Clinical features of neonates born to mothers with coronavirus disease-2019: A systematic review of 105 neonates
- PMID: 32847748
- PMCID: PMC7427525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.07.024
Clinical features of neonates born to mothers with coronavirus disease-2019: A systematic review of 105 neonates
Abstract
Background: Despite the increasingly recognized impact of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), on many aspects of health in adults and children, its effects on neonates born to infected mothers remain unclear. We conducted this study to investigate the outcomes of neonates born to mothers with COVID-19.
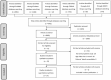
Methods: We searched the medical databases from inception to March 31, 2020 to perform a systematic review of outcomes in neonates born to mothers with COVID-19. Data were pooled using a random effects regression model. Primary and secondary outcomes were neonatal clinical outcomes and infectious status, respectively.
Results: Fourteen studies involving 105 neonates fulfilling the study criteria were identified. The rates of preterm neonates and those small for gestational age (SGA) were 25 (23.8%) and 10 (11.2%), respectively. Among 91 neonates who were tested, 8 (8.8%) were positive for nucleic acids or antibodies for SARS-CoV-2. Additionally, 28 (26.7%) of the neonates were symptomatic and two test-negative neonates died, including one stillbirth. Between test-positive and test-negative groups, the rates of SGA, preterm delivery, duration between maternal symptom onset and delivery, and perinatal complication were not significantly different; but the rate of symptomatic after birth reached significant difference (62.5% vs 20.5%, p = 0.008).
Conclusions: Most neonates born to infected mothers had favorable outcomes. Although direct evidences of intrauterine infection were scarce, the risk of intrauterine infection should be considered based on a positive test in 8.8% of the neonates. Symptomatic neonates born to infected mothers should receive tests for SARS-CoV-2 to initiate appropriate treatment and quarantine. Further studies are warranted to assess the outcomes of COVID-19 in neonates.
Keywords: COVID-19; Intrauterine infection; Neonate; Novel coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2; Vertical transmission.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors had no competing interests to disclose.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

