Association of Age, Sex, Race, and Geographic Region With Variation of the Ratio of Basal Cell to Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinomas in the United States
- PMID: 32845319
- PMCID: PMC7450404
- DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2571
Association of Age, Sex, Race, and Geographic Region With Variation of the Ratio of Basal Cell to Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinomas in the United States
Abstract
Importance: Defining which populations are affected by basal cell carcinoma (BCC) vs cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) may inform targeted public health strategies. Incidence of BCC and cSCC is not reported to national cancer registries, but claims data for the treatment of BCC and cSCC provide insights into the epidemiology of keratinocyte carcinoma.
Objective: To define differences in the ratio of BCC to cSCC in adults (age, ≥18 years) in a large database of patients with commercial insurance and Medicare Advantage coverage.
Design, setting, and participants: This cross-sectional analysis used deidentified data derived from the Optum Clinformatics Data Mart to perform a retrospective evaluation of a large commercially insured cohort based on treatment claims from January 1, 2012, to December 31, 2016. Patients with a diagnosed and treated BCC or cSCC as determined by codes from the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision, and Current Procedural Terminology were included. Data were analyzed from November 30, 2019, to March 20, 2020.
Exposure: Diagnosis and treatment of BCC or cSCC.
Main outcomes and measures: The ratio of BCC to cSCC based on age, sex, race, and geographic location. Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess how demographics were associated with the odds of a treated keratinocyte carcinoma being a BCC.
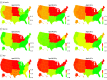
Results: Among the 985 317 claims for patients included in the analysis (61.59% for men; mean [SD] age, 69.82 [12.58] years), BCCs were 1.69 (95% CI, 1.6899-1.6901) times more likely than cSCCs to be treated in the United States from 2012 to 2016. Basal cell carcinomas were significantly more prevalent than cSCCs in younger patients (18-39 years, 9.63 [95% CI, 9.6088-9.6574] BCCs per cSCC; 40-64 years, 2.92 [95% CI, 2.9171-2.9187] BCCs per cSCC; and ≥65 years, 1.33 [95% CI, 1.3289-1.3291] BCCs per cSCC; P < .001). Basal cell carcinomas were significantly more prevalent than cSCCs in women vs men, except in adults 65 years or older (odds ratios [ORs], 0.98 [95% CI, 0.97-0.99] vs 1.67 [95% CI, 1.47-1.88] for those aged 18-39 and 1.15 [95% CI, 1.12-1.19] for those aged 40-64 years; P < .001). The difference in BCC:cSCC ratios between men and women diminished with increasing age (OR, 1.67 for 18-39 years, 1.15 for 40-64 years, and 0.98 for 65 years or older). Basal cell carcinoma was more prevalent than cSCC in all races, including Black patients (BCC:SCC ratios, 1.60 for Asian patients, 1.45 for Black patients, 2.00 for Hispanic patients, and 1.69 for White patients of all ages). The BCC:cSCC ratio varied based on geography, with the highest ratio in the West North Central census division (2.12) and the lowest ratio in the South Atlantic census division (1.35).
Conclusions and relevance: In the absence of a national registry, claims data can improve our understanding of the epidemiology of keratinocyte carcinomas. In this cross-sectional study, basal cell carcinomas were more common than cSCCs for all demographics, including in Black patients. In populations younger than 40 years, BCCs were 12.6 times more likely for women and 7.2 times more likely for men. These demographic groups may benefit from public health education focused on the presentation and management of BCCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiology of basal and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in the U.K. 2013-15: a cohort study.Br J Dermatol. 2019 Sep;181(3):474-482. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17873. Epub 2019 May 6. Br J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30864158 Free PMC article.
-
Voriconazole and the Risk of Keratinocyte Carcinomas Among Lung Transplant Recipients in the United States.JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jul 1;156(7):772-779. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1141. JAMA Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32401271 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of Multiple vs First Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma on a Nationwide Scale and Estimation of Future Incidences of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma.JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Dec 1;156(12):1300-1306. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.3677. JAMA Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 33112377 Free PMC article.
-
Visual inspection and dermoscopy, alone or in combination, for diagnosing keratinocyte skin cancers in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 4;12(12):CD011901. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011901.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30521688 Free PMC article.
-
Reflectance confocal microscopy for diagnosing keratinocyte skin cancers in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 4;12(12):CD013191. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013191. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30521687 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immunosuppressed patients are at increased risk of local recurrence, metastasis, and disease specific death from cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 Jul;315(5):1429-1433. doi: 10.1007/s00403-022-02458-5. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 36416979
-
Investigating Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma in vitro and in vivo: Novel 3D Tools and Animal Models.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 9;9:875517. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.875517. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35646967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting adjuvant radiation therapy benefit in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma with the 40-gene expression profile.Future Oncol. 2024;20(35):2737-2746. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2390820. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Future Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39229801 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the 40-gene Expression Profile (40-GEP) Test in Medicare-eligible Patients Diagnosed with Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cSCC) to Guide Adjuvant Radiation Therapy (ART) Decisions Leads to a Significant Reduction in Healthcare Costs.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024 Jan;17(1):41-44. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38298751 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporation of the 40-Gene Expression Profile (40-GEP) Test to Improve Treatment Decisions in High-Risk Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cSCC) Patients: Case Series and Algorithm.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Apr 5;16:925-935. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S403330. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37051586 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

