Vasospasm induced myocardial ischaemia secondary to sumatriptan use
- PMID: 32843411
- PMCID: PMC7449594
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-235387
Vasospasm induced myocardial ischaemia secondary to sumatriptan use
Abstract
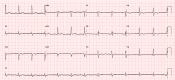
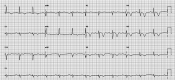
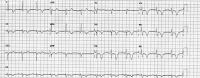
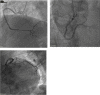
Certain medications have been implicated in causing acute myocardial infarctions (AMI). Sumatriptan, a medication usually prescribed for acute migraine and cluster headaches has been documented as potentially causing coronary vasospasm, thereby leading to MI. This is usually seen in patients with strong risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) or in those with established CAD. Most cases thus far have been reported in patients using the subcutaneous preparation of sumatriptan. Here, we present a case of a patient without prior risk factors for CAD and angiographically unremarkable coronary arteries who presented with evidence of an AMI after oral sumatriptan use for migraines.
Keywords: cardiovascular medicine; ischaemic heart disease; pharmacology and therapeutics.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Joint Formulary Committee British National formulary (online). London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press, 2020. https://www.medicinescomplete.com/#/content/bnfc/_791549275
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous