Polarized human cholangiocytes release distinct populations of apical and basolateral small extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 32845745
- PMCID: PMC7851850
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E19-03-0133
Polarized human cholangiocytes release distinct populations of apical and basolateral small extracellular vesicles
Abstract
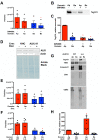
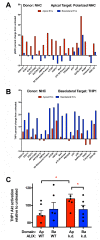
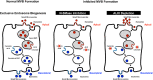
Intercellular communication is critical for organismal homeostasis, and defects can contribute to human disease states. Polarized epithelial cells execute distinct signaling agendas via apical and basolateral surfaces to communicate with different cell types. Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), including exosomes and small microvesicles, represent an understudied form of intercellular communication in polarized cells. Human cholangiocytes, epithelial cells lining bile ducts, were cultured as polarized epithelia in a Transwell system as a model with which to study polarized sEV communication. Characterization of isolated apically and basolaterally released EVs revealed enrichment in sEVs. However, differences in apical and basolateral sEV composition and numbers were observed. Genetic or pharmacological perturbation of cellular machinery involved in the biogenesis of intralumenal vesicles at endosomes (the source of exosomes) revealed general and domain-specific effects on sEV biogenesis/release. Additionally, analyses of signaling revealed distinct profiles of activation depending on sEV population, target cell, and the function of the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT)-associated factor ALG-2-interacting protein X (ALIX) within the donor cells. These results support the conclusion that polarized cholangiocytes release distinct sEV pools to mediate communication via their apical and basolateral domains and suggest that defective ESCRT function may contribute to disease states through altered sEV signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular and functional profiling of apical versus basolateral small extracellular vesicles derived from primary human proximal tubular epithelial cells under inflammatory conditions.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021 Feb;10(4):e12064. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12064. Epub 2021 Feb 16. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021. PMID: 33643548 Free PMC article.
-
Polarized Secretion of Extracellular Vesicles by Mammary Epithelia.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2018 Sep;23(3):165-176. doi: 10.1007/s10911-018-9402-6. Epub 2018 Jul 3. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2018. PMID: 29968174 Free PMC article.
-
ALIX and ceramide differentially control polarized small extracellular vesicle release from epithelial cells.EMBO Rep. 2021 May 5;22(5):e51475. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051475. Epub 2021 Mar 16. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33724661 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis and function of ESCRT-dependent extracellular vesicles.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Feb;74:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.08.022. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 28807885 Review.
-
Polarity signals in epithelial cells.J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:9-12. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.2. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993. PMID: 8144708 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma: The New Biological and Technological Horizons.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;15(8):1011. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15081011. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40310432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Hepatobiliary Health and Disease.Compr Physiol. 2023 Jun 26;13(3):4631-4658. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c210046. Compr Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37358519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polarized Desmosome and Hemidesmosome Shedding via Small Extracellular Vesicles is an Early Indicator of Outer Blood-Retina Barrier Dysfunction.J Extracell Biol. 2023 Oct;2(10):e116. doi: 10.1002/jex2.116. Epub 2023 Oct 11. J Extracell Biol. 2023. PMID: 38108061 Free PMC article.
-
Lipids in Extracellular Vesicles: What Can Be Learned about Membrane Structure and Function?Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2023 Aug 1;15(8):a041415. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041415. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2023. PMID: 37277192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two roads diverged in a cell: insights from differential exosome regulation in polarized cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Sep 2;12:1451988. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1451988. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39286483 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arbelaiz A, Azkargorta M, Krawczyk M, Santos-Laso A, Lapitz A, Perugorria MJ, Erice O, Gonzalez E, Jimenez-Aguero R, Lacasta A, et al (2017). Serum extracellular vesicles contain protein biomarkers for primary sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology , 1125–1143. - PubMed
-
- Baietti MF, Zhang Z, Mortier E, Melchior A, Degeest G, Geeraerts A, Ivarsson Y, Depoortere F, Coomans C, Vermeiren E, et al (2012). Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol , 677–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

