Propranolol, chlorpromazine and diclofenac restore susceptibility of extensively drug-resistant (XDR)-Acinetobacter baumannii to fluoroquinolones
- PMID: 32845920
- PMCID: PMC7449414
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238195
Propranolol, chlorpromazine and diclofenac restore susceptibility of extensively drug-resistant (XDR)-Acinetobacter baumannii to fluoroquinolones
Abstract
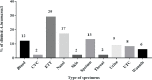
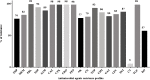
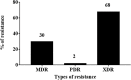
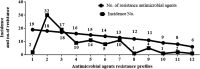
Nosocomial infections caused by extensively drug-resistant (XDR) or Pan-Drug resistant (PDR) Acinetobacter (A.) baumannii have recently increased dramatically creating a medical challenge as therapeutic options became very limited. The aim of our study was to investigate the antibiotic-resistance profiles and evaluate the various combinations of ciprofloxacin (CIP) or levofloxacin (LEV) with antimicrobial agents and non-antimicrobial agents to combat antimicrobial resistance of XDR A. baumannii. A total of 100 (6.25%) A. baumannii clinical isolates were recovered from 1600 clinical specimens collected from hospitalized patients of two major university hospitals in Upper Egypt. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were carried out according to CLSI guidelines. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of the respective isolates showed a high percentage of bacterial resistance to 19 antimicrobial agents ranging from 76 to99%. However, a lower percentage of resistance was observed for only colistin (5%) and doxycycline (57%). The isolates were categorized as PDR (2; 2%), XDR (68; 68%), and multi-drug resistant (MDR) (30; 30%). Genotypic analysis using ERIC-PCR on 2 PDR and 32 selected XDR isolates showed that they were not clonal. Combinations of CIP or LEV with antibiotics (including, ampicillin, ceftriaxone, amikacin, or doxycycline) were tested on these A. baumannii non-clonal isolates using standard protocols where fractional inhibitory concentrations (-FICs) were calculated. Results of the respective combinations showed synergism in 23.5%, 17.65%, 32.35%, 17.65% and 26.47%, 8.28%, 14.71%, 26.47%, of the tested isolates, respectively. CIP or LEV combinations with either chlorpromazine (CPZ) 200 μg/ml, propranolol (PR) in two concentrations, 0.5 mg/ml and 1.0 mg/ml or diclofenac (DIC) 4 mg/ml were carried out and the MIC decrease factor (MDF) of each isolate was calculated and results showed synergism in 44%, 50%, 100%, 100% and 94%, 85%, 100%, 100%, of the tested isolates, respectively. In conclusion, combinations of CIP or LEV with CPZ, PR, or DIC showed synergism in most of the selected PDR and XDR A. baumannii clinical isolates. However, these combinations have to be re-evaluated in vivo using appropriate animal models infected by XDR- or PDR- A. baumannii.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of target site mutations and plasmid associated resistance genes acquisition on resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii to fluoroquinolones.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 11;11(1):20136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99230-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34635692 Free PMC article.
-
[Investigation of fluoroquinolone resistance mechanisms in clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolates].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2016 Apr;50(2):278-86. doi: 10.5578/mb.24126. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2016. PMID: 27175500 Turkish.
-
In Vitro Synergistic Effects of Antimicrobial Combinations on Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates.Ann Lab Med. 2016 Mar;36(2):138-44. doi: 10.3343/alm.2016.36.2.138. Ann Lab Med. 2016. PMID: 26709261 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of control groups when delineating antibiotic use as a risk factor for carbapenem resistance, extreme-drug resistance, and pan-drug resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2018 Nov;76:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.05.017. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Int J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29870795
-
Acinetobacter baumannii meningitis in children: a case series and literature review.Infection. 2019 Aug;47(4):643-649. doi: 10.1007/s15010-018-1234-1. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Infection. 2019. PMID: 30328074 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of traditional Chinese medicine monomers interfering with quorum-sensing on virulence factors of extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 30;14:1135180. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1135180. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37063277 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Activity of Peptide Antibiotics in Combination With Other Antimicrobials on Extensively Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in the Planktonic and Biofilm Cell.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 11;13:890955. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.890955. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35645826 Free PMC article.
-
Propranolol restores susceptibility of XDR Gram-negative pathogens to meropenem and Meropenem combination has been evaluated with either tigecycline or amikacin.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Jul 22;23(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02934-6. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37481513 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of target site mutations and plasmid associated resistance genes acquisition on resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii to fluoroquinolones.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 11;11(1):20136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99230-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34635692 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of diclofenac against levofloxacin-resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates; emphasizing repurposing of diclofenac.Iran J Microbiol. 2024 Apr;16(2):166-175. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v16i2.15349. Iran J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38854979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Čiginskienė A, Dambrauskienė A, Rello J, Adukauskienė D. Ventilator-associated pneumonia due to drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: risk factors and mortality relation with resistance profiles, and independent predictors of in-hospital mortality. Medicina. 2019;55(2):49 10.3390/medicina55020049 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tripodi M-F, Durante-Mangoni E, Fortunato R, Utili R, Zarrilli R. Comparative activities of colistin, rifampicin, imipenem and sulbactam/ampicillin alone or in combination against epidemic multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates producing OXA-58 carbapenemases. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007;30(6):537–40. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.07.007 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

