Deep Mutational Scanning of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Reveals Constraints on Folding and ACE2 Binding
- PMID: 32841599
- PMCID: PMC7418704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.012
Deep Mutational Scanning of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Reveals Constraints on Folding and ACE2 Binding
Abstract
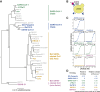
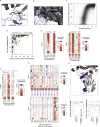
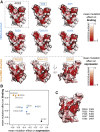
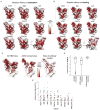
The receptor binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein mediates viral attachment to ACE2 receptor and is a major determinant of host range and a dominant target of neutralizing antibodies. Here, we experimentally measure how all amino acid mutations to the RBD affect expression of folded protein and its affinity for ACE2. Most mutations are deleterious for RBD expression and ACE2 binding, and we identify constrained regions on the RBD's surface that may be desirable targets for vaccines and antibody-based therapeutics. But a substantial number of mutations are well tolerated or even enhance ACE2 binding, including at ACE2 interface residues that vary across SARS-related coronaviruses. However, we find no evidence that these ACE2-affinity-enhancing mutations have been selected in current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic isolates. We present an interactive visualization and open analysis pipeline to facilitate use of our dataset for vaccine design and functional annotation of mutations observed during viral surveillance.
Keywords: ACE2; SARS-CoV-2; deep mutational scanning; receptor-binding domain.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests N.P.K. is a co-founder, shareholder, and chair of the scientific advisory board of Icosavax, Inc.
Figures








Update of
-
Deep mutational scanning of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain reveals constraints on folding and ACE2 binding.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jun 17:2020.06.17.157982. doi: 10.1101/2020.06.17.157982. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell. 2020 Sep 3;182(5):1295-1310.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.012. PMID: 32587970 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Constrained surfaces: promising therapeutic targets for COVID-19 determined by systematically mutational analysis.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jan 29;6(1):38. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00469-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33514688 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron RBD shows weaker binding affinity than the currently dominant Delta variant to human ACE2.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jan 5;7(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00863-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 34987150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baum A., Fulton B.O., Wloga E., Copin R., Pascal K.E., Russo V., Giordano S., Lanza K., Negron N., Ni M. Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies. Science. 2020:eabd0831. doi: 10.1126/science.abd0831. Published online June 15, 2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

