Long-term robustness of a T-cell system emerging from somatic rescue of a genetic block in T-cell development
- PMID: 32841837
- PMCID: PMC7452388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102961
Long-term robustness of a T-cell system emerging from somatic rescue of a genetic block in T-cell development
Abstract
Backgound: The potential of a single progenitor cell to establish and maintain long-term protective T-cell immunity in humans is unknown. For genetic disorders disabling T-cell immunity, somatic reversion was shown to support limited T-cell development attenuating the clinical phenotype. However, the cases reported so far deteriorated over time leaving unanswered the important question of long-term activity of revertant precursors and the robustness of the resulting T-cell system.
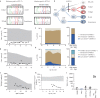
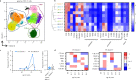
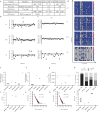
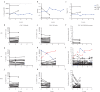
Methods: We applied TCRβ-CDR3 sequencing and mass cytometry on serial samples of a now 18 year-old SCIDX1 patient with somatic reversion to analyse the longitudinal diversification and stability of a T-cell system emerging from somatic gene rescue.
Findings: We detected close to 105 individual CDR3β sequences in the patient. Blood samples of equal size contained about 10-fold fewer unique CDR3β sequences compared to healthy donors, indicating a surprisingly broad repertoire. Despite dramatic expansions and contractions of individual clonotypes representing up to 30% of the repertoire, stable diversity indices revealed that these transient clonal distortions did not cause long-term repertoire imbalance. Phenotypically, the T-cell system did not show evidence for progressive exhaustion. Combined with immunoglobulin substitution, the limited T-cell system in this patient supported an unremarkable clinical course over 18 years.
Interpretation: Genetic correction in the appropriate cell type, in our patient most likely in a T-cell biased self-renewing hematopoietic progenitor, can yield a diverse T-cell system that provides long-term repertoire stability, does not show evidence for progressive exhaustion and is capable of providing protective and regulated T-cell immunity for at least two decades.
Funding: DFG EH 145/9-1, DFG SCHW 432/4-1 and the German Research Foundation under Germany's Excellence Strategy-EXC-2189-Project ID: 390939984.
Keywords: Immunodeficiency; T cells; T-cell development; TCR diversity.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and immunologic consequences of a somatic reversion in a patient with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency.Blood. 2008 Nov 15;112(10):4090-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-153361. Epub 2008 Aug 26. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18728247
-
T+ NK+ IL-2 Receptor γ Chain Mutation: a Challenging Diagnosis of Atypical Severe Combined Immunodeficiency.J Clin Immunol. 2018 May;38(4):527-536. doi: 10.1007/s10875-018-0514-y. Epub 2018 Jun 9. J Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29948574
-
Progressive B Cell Loss in Revertant X-SCID.J Clin Immunol. 2020 Oct;40(7):1001-1009. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00825-3. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32681206 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Mass Cytometry to Profile Human T Cell Exhaustion.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 22;10:3039. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03039. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32038613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the road: progress in finding the unique pathway of invariant NKT cell differentiation.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Apr;19(2):186-93. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.02.009. Epub 2007 Feb 15. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17303398 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges in Gene Therapy for Somatic Reverted Mosaicism in X-Linked Combined Immunodeficiency by CRISPR/Cas9 and Prime Editing.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 13;13(12):2348. doi: 10.3390/genes13122348. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553615 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy for inborn errors of immunity: past, present and future.Nat Rev Immunol. 2023 Jun;23(6):397-408. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00800-6. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36434109 Review.
-
An adequate human T cell repertoire from a single T cell progenitor: Lessons from an experiment of nature.EBioMedicine. 2020 Oct;60:103015. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103015. Epub 2020 Sep 22. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32977163 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Somatic Reversion of a Novel IL2RG Mutation Resulting in Atypical X-Linked Combined Immunodeficiency.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 23;13(1):35. doi: 10.3390/genes13010035. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fischer A, Notarangelo LD, Neven B, Cavazzana M, Puck JM. Severe combined immunodeficiencies and related disorders. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015 29;1:15061. - PubMed
-
- Revy P, Kannengiesser C, Fischer A. Somatic genetic rescue in Mendelian haematopoietic diseases. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(10):582–598. - PubMed
-
- Morsheimer M, Brown Whitehorn TF, Heimall J, Sullivan KE. The immune deficiency of chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2017 Sep;173(9):2366–2372. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

