontinuation versus maintenance therapy of antipsychotic medication in patients with newly diagnosed schizophrenia or schizophreniform psychosis in remission of psychotic symptoms. https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2016-00056... 2017. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stuerup AE, Jensen H, Dolmer S, Albert N, Birk M, Hjorthoj C, et al. Discontinuation versus maintenance therapy with antipsychotic medication in schizophrenia. TAILOR: a randomized controlled trial. Early Interventions in Psychiatry 2018;12:141.
-
- Stuerup AE, Jensen HD, Dolmer S, Birk M, Albert N, Nielsen M, et al. TAILOR - tapered discontinuation versus maintenance therapy of antipsychotic medication in patients with newly diagnosed schizophrenia or persistent delusional disorder in remission of psychotic symptoms: study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. Trials 2017;18(1):445. - PMC - PubMed
Sumitomo 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma. Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, confirmatory study of SM-13496 (lurasidone HCl) in patients with schizophrenia: a phase III study. Summary of study results. Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Reports 2008.
Vaddadi 1986 {published data only}
-
- Vaddadi KS, Gilleard CJ, Mindham RH, Butler R. A controlled trial of prostaglandin E1 precursor in chronic neuroleptic resistant schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 1986;88:362-7. - PubMed
Van Kammen 1982 {published data only}
-
- Van Kammen DP, Bunney WE Jr, Docherty JP, Marder SR, Ebert MH, Rosenblatt JE, et al. D-Amphetamine-induced heterogeneous changes in psychotic behavior in schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1982;139:991-7. - PubMed
-
- Van Kammen DP, Bunney WE, Docherty JP, Jimerson DC, Post RM, Siris P, et al. Amphetamine-induced catecholamine activation in schizophrenia and depression: behavioral and physiological effects. Advances in Biochemical Psychopharmacology 1977;16:655-9. - PubMed
-
- Van Kammen DP, Docherty JP, Marder SR, Schulz SC, Bunney WE Jr. Lack of behavioral supersensitivity to d-amphetamine after pimozide withdrawal. A trial with schizophrenic patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1980;37:287-90. - PubMed
-
- Van Kammen DP, Docherty JP, Marder SR, Siris SG, Bunney WE Jr. D amphetamine raises serum prolactin in man: evaluations after chronic placebo, lithium and pimozide treatment. Life Sciences 1978;23:1487-92. - PubMed
Vanover 2018 {published data only}
-
- Vanover K, Dmitrienko A, Glass S, Kozauer S, Saillard J, Weingart M, et al. Lumateperone (ITI-007) for the treatment of schizophrenia: placebo-controlled clinical trials and an open-label safety switching study. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2018;44(Suppl 1):S341.
Van Praag 1973 {published data only}
-
- Van Praak HM, Dols LC. Fluphenazine enanthate and fluphenazine decanoate: a comparison of their duration of action and motor side effects. American Journal of Psychiatry 1973;130:801-4. - PubMed
Weller 2018 {published data only}
-
- Weller A, Killackey E, Gleeson J, Allott K, Alvarez-Jimenez M, Bendall S, et al. Less is more? An Australian RCT comparing dose reduction of anti-psychotic medication to maintenance treatment. Early Interventions in Psychiatry 2018;12(Suppl 1):207.
-
- Weller A, et al. Can antipsychotic dose reduction lead to better functional recovery in first episode psychosis? A randomized controlled trial of antipsychotic dose reduction: the REDUCE trial: study protocol. Early Intervention in Psychiatry 2019;13(6):1345-1356. - PubMed
Wiedemann 2001 {published data only}
-
- Wiedemann G, Hahlweg K, Muller U, Feinstein E, Hank G, Dose M. Effectiveness of targeted intervention and maintenance pharmacotherapy in conjunction with family intervention in schizophrenia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2001;251:72-84. - PubMed
Wright 1964 {published data only}
-
- Wright RL, Lynes PG. Value of continuous drug administration for chronic long-term mental hospital patients. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1964;60:352-7. - PubMed
Wunderink 2006 {published data only}
-
- Faber G, Smid HG, Van Gool AR, Wiersma D, Van Den Bosch RJ. The effect of guided discontinuation of antipsychotics on neurocognition in first onset psychosis. European Psychiatry 2012;27:275-80. - PubMed
-
- Wunderink A, Nienhuis, Sytema S, Wiersma D. Guided discontinuation versus maintenance treatment in remitted first episode psychosis: relapse rates and functional outcome. Schizophrenia Research 2006;86:S51. - PubMed
Zeller 1956 {published data only}
-
- Zeller WW, Graffagnino PN, Cullen CF, Rietman HJ. Use of chlorpromazine and reserpine in the treatment of emotional disorders. Journal of the American Medical Association 1956;160:179-84. - PubMed
Zou 2018 {published data only}
Zwanikken 1973 {published data only}
-
- Zwanikken 1973. Penfluridol (R 16341). A long-acting oral neuroleptic, as maintenance therapy for schizophrenic and mentally retarded patients. Psychiatria, Neurologia, Neurochirurgia 1973;76:83-92. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ascher‐Svanum 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ascher-Svanum H, Nyhuis A, Faries D, Novick D, Kinon B. Differences between schizophrenia patients who switch vs discontinue antipsychotic therapy. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2011 March;37(Suppl 1, Abstracts for the 13th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research (ICOSR)):96.
Decot 2011 {published data only}
-
- Decot H, Zhang F, Weinberger DR, Apud J. Effect of placebo and reintroduction of antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia based on COMT Val108/158Met polymorphism. In: International Congress on Schizophrenia Research 84, downloaded from: schizophreniabulletin.oxfordjournals.org,. 2011.
Eisenberg 2016 {published data only}
-
- Eisenberg D, Yankowitz L, Kohn P, Hegarty C, Ianni A, Rubinstein D, Gregory M, Dickinson D, Apud J, Berman K. Neuroleptic-induced striatal blood flow changes and neurocognitive functioning in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016;41:S223-4.
EUCTR2005‐005499‐34 {published and unpublished data}
-
- EUCTR2005-005499-34. A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, quetiapine-referenced, multicentre study of the long-term bifeprunox efficacy, safety and tolerability in patients with stable schizophrenia. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu.
Zhang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zhang Q, He FR, Tian YL, Zhao S, Sun ZH. Double blind study of the contact between antipsychotic and the negative symptoms of the deteriorated schizophrenia. Medical Journal of Chinese People Health 2006;3:182-3.
References to ongoing studies
NCT03503318 {published data only}
-
- NCT03503318. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of risperidone extended-release injectable suspension (TV-46000) for subcutaneous use as maintenance treatment in adult and adolescent patients with schizophrenia. https://clinicaltrials.gov.
NCT03593213 {published data only}
-
- NCT03593213. Clinical trial evaluating the efficacy, safety and tolerability of cariprazine in a dose-reduction paradigm in the prevention of relapse in patients with schizophrenia. https://clinicaltrials.gov.
NCT03893825 {published data only}
-
- NCT03893825. A study to test if TV-46000 is safe for maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. https://clinicaltrials.gov.
Additional references
Almerie 2007
Altman 1996
American Psychiatric Association 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd rev edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1987.
Andreasen 2005
-
- Andreasen NC, Carpenter WT Jr, Kane JM, Lasser RA, Marder SR, Weinberger DR. Remission in schizophrenia: proposed criteria and rationale for consensus. American Journal of Psychiatry 2005;162(3):441-9. - PubMed
Auquier 2003
-
- Auquier P, Simeoni MC, Sapin C, Reine G, Aghababian V, Cramer J, et al. Development and validation of a patient-based health-related quality of life questionnaire in schizophrenia: the S-QoL. Schizophrenia Research 2003;63(1-2):137-49. - PubMed
Baldessarini 1985
-
- Baldessarini RJ. Chemotherapy in Psychiatry: Principles and Practice. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1985.
Barnes 1989
-
- Barnes TR. A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1989;154:672-6. - PubMed
Berger 2003
-
- Berger M. Psychische Erkrankungen. Klinik und Therapie. 2nd edition. München: Urban & Fischer, 2003.
Bland 1997
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, et al. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices. 3. Comparison of the indices and their use. Therapie 1999;54(4):405-11. - PubMed
Borenstein 2006 [Computer program]
-
- Comprehensive Meta-analysis Version 2. Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein H. Biostat, 2006.
Boyer 2010
-
- Boyer L, Simeoni MC, Loundou A, D'Amato T, Reine G, Lancon C, et al. The development of the S-QoL 18: a shortened quality of life questionnaire for patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2010;121:241-50. - PubMed
Burns 2007
-
- Burns T, Patrick D. Social functioning as an outcome measure in schizophrenia studies. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2007;116:403-18. - PubMed
Carpenter 1994
-
- Carpenter WT, Buchanan RW. Schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330:681-90. - PubMed
Davis 1974
-
- Davis JM. Dose equivalence of the antipsychotic drugs. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1974;11:65-9. - PubMed
Davis 1975
-
- Davis JM. Overview: maintenance therapy in psychiatry: I. Schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1975;132(12):1237-45. - PubMed
Davis 1989
-
- Davis JM, Barter JT, Kane JM. Antipsychotic drugs. In: Kaplan HI, Sadock BJ, editors(s). Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry. 5th edition. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1989:1591-626.
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta-analyses of binary data. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Cochrane Colloquium; 2000 Oct 25-28; Cape Town, South Africa. 2000.
Der‐Simonian 1986
-
- Der-Simonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:177-88. - PubMed
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazer LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7:623-9. - PubMed
Duggan 2005
Duval 2000
-
- Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000;56:455-63. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JP, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta-analyses involving cross-over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31:140-9. - PubMed
Endicott 1976
-
- Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Fleiss JL, Cohen J. The global assessment scale. A procedure for measuring overall severity of psychiatric disturbance. Archives of General Psychiatry 1976;33(6):766-71. - PubMed
EuroQol 1990
-
- The EuroQol Group. EuroQol - a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16(3):199-208. - PubMed
Gardner 2010
-
- Gardner DM, Murphy AL, O'Donnell H, Centorrino F, Baldessarini RJ. International consensus study of antipsychotic dosing. American Journal of Psychiatry 2010;167(6):686-93. - PubMed
Gilbert 1995
-
- Gilbert P, Harris MJ, McAdams LA, Bowers MB, Charney DS, Glazer WM. Neuroleptic withdrawal in schizophrenic patients. A review of the literature. Archives of General Psychiatry 1995;52:173-88. - PubMed
Gopal 2010
-
- Gopal S, Gassman-Mayer C, Palumbo J, Samtani MN, Shiwach R, Alphs L. Practical guidance or dosing and switching paliperidone palmitate treatment in patients with schizophrenia. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2010;26(2):377-87. - PubMed
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC, Ukoumunne OC, Chinn S. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community-based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876-83. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology-revised 1976. Washington, DC: DHEW. National Institute of Mental Health, 1976.
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated September 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Kalali 1999
-
- Kalali A. Patient satisfaction with, and acceptability of, atypical antipsychotics. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1999;15:135-7. - PubMed
Kane 1988
-
- Kane JM, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H, and the Clozaril Collaborative study group. Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Archives of General Psychiatry 1988;45:789-96. - PubMed
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive And Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Manual. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi-Health Systems, 1986.
Kellner 1973
-
- Kellner R, Sheffield BF. A self-rating scale of distress. Psychological Medicine 1973;3:88-100. - PubMed
Kishi 2019
-
- Kishi T, Ikuta T, Matsui Y, Inada K, Matsuda Y, Mishima K, et al. Effect of discontinuation vs maintenance of antipsychotic medication on relapse rates in patients with remitted/stable first-episode psychosis: a meta-analysis. Psychological Medicine 2019;49(5):772-9. - PubMed
Kishimoto 2014
Klein 1969
-
- Klein DF, Davis JM. Diagnosis and Drug Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1969.
Leon 2006
-
- Leon AC, Mallinckrodt CH, Chuang-Stein C, Archibald DG, Archer GE, Chartier K. Attrition in randomised controlled clinical trials: methodological issues in psychopharmacology. Biological Psychiatry 2006;59:1001-5. - PubMed
Leucht 2003
-
- Leucht S, Barnes TR, Kissling W, Engel RR, Correll C, Kane JM. Relapse prevention in schizophrenia with new-generation antipsychotics: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis of randomised, controlled trials. American Journal of Psychiatry 2003;160:1209-22. - PubMed
Leucht 2005a
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale scores. British Journal of Psychiatry 2005;187:366-71. - PubMed
Leucht 2005b
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel RR. What does the PANSS mean? Schizophrenia Research 2005;79(2-3):231-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Leucht 2009
-
- Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, Engel R, Li C, Davis JM. A meta-analysis comparing second-generation and first-generation antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Lancet 2009;373:31-41. - PubMed
Leucht 2009a
-
- Leucht S, Komossa K, Rummel-Kluge C, Corves C, Hunger H, Schmid F, et al. A meta-analysis of head to head comparisons of second generation antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 2009;166:152-63. - PubMed
Leucht 2009b
-
- Leucht S, Arbter D, Engel RR, Kissling W, Davis JM. How effective are second-generation antipsychotic drugs? A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Molecular Psychiatry 2009;14:429-47. - PubMed
Leucht 2011
-
- Leucht C, Heres S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Davis JM, Leucht S. Oral versus depot antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia - a critical systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised long-term trials. Schizophrenia Research 2011;127:83-92. - PubMed
Leucht 2013
-
- Leucht S, Cipriani A, Spineli L, Mavridis M, Orey D, Richter F, et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet 2013;382(9896):951962. - PubMed
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Bradley C, Adams C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales: a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249-52. - PubMed
Marvaha 2004
-
- Marwaha S, Johnson S. Schizophrenia and employment? A review. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 2004;39:337-49. - PubMed
McGrath 2008
-
- McGrath J, Saha S, Chant D, Welham J. Schizophrenia: a concise overview of incidence, prevalence, and mortality.. Epidemiologic Reviews 2008;30:67-76. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel-group randomised trials. JAMA 2001;285:1987-1. - PubMed
Moncrieff 2006
-
- Moncrieff J. Does antipsychotic withdrawal provoke psychosis? Review of the literature on rapid onset psychosis (supersensitivity psychosis) and withdrawal-related relapse. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2006;114(1):3-13. - PubMed
Morosini 2000
-
- Morosini PL, Magliano L, Brambilla L, Ugolini S, Pioli R. Development, reliability and acceptability of a new version of the DSM-IV Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment Scale (SOFAS) to assess routine social functioning. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2000;101:323-9. - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799-12.
Papanikolaou 2004
-
- Papanikolaou PN, Churchill R, Wahlbeck K, Ioannidis JP. Safety reporting in randomised trials of mental health interventions. American Journal of Psychiatry 2004;161:1692-7. - PubMed
Peters 2008
-
- Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Contour-enhanced meta-analysis funnel plots help distinguish publication bias from other causes of asymmetry. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61:991-6. - PubMed
Pope 2010
-
- Pope A, Adams C, Paton C, Weaver T, Barnes TR. Assessment of adverse effects in clinical studies of antipsychotic medication: survey of methods used. British Journal of Psychiatry 2010;197:67-72. - PubMed
R Core Team 2018 [Computer program]
-
- Foundation for Statistical Computing R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Core Team, Version 3.6.2. Vienna: Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2018.
Ray 2009
Robinson 1999
-
- Robinson D, Woerner MG, Alvir JM, Bilder R, Goldman R, Geisler S, et al. Predictors of relapse following response from a first episode of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry 1999;56:241-7. - PubMed
Schneider 1983
-
- Schneider LC, Struening EL. SLOF: a behavioural rating scale for assessing the mentally ill. Social Work Research & Abstracts 1983 Fall;19:9-21. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408-12. - PubMed
Schwarzer 2007
-
- Schwarzer G. Meta: an R package for meta-analyses. R News 2007;7(3):40-5.
Shaffer 1983
-
- Shaffer D, Gould MS, Brasic J, Ambrosini P, Fisher P, Bird H, et al. A Children's Global Assessment Scale (CGAS). JAMA Psychiatry 1983;40:1228-31. - PubMed
Sheenan 1983
-
- Sheenan DV. The Sheenan Disability Scale. In: The Anxiety Disease and How to Overcome it. New York: Charles Scribner and Sons, 1983:151.
Shokraneh 2017
Simpson 1970
-
- Simpson EN, Angus JW. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side-effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1970;212:11-9. - PubMed
Srisurapanont 2004
Stata 2002 [Computer program]
-
- Intercooled Stata 7.0 for Windows. Stata Corporation. Stata Corporation, 2002.
Tiihonen 2009
-
- Tiihonen J, Lönnqvist J, Wahlbeck K, Klaukka T, Niskanen L, Tanskanen A, et al. 11-year follow-up of mortality in patients with schizophrenia: a population-based cohort study (FIN11 study). Lancet 2009;374:620-7. - PubMed
Tsuang 1978
-
- Tsuang MT. Suicide in schizophrenics, manics, depressives, and surgical controls: a comparison with general population suicide mortality. Archives of General Psychiatry 1978;35:153-5. - PubMed
Vernon 2010
-
- Vernon MK, Revicki DA, Awad G, Dirani R, Panish J, Canuso CM, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the Medication Satisfaction Questionnaire (MSQ) to assess satisfaction with antipsychotic medication among schizophrenia patients. Schizophrenia Research 2010;118(1-3):271-8. - PubMed
Viguera 1997
-
- Viguera AC, Baldessarini RJ, Hegarty JD, Kammen DP, Tohen M. Clinical risk following abrupt and gradual withdrawal of maintenance neuroleptic treatment. Archives of General Psychiatry 1997;54:49-55. - PubMed
Vita 2018
-
- Vita A, Barlati S. Recovery from schizophrenia: is it possible? Curr Opin Psychiatry 2018;31(00):1-10. - PubMed
Wahlbeck 1999
Walsh 2002
-
- Walsh E, Buchanan A, Fahy T. Violence and schizophrenia: examining the evidence. British Journal of Psychiatry 2002;180:490-5. - PubMed
Weinmann 2009
-
- Weinmann S, Read J, Aderhold V. Influence of antipsychotics on mortality in schizophrenia: systematic review. Schizophrenia Research 2009;113(1):1-11. - PubMed
Wilkinson 2000
-
- Wilkinson G, Hesdon B, Wild D, Cookson R, Farina C, Sharma V, et al. Self-report quality of life measure for people with schizophrenia: the SQLS. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;177:42-6. - PubMed
Xia 2009
-
- Xia J, Adams CE, Bhagat N, Bhagat V, Bhoopathi P, El-Sayeh H, et al. Loss to outcomes stakeholder survey: the LOSS study. Psychiatric Bulletin 2009;33(7):254-7.
References to other published versions of this review
Bergman 2016
-
- Bergman H, Davies S, Dawson S, Kakourou A, Spineli L. Targeted update of Maintenance treatment with antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia. The Cochrane Collaboration, Targeted Updates Project 2016. [https://community.cochrane.org/news/targeted-updates-project-case-study-b]
Komossa 2009
Leucht 2012a
-
- Leucht S, Tardy M, Komossa K, Heres S, Kissling W, Salanti G, et al. Antipsychotic drugs versus placebo for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2012;379(9831):2063-71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

