Real-World Patient-Reported Outcomes and Glycemic Results with Initiation of Control-IQ Technology
- PMID: 32846114
- PMCID: PMC7868573
- DOI: 10.1089/dia.2020.0388
Real-World Patient-Reported Outcomes and Glycemic Results with Initiation of Control-IQ Technology
Abstract
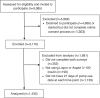
Background: The t:slim X2™ insulin pump with Control-IQ™ technology, an advanced hybrid closed-loop system, became available in the United States in early 2020. Real-world outcomes with use of this system have not yet been comprehensively reported. Methods: Individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D) (≥14 years of age) who had ≥21 days of pump usage data were invited via email to participate. Participants completed psychosocial questionnaires (Technology Acceptance Scale [TAS], well-being index [WHO-5], and Diabetes Impact and Devices Satisfaction [DIDS] scale) at timepoint 1 (T1) (at least 3 weeks after starting Control-IQ technology) and the DIDS and WHO-5 at timepoint 2 (T2) (4 weeks from T1). Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and glycemic outcomes were reviewed at each timepoint. Results: Overall, 9,085 potentially eligible individuals received the study invite. Of these, 3,116 consented and subsequently 1,435 participants completed questionnaires at both T1 and T2 and had corresponding glycemic data available on the t:connect® web application. Time in range was 78.2% (70.2%-85.1%) at T1 and 79.2% (70.3%-86.2%) at T2. PROs reflected high device-related satisfaction and reduced diabetes impact at T2. Factors contributing to high trust in the system included sensor accuracy, improved diabetes control, reduction in extreme blood glucose levels, and improved sleep quality. In addition, participants reported improved quality of life, ease of use, and efficient connectivity to the continuous glucose monitoring system as being valuable features of the system. Conclusions: Continued real-world use of the t:slim X2 pump with Control-IQ technology showed improvements in psychosocial outcomes and persistent achievement of recommended TIR glycemic outcomes in people with T1D.
Keywords: Artificial pancreas; Automated insulin delivery; Glycemic control; Patient-reported outcomes; Type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
J.E.P. reports grant support, provided to his institution, consulting fees, and speaker fees from Tandem Diabetes Care, Inc; grant support, provided to his institution, and advisory board fees from Medtronic; grant support, provided to his institution, and consulting fees from Eli Lilly; grant support and supplies, provided to his institution, from Insulet; and supplies, provided to his institution, from Dexcom, Inc., L.M. reports grant support from Dexcom, Inc., and consulting from Tandem Diabetes Care, Inc., A.C., S.L., M.M., M.M.M., H.S., and S.H. are employees of Tandem Diabetes Care, Inc.,
Similar articles
-
Impact of glycaemic technologies on quality of life and related outcomes in adults with type 1 diabetes: A narrative review.Diabet Med. 2023 Jan;40(1):e14944. doi: 10.1111/dme.14944. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Diabet Med. 2023. PMID: 36004676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One Year Real-World Use of the Control-IQ Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop Technology.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021 Sep;23(9):601-608. doi: 10.1089/dia.2021.0097. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33784196 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world use of Control-IQ™ technology automated insulin delivery in pregnancy: A case series with qualitative interviews.Diabet Med. 2023 Jun;40(6):e15086. doi: 10.1111/dme.15086. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Diabet Med. 2023. PMID: 36924086
-
Prospective Analysis of the Impact of Commercialized Hybrid Closed-Loop System on Glycemic Control, Glycemic Variability, and Patient-Related Outcomes in Children and Adults: A Focus on Superiority Over Predictive Low-Glucose Suspend Technology.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020 Dec;22(12):912-919. doi: 10.1089/dia.2019.0400. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31855446
-
A clinical review of the t:slim X2 insulin pump.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Dec;17(12):1675-1687. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1814734. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32842794 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Technology's Influence on Health Behaviours and Well-being in Type 1 Diabetes: a Review.Curr Diab Rep. 2024 Apr;24(4):61-73. doi: 10.1007/s11892-024-01534-6. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Curr Diab Rep. 2024. PMID: 38294726 Review.
-
Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) Systems: Use and Efficacy in Children and Adults with Type 1 Diabetes and Other Forms of Diabetes in Europe in Early 2023.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;13(3):783. doi: 10.3390/life13030783. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Timescale Rhythmicity of Blood Glucose and Insulin Delivery Reveals Key Advantages of Hybrid Closed Loop Therapy.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2022 Jul;16(4):912-920. doi: 10.1177/1932296821994825. Epub 2021 Mar 10. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 33719596 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of automated insulin delivery systems on person-reported outcomes in people with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Sep 21;76:102852. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102852. eCollection 2024 Oct. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39364272 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of glycaemic technologies on quality of life and related outcomes in adults with type 1 diabetes: A narrative review.Diabet Med. 2023 Jan;40(1):e14944. doi: 10.1111/dme.14944. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Diabet Med. 2023. PMID: 36004676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dadlani V, Pinsker JE, Dassau E, Kudva YC: Advances in closed-loop insulin delivery systems in patients with type 1 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 2018;18:88. - PubMed
-
- Pinsker JE, Li Z, Buckingham BA, et al. : Exceptional usability of Tandem t:slim X2 with Basal-IQ predictive low-glucose suspend (PLGS)—The PROLOG Study. Diabetes 2018;67:db18-86-LB.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous