Effect of rapid maxillary expansion on nasal cavity assessed with cone-beam computed tomography
- PMID: 32844972
- PMCID: PMC7437151
- DOI: 10.1590/2177-6709.25.3.039-045.oar
Effect of rapid maxillary expansion on nasal cavity assessed with cone-beam computed tomography
Abstract
Introduction: Rapid maxillary expansion (RME) is assumed as a well established procedure; although, some effects on facial complex are not yet fully understood.
Objective: The aim of this research was to verify, using cone-beam computed tomography, the effect on linear dimensions of the nasal cavity.
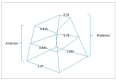
Methods: Sample consisted of twenty patients aged 7 to 16 years, with skeletal deformity that justified the use of CT scans, and who required the RME as part of the orthodontic treatment planning. Scans were taken before clinical procedures were performed (T0) and after stabilizing the expander screw (T1). Dolphin Imaging v. 11.5 3D software was used to measure six areas on nasal cavity: three at the anterior portion (upper, middle, and lower) and other three at the posterior portion (also upper, middle, and lower). Data were statistically treated using Shapiro-Wilk test to verify normality. Differences between T0 and T1 were calculated using the Spearman correlation and paired Student's t-test, with a significance level of 5%.
Results: All linear measurements presented a significant increase (p< 0.05) after RME, both in the anterior and posterior regions, suggesting some parallelism on the opening pattern, especially at the lower portion (p< 0.001).
Conclusions: RME was able to significantly modify the internal dimensions of the nasal cavity.
Introdução:: A expansão rápida da maxila (ERM) é um procedimento bem estabelecido. Entretanto, alguns efeitos no complexo facial ainda não foram completamente compreendidos.
Objetivo:: O objetivo do presente estudo foi verificar o efeito da ERM nas medidas lineares da cavidade nasal, utilizando a tomografia computadorizada de feixe cônico (TCFC).
Métodos:: A amostra foi composta por 20 pacientes da Universidade Federal da Bahia, com idades entre 7 e 16 anos, com deformidades esqueléticas que justificavam o uso da TCFC e que necessitavam da ERM como parte do tratamento ortodôntico. As imagens tomográficas foram realizadas antes dos procedimentos clínicos (T0) e após estabilização do parafuso expansor (T1). O software Dolphin Imaging v. 11.5 3D (Dolphin, Chatsworth, CA, EUA) foi utilizado para mensurar seis áreas na cavidade nasal, três delas na região anterior (superior, média e inferior) e outras três na região posterior (também superior, média e inferior). Os dados foram trabalhados estatisticamente, utilizando o teste de Shapiro-Wilk para avaliar a normalidade. Diferenças entre T0 e T1 foram calculadas usando a Correlação de Spearman e o teste t de Student pareado, usando um nível de significância de 5%.
Resultados:: Todas as mensurações lineares apresentaram um aumento significativo (p< 0,05) após a ERM, tanto na região anterior quanto na posterior, sugerindo algum paralelismo no padrão de abertura, principalmente na porção inferior (p< 0,001).
Conclusão:: A ERM foi capaz de modificar significativamente as dimensões internas da cavidade nasal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no commercial, proprietary or financial interest in the products or companies described in this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of orthopedic maxillary expansion on nasal cavity size in growing subjects: a low dose computer tomography clinical trial.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Nov;76(11):1547-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.07.008. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22840779
-
Immediate effects of rapid maxillary expansion on the naso-maxillary facial soft tissue using 3D stereophotogrammetry.Surgeon. 2016 Apr;14(2):63-8. doi: 10.1016/j.surge.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Surgeon. 2016. PMID: 24947501
-
Skeletal effects to the maxilla after rapid maxillary expansion assessed with cone-beam computed tomography.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008 Jul;134(1):8-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.06.004. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008. PMID: 18617096
-
Three-dimensional analyses of short- and long-term effects of rapid maxillary expansion on nasal cavity and upper airway: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2020 Aug;23(3):250-276. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12378. Epub 2020 May 5. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2020. PMID: 32248642
-
Three-dimensional analysis of effects of rapid maxillary expansion on facial sutures and bones.Angle Orthod. 2013 Nov;83(6):1074-82. doi: 10.2319/020413-103.1. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Angle Orthod. 2013. PMID: 23745976 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Skeletal and Dentoalveolar Changes in Growing Patients Treated with Rapid Maxillary Expansion Measured in 3D Cone-Beam Computed Tomography.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 13;11(12):3305. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123305. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137526 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of dilacerated impacted maxillary central incisors on the incisive canal and nasal cavity characteristics: a retrospective comparative study.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 19;25(1):603. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05899-2. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40253340 Free PMC article.
-
Polygraphic evaluation of the effects of different rapid maxillary expansion appliances on sleep quality: A randomized clinical trial.Sleep Breath. 2023 May;27(2):651-659. doi: 10.1007/s11325-022-02677-0. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Sleep Breath. 2023. PMID: 35789454 Clinical Trial.
-
Three-Dimensional Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Changes in Naso-Maxillary Complex Associated with Rapid Palatal Expansion.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Apr 2;13(7):1322. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13071322. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haas AJ. Rapid expansion of the maxillary dental arch and nasal cavity by opening the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1961;31(2):73–90.
-
- Haas AJ. The treatment of maxillary deficiency by opening the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1965;35:200–217. - PubMed
-
- Haas AJ. Palatal expansion just the beginning of dentofacial orthopedics. Am J Orthod. 1970;57(3):219–255. - PubMed
-
- Wertz RA. Skeletal and dental changes accompanying rapid midpalatal suture opening. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1970;58(1):41–66. - PubMed
-
- Cross DL, McDonald JP. Effect of rapid maxillary expansion on skeletal, dental, and nasal structures a postero-anterior cephalometric study. Eur J Orthod. 2000;22(5):519–528. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

