Our experiences of resuming services in ENT departments in Wuhan, once a COVID-19 epicenter
- PMID: 32846406
- PMCID: PMC7425674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102678
Our experiences of resuming services in ENT departments in Wuhan, once a COVID-19 epicenter
Abstract
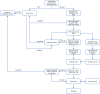
The pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) showed a significant impact on routine daily services in departments of otorhinolaryngology head and neck surgery. The city of Wuhan, as the first reported epicenter in the world, resumed medical service since April 8, 2020. As the biggest ENT services provider in Wuhan, we share out institution's triage and screening system in the resuming period.
Keywords: COVID-19; Resumption; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Otolaryngology During the COVID-19 Pandemic: What We Have Learned in Year One.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2020 Dec;53(6):xxiii-xxv. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2020.09.008. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 33039098 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
How to Manage Pediatric Orthopaedic Patients: Strategies to Provide Safer Care During the COVID-19 Outbreak in Wuhan, People's Republic of China.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020 Aug 5;102(15):e86. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.20.00521. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020. PMID: 32769592 No abstract available.
-
Rising to the Challenge: Otolaryngologists in the COVID-19 Pandemic.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2020 Dec;53(6):xxvii-xxviii. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2020.09.019. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 33127044 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
[The COVID-19 pandemic and otolaryngology: What it comes down to?].Laryngorhinootologie. 2020 May;99(5):287-291. doi: 10.1055/a-1095-2344. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Laryngorhinootologie. 2020. PMID: 32215896 Review. German.
-
Applying triage principles of mass casualty events to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: From the perspective of the acute care surgeons at Long Island Jewish Medical Center in the COVID epicenter of the United States.Surgery. 2020 Sep;168(3):408-410. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2020.06.004. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Surgery. 2020. PMID: 32684335 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wuhan Municipal Health Commission Update on the novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreak in Wuhan. http://wjw.wuhan.gov.cn/ztzl_28/fk/yqtb/ Available at:
-
- National Health Commission of the People'’s Republic of China Update on the novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreak. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/list_gzbd.shtml Available at.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous