Influenza-Induced Oxidative Stress Sensitizes Lung Cells to Bacterial-Toxin-Mediated Necroptosis
- PMID: 32846120
- PMCID: PMC7570217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108062
Influenza-Induced Oxidative Stress Sensitizes Lung Cells to Bacterial-Toxin-Mediated Necroptosis
Abstract
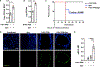
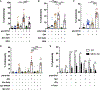
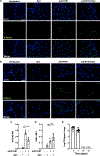
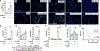
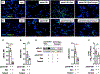
Pneumonias caused by influenza A virus (IAV) co- and secondary bacterial infections are characterized by their severity and high mortality rate. Previously, we have shown that bacterial pore-forming toxin (PFT)-mediated necroptosis is a key driver of acute lung injury during bacterial pneumonia. Here, we evaluate the impact of IAV on PFT-induced acute lung injury during co- and secondary Streptococcus pneumoniae (Spn) infection. We observe that IAV synergistically sensitizes lung epithelial cells for PFT-mediated necroptosis in vitro and in murine models of Spn co-infection and secondary infection. Pharmacoelogical induction of oxidative stress without virus sensitizes cells for PFT-mediated necroptosis. Antioxidant treatment or inhibition of necroptosis reduces disease severity during secondary bacterial infection. Our results advance our understanding on the molecular basis of co- and secondary bacterial infection to influenza and identify necroptosis inhibition and antioxidant therapy as potential intervention strategies.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; cell death; co-infections; epithelial cells; inflammation; influenza A virus; necroptosis; oxidative stress; pneumonia; secondary bacterial infection.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
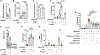
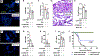
References
-
- Byrn RA, Jones SM, Bennett HB, Bral C, Clark MP, Jacobs MD, Kwong AD, Ledeboer MW, Leeman JR, McNeil CF, et al. (2015). Pre-clinical activity of VX-787, a first-in-class, orally bioavailable inhibitor of the influenza virus polymerase PB2 subunit. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 59, 1569–1582. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

