Hif-1α Inhibitors Could Successfully Inhibit the Progression of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Vitro
- PMID: 32847004
- PMCID: PMC7558478
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13090208
Hif-1α Inhibitors Could Successfully Inhibit the Progression of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Vitro
Abstract
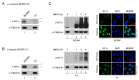
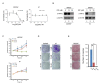
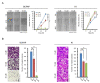
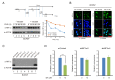
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α plays an important role in cancer progression. In various cancers, including thyroid cancer, overexpression of HIF-1α is related to poor prognosis or treatment response. However, few studies have investigated the role of HIF-1α inhibition in thyroid cancer progression. We evaluated the utility of the HIF-1α inhibitor IDF-11774 in vitro utilizing two thyroid cancer cell lines, K1 and BCPAP. Both cell lines were tested to elucidate the effects of IDF-11774 on cell proliferation and migration using soft agar and invasion assays. Here, we found that a reduction of HIF-1α expression in BCPAP cells was observed after treatment with IDF-11774 in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, cell proliferation, migration, and anchorage-independent growth were effectively inhibited by IDF-11774 in BCPAP cells but not in K1 cells. Additionally, invasion of BCPAP but not K1 cells was controlled with IDF-11774 in a dose-dependent manner. Our findings suggest that promoting the degradation of HIF-1α could be a strategy to manage progression and that HIF-1α inhibitors are potent drugs for thyroid cancer treatment.
Keywords: HIF-1α; IDF-11774; thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Durante C., Haddy N., Baudin E., Leboulleux S., Hartl D., Travagli J.P., Caillou B., Ricard M., Lumbroso J.D., de Vathaire F., et al. Long-term outcome of 444 patients with distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma: Benefits and limits of radioiodine therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006;91:2892–2899. doi: 10.1210/jc.2005-2838. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

