Epidemiology of tuberculosis in Sabah, Malaysia, 2012-2018
- PMID: 32843089
- PMCID: PMC7447595
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-020-00739-7
Epidemiology of tuberculosis in Sabah, Malaysia, 2012-2018
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) is of high public health importance in Malaysia. Sabah State, located on the island of Borneo, has previously reported a particularly high burden of disease and faces unique contextual challenges compared with peninsular Malaysia. The aim of this study is to describe the epidemiology of TB in Sabah to identify risk groups and hotspots of TB transmission.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of TB cases notified in Sabah, Malaysia, between 2012 and 2018. Using data from the state's 'myTB' notification database, we calculated the case notification rate and described trends in the epidemiology, diagnostic practices and treatment outcomes of TB in Sabah within this period. The Chi-squared test was used for determining the difference between two proportions.
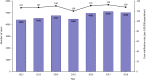
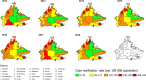
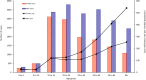
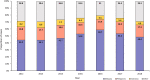
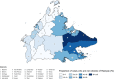
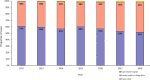
Results: Between 2012 and 2018 there were 33 193 cases of TB reported in Sabah (128 cases per 100 000 population). We identified several geographic hotspots, including districts with > 200 cases per 100 000 population per year. TB rates increased with age and were highest in older males. Children < 15 years accounted for only 4.6% of cases. Moderate or advanced disease on chest X-ray and sputum smear positivity was high (58 and 81% of cases respectively), suggesting frequent late diagnosis. Multi-drug resistant (MDR) TB prevalence was low (0.3% of TB cases), however, rapid diagnostic test coverage was low (1.2%) and only 18% of all cases had a positive culture result. Treatment success was 83% (range: 81-85%) in those with drug-sensitive TB and 36% (range: 25-45%) in cases of MDR-TB.
Conclusion: Between 2012 and 2018, TB notifications in Sabah State equated to 20% of Malaysia's total TB notifications, despite Sabah representing only 10% of Malaysia's population. We found hotspots of TB in urbanised population hubs and points of migration, as well as evidence of late presentation and diagnosis. Ensuring universal health coverage and expansion of GeneXpert® coverage is recommended to reduce barriers to care and early diagnosis and treatment for TB.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Malaysia; Sabah; Surveillance; Tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Tuberculosis Report 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
-
- The World Bank . World Bank Country and Lending Groups. Washington: The World Bank; 2019.
-
- World Health Organization . The end TB strategy: global strategy and targets for tuberculosis prevention, care and control after 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

