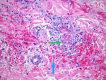
Apixaban-induced cutaneous leucocytoclastic vasculitis
- PMID: 32843390
- PMCID: PMC7449564
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-237043
Apixaban-induced cutaneous leucocytoclastic vasculitis
Keywords: dermatology; pathology; pharmacology and therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Dean R, Messer AM, Pickett M, et al. . A case of leukocytoclastic vasculitis caused by novel anticoagulant rivaroxaban. Dermatol Online J 2017;23. [Epub ahead of print: 15 Nov 2017]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
